A Journey Through Geography: Exploring Russia And Central Asia
By admin / August 24, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
A Journey Through Geography: Exploring Russia and Central Asia
Related Articles: A Journey Through Geography: Exploring Russia and Central Asia
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Geography: Exploring Russia and Central Asia. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Geography: Exploring Russia and Central Asia

The vast expanse of Russia and Central Asia, stretching across a significant portion of the Eurasian landmass, presents a captivating tapestry of diverse landscapes, cultures, and histories. Understanding the region’s geography is crucial for appreciating its complex dynamics, from its historical significance to its current geopolitical relevance. This article delves into the map of Russia and Central Asia, highlighting its key features, geographical significance, and the multifaceted relationships it reveals.
A Land of Extremes: Geographical Features of Russia and Central Asia
Russia, the world’s largest country by land area, dominates the northern portion of the region. Its immense territory encompasses a wide range of geographical features, from the vast Siberian plains to the towering Ural Mountains and the frozen Arctic coast. Central Asia, nestled south of Russia, comprises five former Soviet republics: Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Turkmenistan. This region is characterized by its mountainous terrain, arid deserts, and fertile river valleys, providing a unique mosaic of ecosystems.
Russia:
- The Great Russian Plain: This vast expanse, extending from the Baltic Sea to the Ural Mountains, is the heartland of Russia, home to its major cities and agricultural regions.
- The Ural Mountains: Serving as a natural boundary between Europe and Asia, the Ural Mountains stretch for over 2,000 kilometers, offering rich mineral resources and diverse landscapes.
- Siberia: This sprawling region, encompassing over 75% of Russia’s landmass, is characterized by its vast taiga forests, permafrost, and abundant natural resources like oil, gas, and timber.
- The Caucasus Mountains: Located on Russia’s southwestern border, the Caucasus Mountains are a rugged and strategically important region, home to diverse ethnic groups and a rich cultural heritage.
- The Far East: This remote region, bordering the Pacific Ocean, is characterized by its mountainous terrain, volcanic activity, and rich biodiversity.
Central Asia:
- The Tian Shan Mountains: These towering mountains, stretching across Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan, and China, are a significant geographical feature of Central Asia, home to glaciers, alpine meadows, and diverse wildlife.
- The Pamir Mountains: Located in Tajikistan, the Pamir Mountains are known as the "Roof of the World," with some of the highest peaks in the world.
- The Karakum Desert: This vast desert, covering much of Turkmenistan, is one of the largest in the world, characterized by its harsh climate and sparse vegetation.
- The Aral Sea: Once the world’s fourth-largest inland lake, the Aral Sea has suffered significant shrinkage due to water diversion for irrigation, highlighting the environmental challenges facing the region.
- The Fergana Valley: This fertile valley, located in Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan, is known for its cotton production and its rich history.
Beyond Geography: The Significance of the Map
The map of Russia and Central Asia reveals more than just geographical features; it unveils a complex interplay of historical, cultural, and geopolitical factors that have shaped the region’s destiny.
Historical Significance:
- The Silk Road: This ancient trade route, connecting the East and West, traversed the heart of Central Asia, facilitating cultural exchange and economic prosperity for centuries.
- The Soviet Union: The region’s history is deeply intertwined with the Soviet Union, which brought significant political, economic, and social changes, leaving lasting impacts on its culture, infrastructure, and political landscape.
- The Collapse of the Soviet Union: The dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991 led to the emergence of independent states in Central Asia, ushering in a new era of political and economic transition.
Geopolitical Relevance:
- Energy Resources: Russia and Central Asia are rich in energy resources, particularly oil and natural gas, making the region a crucial player in global energy markets.
- Strategic Location: Situated between Europe and Asia, the region holds strategic importance for global powers, influencing trade routes, political alliances, and military deployments.
- Cultural Diversity: The region is home to a wide range of ethnicities, languages, and religions, contributing to its cultural richness and complexity.
Understanding the Interconnections:
The map of Russia and Central Asia reveals the interconnectedness of its diverse components. The flow of rivers, the movement of people, the exchange of ideas, and the distribution of resources all contribute to the intricate web of relationships within the region.
- Water Resources: The region’s rivers, such as the Volga, the Amu Darya, and the Syr Darya, are vital for agriculture, industry, and human settlements, creating shared resources and potential for conflict.
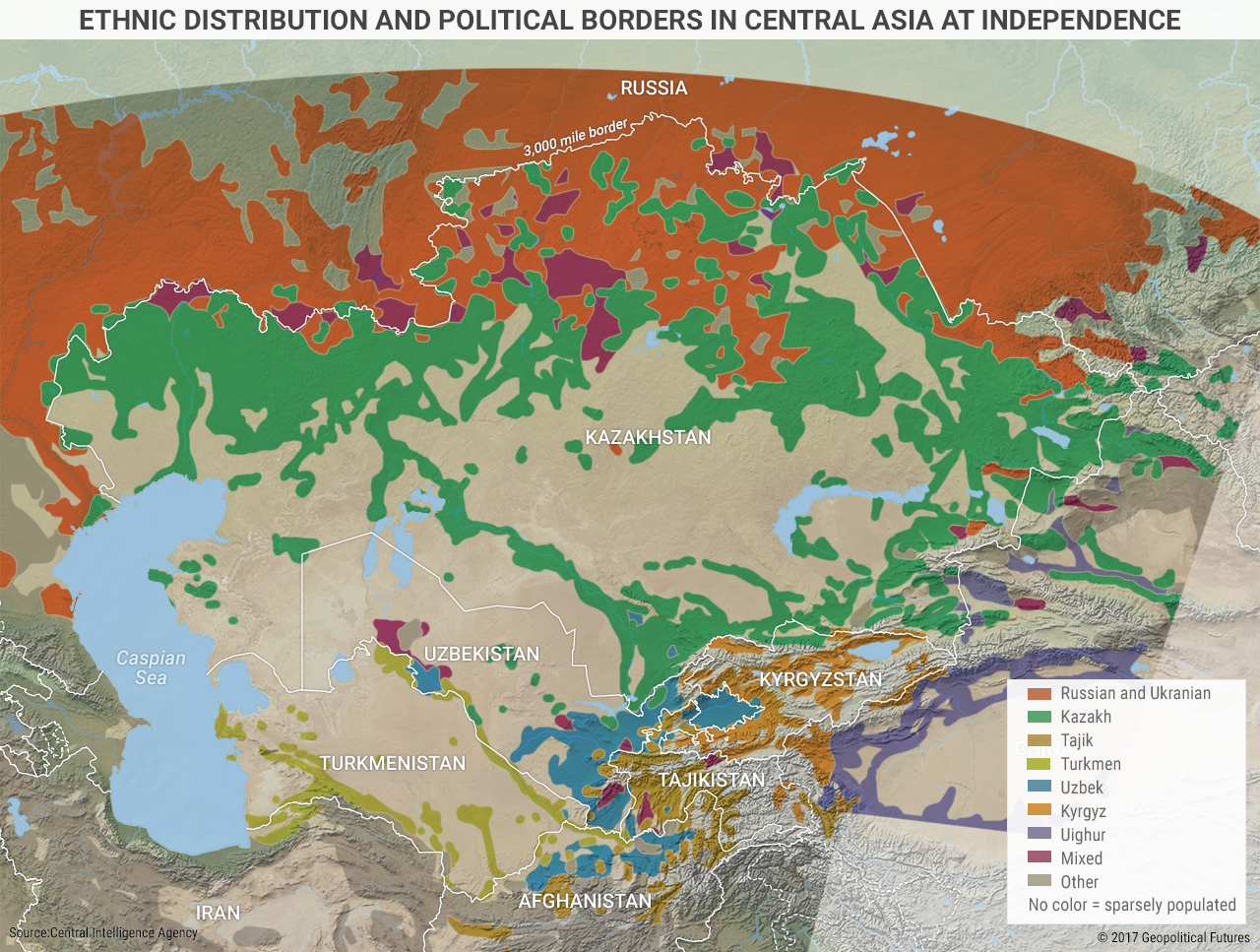
- Ethnicities and Languages: The region’s diverse ethnicities and languages, including Russian, Kazakh, Uzbek, Kyrgyz, Tajik, and Turkmen, reflect its rich cultural heritage and the complex history of migration and cultural exchange.
- Political and Economic Ties: The region’s history, shared resources, and strategic location have fostered complex political and economic ties, leading to cooperation and competition among its various states.
Challenges and Opportunities:
The map of Russia and Central Asia also highlights the challenges and opportunities facing the region in the 21st century.
- Environmental Degradation: Issues like water scarcity, desertification, and pollution pose significant challenges to the region’s environment and sustainable development.
- Economic Development: The region faces challenges in diversifying its economies, reducing poverty, and creating new opportunities for its citizens.
- Political Stability: The region is prone to political instability, ethnic tensions, and conflict, requiring collaborative efforts to promote peace and security.
- Globalization and Integration: The region faces the challenge of integrating into the global economy while preserving its cultural identity and traditions.
FAQs about the Map of Russia and Central Asia:
1. What is the largest country in the region?
Russia is the largest country in the region, covering over 17 million square kilometers.
2. What is the highest mountain in the region?
Mount Everest, located in the Himalayas on the border of Nepal and China, is the highest mountain in the world and is part of the broader Himalayan region that extends into Central Asia. However, the highest peak within the region itself is Mount Communism (also known as Ismail Samani Peak) in the Pamir Mountains of Tajikistan.
3. What is the significance of the Aral Sea?
The Aral Sea was once a vital source of water and livelihood for the region, but it has suffered significant shrinkage due to water diversion for irrigation, leading to environmental degradation and economic hardship.
4. What are the major religions practiced in the region?
The region is home to a diverse range of religions, including Islam, Christianity, Buddhism, and Judaism. Islam is the dominant religion in Central Asia, while Christianity is prevalent in Russia.
5. What are the major languages spoken in the region?
The region is home to a wide variety of languages, including Russian, Kazakh, Uzbek, Kyrgyz, Tajik, Turkmen, and many others.
Tips for Studying the Map of Russia and Central Asia:
- Use a physical map: A physical map, showing the region’s terrain, rivers, and mountains, can provide a better understanding of its geographical features.
- Explore online resources: Websites like Google Maps, Wikipedia, and the CIA World Factbook offer detailed information about the region’s geography, history, and culture.
- Read books and articles: Books and articles by historians, geographers, and political scientists can provide in-depth insights into the region’s complexities.
- Watch documentaries: Documentaries about the region can offer a visual and engaging perspective on its diverse landscapes, cultures, and challenges.
- Engage in discussions: Discussions with experts, scholars, and individuals from the region can provide valuable insights and perspectives.
Conclusion:
The map of Russia and Central Asia is a powerful tool for understanding the region’s unique geographical features, historical significance, and complex geopolitical dynamics. It reveals a tapestry of diverse landscapes, cultures, and challenges, highlighting the interconnectedness of its various components. By studying this map, we gain a deeper appreciation for the region’s rich history, its present-day challenges, and its potential for future development. As the world continues to evolve, the region’s importance will undoubtedly continue to grow, making it a crucial focal point for understanding global affairs and shaping a more interconnected and sustainable future.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Geography: Exploring Russia and Central Asia. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!