A Journey Through Italy’s Diverse Landscape: Understanding The Physical Map
By admin / April 5, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
A Journey Through Italy’s Diverse Landscape: Understanding the Physical Map
Related Articles: A Journey Through Italy’s Diverse Landscape: Understanding the Physical Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Italy’s Diverse Landscape: Understanding the Physical Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Italy’s Diverse Landscape: Understanding the Physical Map
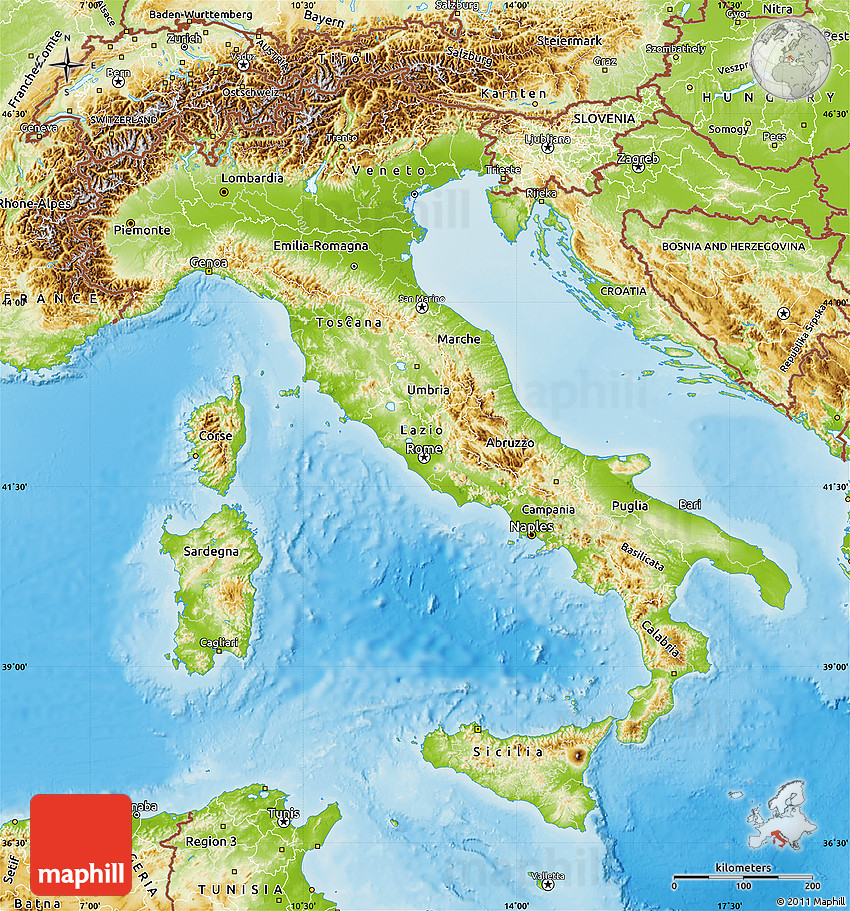
Italy, a nation renowned for its rich history, vibrant culture, and delectable cuisine, boasts a landscape as diverse and captivating as its heritage. The Italian peninsula, shaped like a boot kicking its heel into the Mediterranean Sea, presents a fascinating tapestry of mountains, plains, rivers, and coasts, each contributing to the country’s unique character. Understanding the physical map of Italy reveals the underlying forces that have shaped its geography, influenced its history, and continue to impact its daily life.
A Mountainous Spine: The Italian Alps and Apennines
The Italian Alps, forming the northern border of the country, are a formidable presence, towering over the Po Valley and extending into France, Switzerland, and Austria. These majestic peaks, including iconic peaks like Monte Rosa and the Matterhorn, are a testament to the powerful tectonic forces that have shaped the region. The Alps are not only a source of breathtaking beauty, but also play a crucial role in regulating Italy’s climate and serving as a vital source of water for the country.
The Apennines, a less imposing but equally significant mountain range, form the backbone of the Italian peninsula, running from the north to the south. This range, which includes the highest peak on the Italian mainland, Mount Corno, is characterized by rugged terrain, deep valleys, and rolling hills. The Apennines are a defining feature of the Italian landscape, influencing the country’s climate, agriculture, and even its cultural identity.
The Fertile Po Valley: A Cradle of Civilization
Nestled between the Alps and the Apennines lies the Po Valley, Italy’s largest plain and a vital agricultural region. This fertile land, irrigated by the mighty Po River, has been a cradle of civilization since ancient times, providing sustenance and resources for countless generations. The Po Valley is also a hub of industry and population, with major cities like Milan, Turin, and Bologna contributing significantly to the country’s economy.
The Mediterranean Coast: A Blend of Beauty and Bounty
Italy’s coastline, stretching over 7,600 kilometers, is a treasure trove of diverse landscapes. From the rugged cliffs of the Cinque Terre to the pristine beaches of Sardinia, from the volcanic beauty of the Aeolian Islands to the vibrant cities of Naples and Genoa, the Italian coastline offers a kaleidoscope of experiences. This coastal region has historically been a center of trade and cultural exchange, with its ports serving as gateways to the Mediterranean world.
Volcanic Landscapes: A Testament to Earth’s Power
Italy is home to a number of active and dormant volcanoes, reminding us of the dynamic nature of the Earth’s crust. Mount Vesuvius, overlooking the Bay of Naples, is perhaps the most famous, known for its devastating eruption that buried the ancient Roman cities of Pompeii and Herculaneum. Other notable volcanoes include Mount Etna in Sicily, Europe’s largest active volcano, and Stromboli, famous for its frequent eruptions. These volcanic landscapes, while potentially dangerous, have also enriched the soil, contributing to the country’s agricultural bounty.
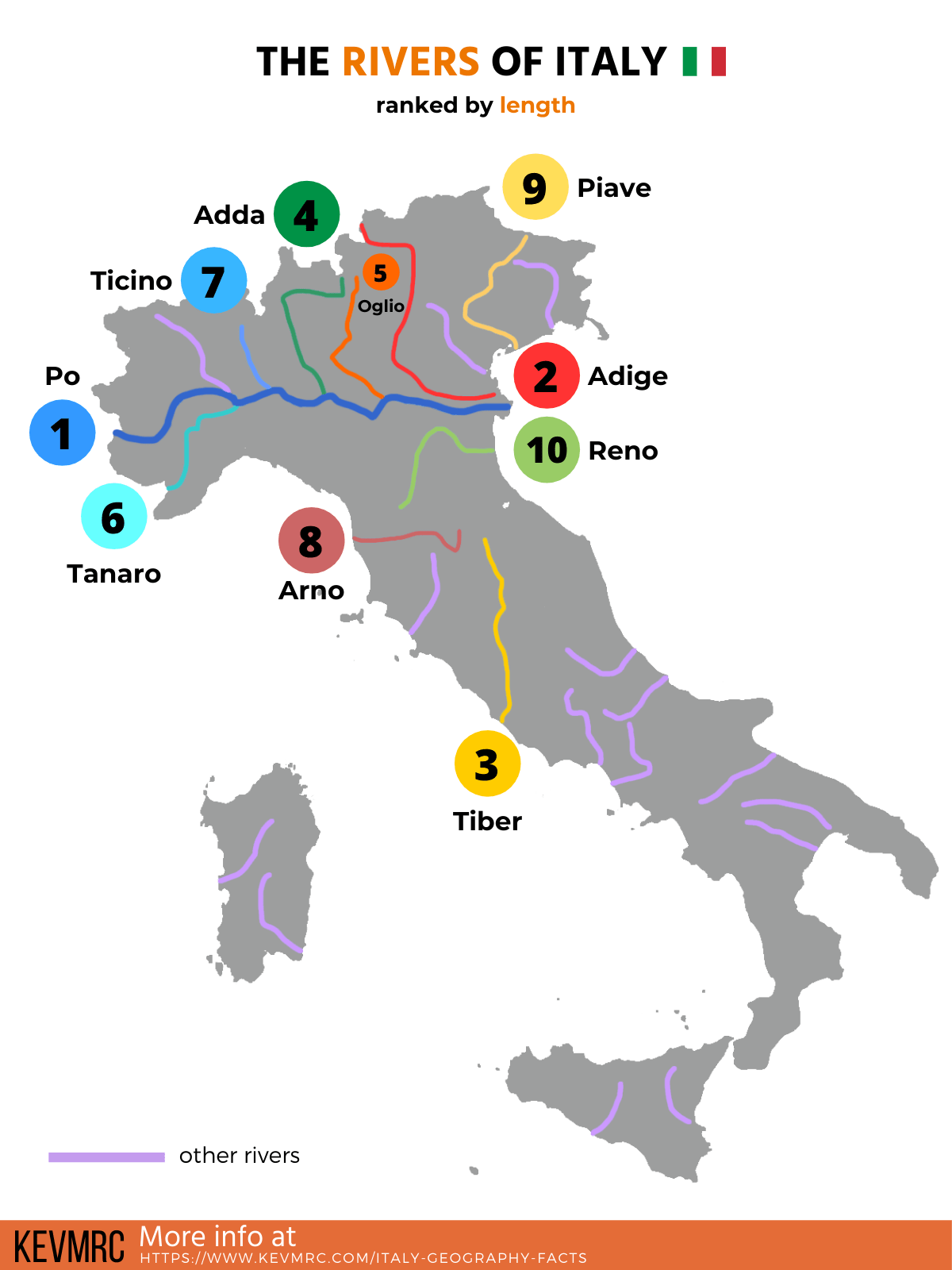
Rivers and Lakes: Veins of Life
Italy’s network of rivers and lakes plays a vital role in its ecosystem and economy. The Po River, the longest in Italy, is a lifeline for the Po Valley, providing water for irrigation and transportation. Other significant rivers include the Tiber, which flows through Rome, and the Arno, which runs through Florence. Italy also boasts a number of picturesque lakes, including Lake Garda, Lake Maggiore, and Lake Como, renowned for their beauty and recreational opportunities.
The Importance of the Physical Map
Understanding the physical map of Italy is crucial for appreciating its history, culture, and present-day challenges. The country’s mountainous terrain has historically influenced its political and economic development, shaping its regional identities and influencing its transportation infrastructure. The fertile plains have been crucial for agriculture, contributing to the country’s culinary heritage and economic prosperity. The coastline has served as a bridge to the Mediterranean world, facilitating trade and cultural exchange.
FAQs about the Physical Map of Italy
1. What are the major mountain ranges in Italy?
The major mountain ranges in Italy are the Alps in the north and the Apennines running down the peninsula.
2. What is the significance of the Po Valley?
The Po Valley is Italy’s largest plain and a vital agricultural region, providing sustenance and resources for the country. It is also a hub of industry and population.
3. What are some of the key features of the Italian coastline?
Italy’s coastline is characterized by its diverse landscapes, ranging from rugged cliffs to pristine beaches, volcanic islands to vibrant cities.
4. How have volcanoes influenced the Italian landscape?
Volcanoes have enriched the soil, contributing to the country’s agricultural bounty, but they have also posed a threat with their destructive eruptions.
5. What is the role of rivers and lakes in Italy?
Rivers and lakes provide water for irrigation, transportation, and recreation, playing a vital role in the country’s ecosystem and economy.
Tips for Studying the Physical Map of Italy
- Use interactive maps: Explore online maps that allow you to zoom in and out, label features, and access additional information.
- Focus on key regions: Identify the major mountain ranges, plains, rivers, and coastal areas to understand the country’s geographical divisions.
- Connect geography to history and culture: Explore how the physical landscape has influenced Italy’s history, culture, and economy.
- Visit Italy: Experiencing the country firsthand will deepen your understanding of its physical map and its diverse landscapes.
Conclusion
The physical map of Italy is a captivating story of natural forces, historical influences, and human ingenuity. From the towering Alps to the fertile plains, from the rugged coastline to the volcanic landscapes, each feature contributes to the country’s unique character and its enduring appeal. Understanding this geographical tapestry is essential for appreciating Italy’s rich history, diverse culture, and the ongoing challenges it faces. By exploring the physical map, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate relationship between land and people, and the profound impact that geography has on shaping a nation’s destiny.
/the-geography-of-italy-4020744-CS-5c3df74a46e0fb00018a8a3a.jpg)
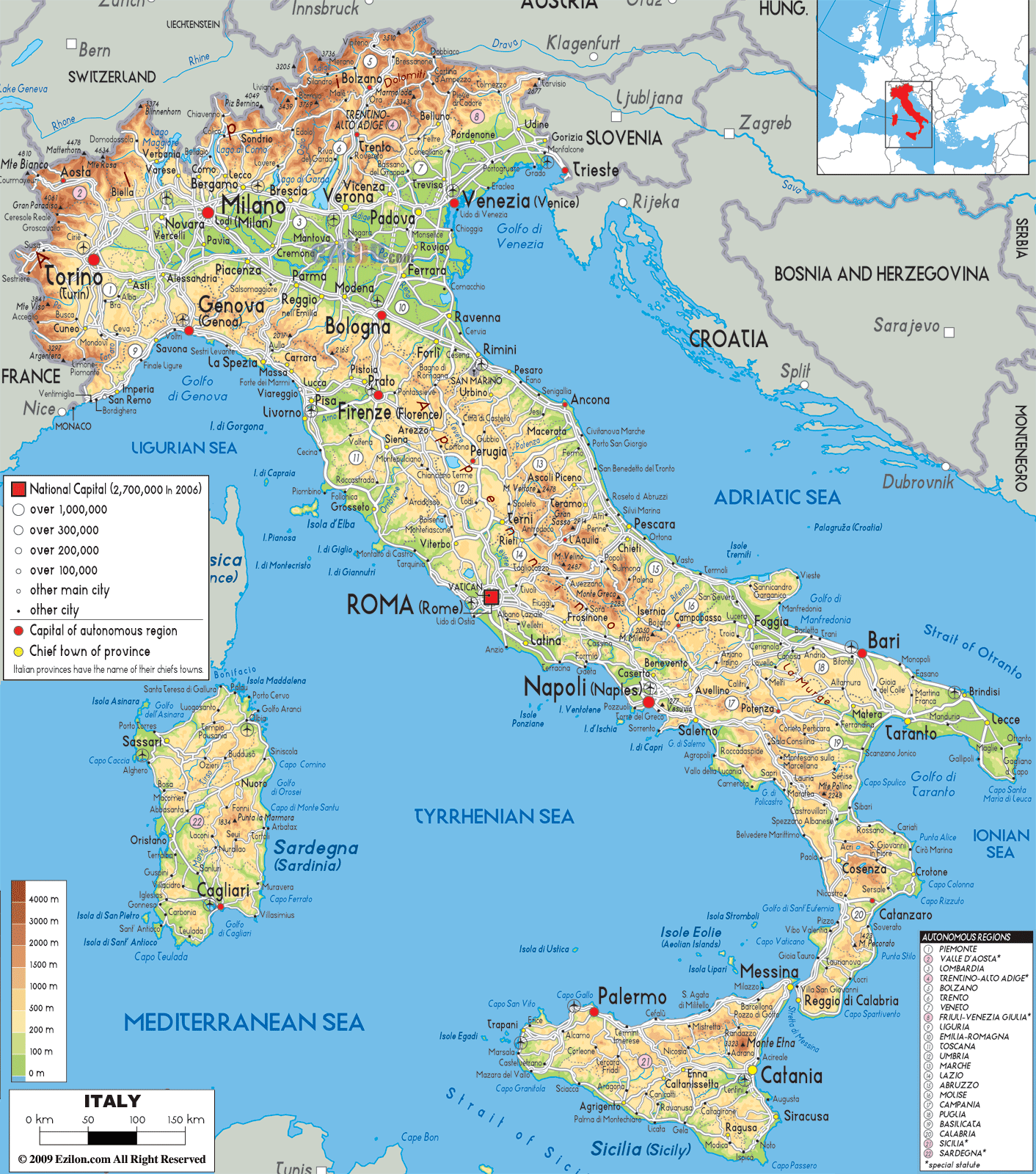


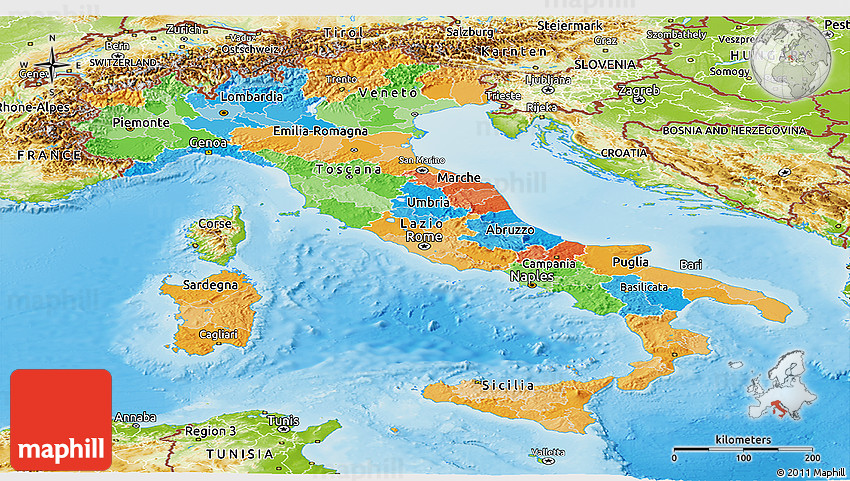

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Italy’s Diverse Landscape: Understanding the Physical Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!