A Journey Through Texas’s Diverse Landscapes: Understanding The Ecoregions Of The Lone Star State
By admin / September 20, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
A Journey Through Texas’s Diverse Landscapes: Understanding the Ecoregions of the Lone Star State
Related Articles: A Journey Through Texas’s Diverse Landscapes: Understanding the Ecoregions of the Lone Star State
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Texas’s Diverse Landscapes: Understanding the Ecoregions of the Lone Star State. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Texas’s Diverse Landscapes: Understanding the Ecoregions of the Lone Star State

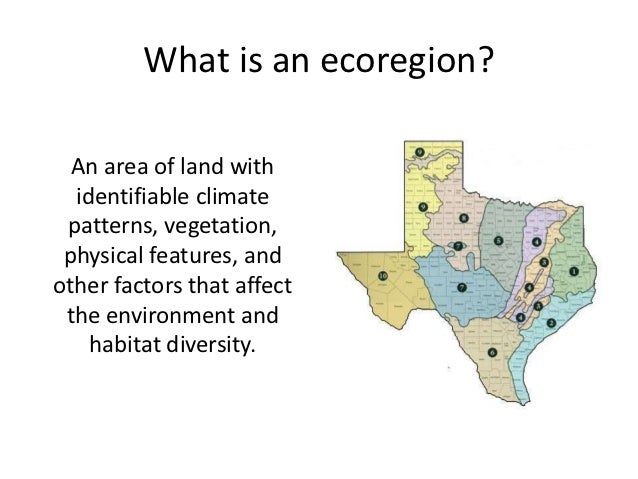
Texas, the second-largest state in the contiguous United States, boasts a captivating tapestry of landscapes, each with its unique ecological character. This diversity is not merely aesthetic; it reflects the intricate interplay of climate, geology, and biological evolution, shaping a mosaic of ecosystems that are vital to the state’s natural heritage and human well-being. To understand this rich complexity, a powerful tool emerges: the Texas Ecoregion Map.
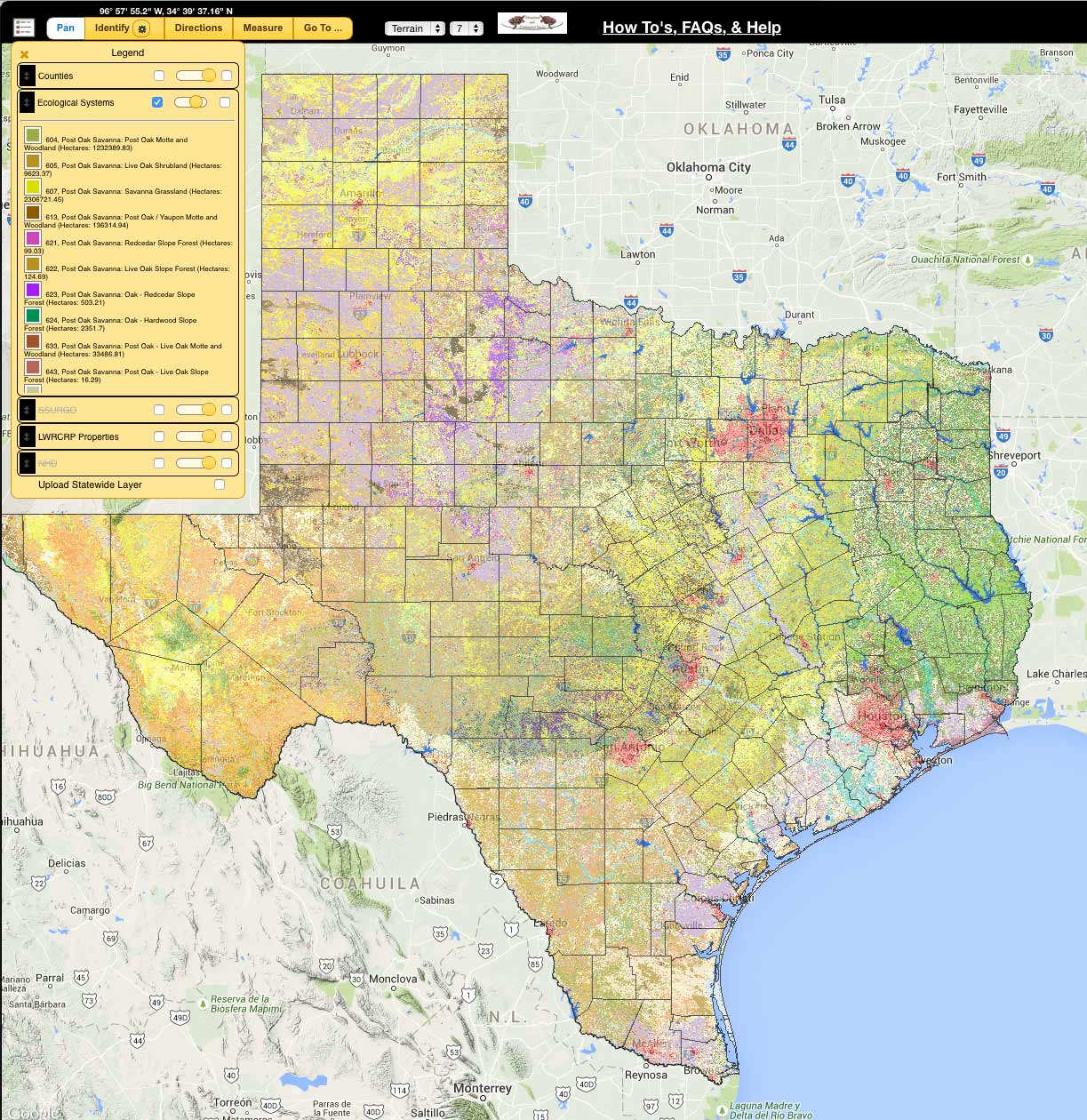
This map, developed by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Texas Parks and Wildlife Department (TPWD), divides the state into distinct ecological units called ecoregions. These ecoregions are defined by shared characteristics such as climate, soil type, vegetation, and animal life. By mapping these regions, scientists and policymakers can gain a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of Texas’s natural systems and develop strategies for conservation, resource management, and sustainable development.
Unveiling the Ecoregions:
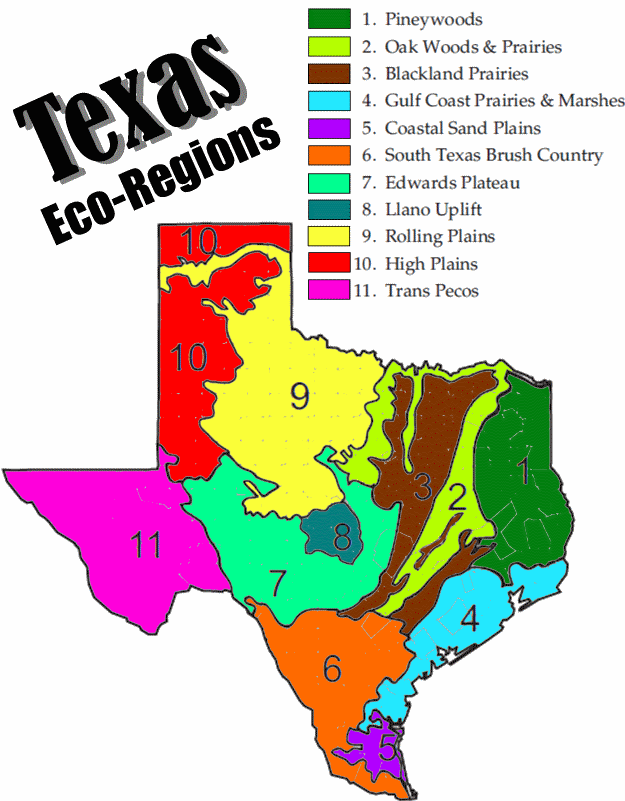
The Texas Ecoregion Map highlights eight major ecoregions, each with its own distinctive features:
1. The High Plains: This ecoregion, covering the northwestern portion of the state, is characterized by vast grasslands, rolling hills, and a semi-arid climate. The dominant vegetation consists of shortgrass and mixed-grass prairies, supporting a diverse array of wildlife, including bison, pronghorn antelope, and numerous bird species.
2. The Edwards Plateau: Located in central Texas, the Edwards Plateau is a rugged, limestone plateau with a unique ecosystem shaped by its karst topography. This region is known for its diverse flora, including juniper, oak, and mesquite trees, and its rich fauna, including white-tailed deer, black-tailed jackrabbits, and various reptiles.
3. The Trans-Pecos: This arid ecoregion in far west Texas is dominated by mountains and desert landscapes. The Chihuahuan Desert, with its iconic saguaro cacti and diverse desert flora and fauna, is a prominent feature. The Trans-Pecos is also home to unique species like the desert tortoise and the Mexican spotted owl.
4. The Southern Texas Plains: This ecoregion spans the southern portion of the state, encompassing the coastal plain and the Rio Grande Valley. The climate is subtropical, with warm temperatures and abundant rainfall. The region is characterized by grasslands, woodlands, and wetlands, supporting a rich biodiversity, including the endangered ocelot and the Rio Grande silvery minnow.
5. The Gulf Coastal Plains: This ecoregion, extending along the Gulf Coast, is characterized by flat, low-lying terrain, sandy soils, and a humid subtropical climate. The region is home to diverse habitats, including coastal marshes, pine forests, and prairies, supporting a rich array of wildlife, including alligators, sea turtles, and numerous bird species.
6. The Piney Woods: Located in eastern Texas, the Piney Woods is dominated by dense pine forests, with a humid subtropical climate. This region is known for its diverse flora, including longleaf pine, loblolly pine, and various hardwoods, and its abundant fauna, including white-tailed deer, black bears, and numerous bird species.
7. The Blackland Prairie: This ecoregion, located in central Texas, is characterized by fertile black soils and a humid subtropical climate. The region was once dominated by tallgrass prairies, but much of it has been converted to agriculture. However, remnants of this rich ecosystem remain, supporting a diverse array of wildlife, including bison, prairie chickens, and numerous bird species.
8. The Western Gulf Coastal Plain: This ecoregion, located along the western portion of the Gulf Coast, is characterized by a mix of coastal plains, rolling hills, and riverine systems. The climate is humid subtropical, with warm temperatures and abundant rainfall. The region is home to a variety of habitats, including coastal marshes, pine forests, and grasslands, supporting a rich array of wildlife, including alligators, sea turtles, and numerous bird species.
The Importance of Understanding Ecoregions:
The Texas Ecoregion Map is a powerful tool for understanding the complex interplay of natural systems in the state. It provides a framework for:
- Conservation and Management: Identifying and prioritizing conservation efforts for unique ecosystems and endangered species.
- Resource Management: Understanding the distribution of natural resources, such as water, soil, and timber, and developing sustainable management practices.
- Sustainable Development: Guiding land-use decisions to minimize environmental impact and ensure the long-term health of Texas’s ecosystems.
- Climate Change Adaptation: Assessing the vulnerability of different ecoregions to climate change and developing strategies for adaptation and mitigation.
- Education and Outreach: Raising awareness about the importance of Texas’s diverse ecosystems and engaging the public in conservation efforts.
FAQs about the Texas Ecoregion Map:
Q: What are the benefits of using the Texas Ecoregion Map?
A: The map provides a valuable framework for understanding and managing Texas’s diverse ecosystems, supporting conservation efforts, guiding sustainable development, and adapting to climate change.
Q: How can the Texas Ecoregion Map be used to address climate change?
A: The map helps identify ecoregions that are most vulnerable to climate change impacts, allowing for targeted adaptation strategies and mitigation efforts.
Q: What are some examples of how the Texas Ecoregion Map is being used in practice?
A: The map is used by various organizations, including TPWD, EPA, and conservation groups, to guide conservation planning, resource management, and land-use decisions.
Q: How can I learn more about the Texas Ecoregion Map?
A: Information about the map and its applications can be found on the websites of the EPA and TPWD.
Tips for Using the Texas Ecoregion Map:
- Explore the Map: Familiarize yourself with the different ecoregions and their characteristics.
- Connect with Local Experts: Seek guidance from local ecologists, naturalists, and conservation organizations.
- Support Conservation Efforts: Contribute to organizations working to protect and restore Texas’s ecosystems.
- Make Informed Decisions: Use the map to guide your land-use decisions and support sustainable practices.
Conclusion:
The Texas Ecoregion Map is a valuable resource for understanding the state’s diverse landscapes and the interconnectedness of its natural systems. By leveraging this map, scientists, policymakers, and individuals can work together to protect and manage Texas’s natural heritage, ensuring the long-term health and sustainability of its ecosystems for generations to come.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Texas’s Diverse Landscapes: Understanding the Ecoregions of the Lone Star State. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!