A Tapestry Of Resources: Understanding Africa’s Natural Wealth
By admin / May 3, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
A Tapestry of Resources: Understanding Africa’s Natural Wealth
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Resources: Understanding Africa’s Natural Wealth
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Resources: Understanding Africa’s Natural Wealth. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Resources: Understanding Africa’s Natural Wealth
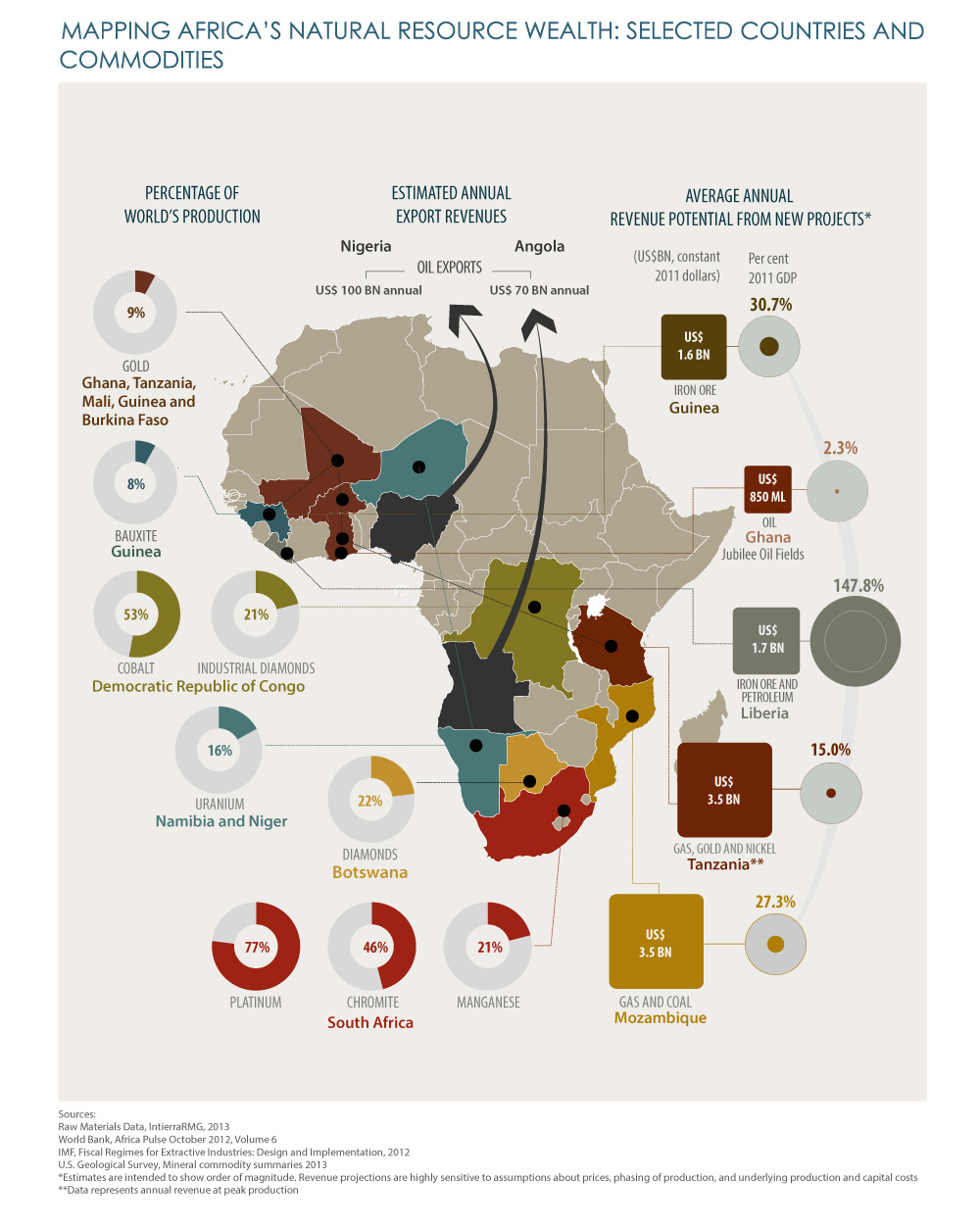
Africa, the second-largest continent by both landmass and population, is renowned for its immense natural wealth. This vast array of resources, spanning minerals, energy sources, agricultural land, and biodiversity, holds immense potential for economic growth and development. A comprehensive understanding of Africa’s resource map is crucial for unlocking this potential and fostering sustainable prosperity.
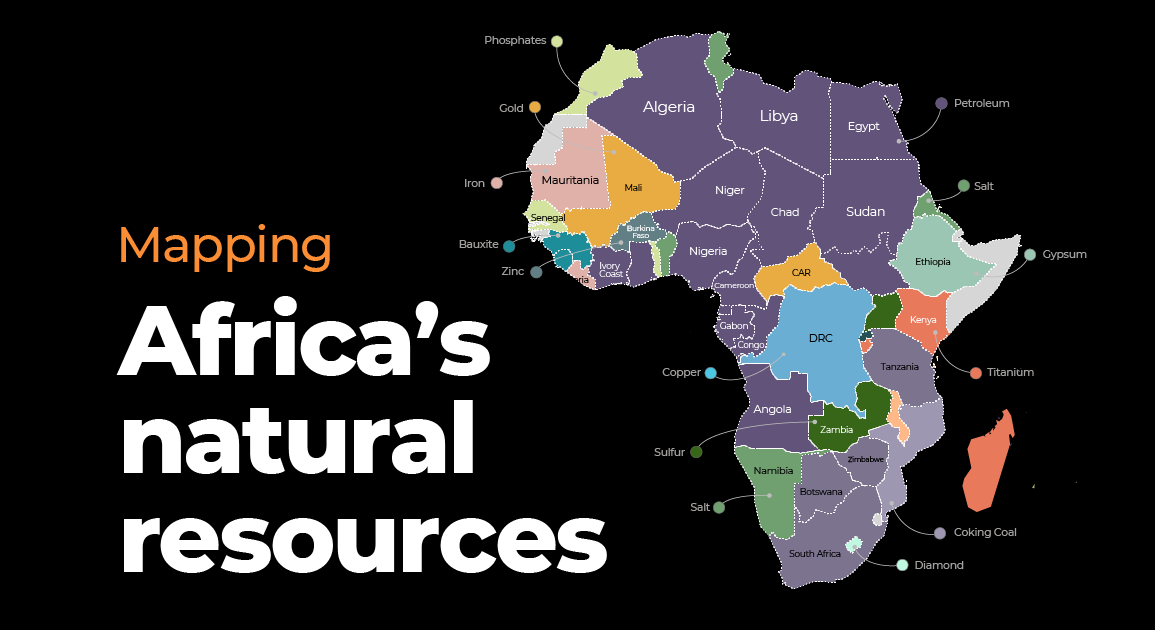
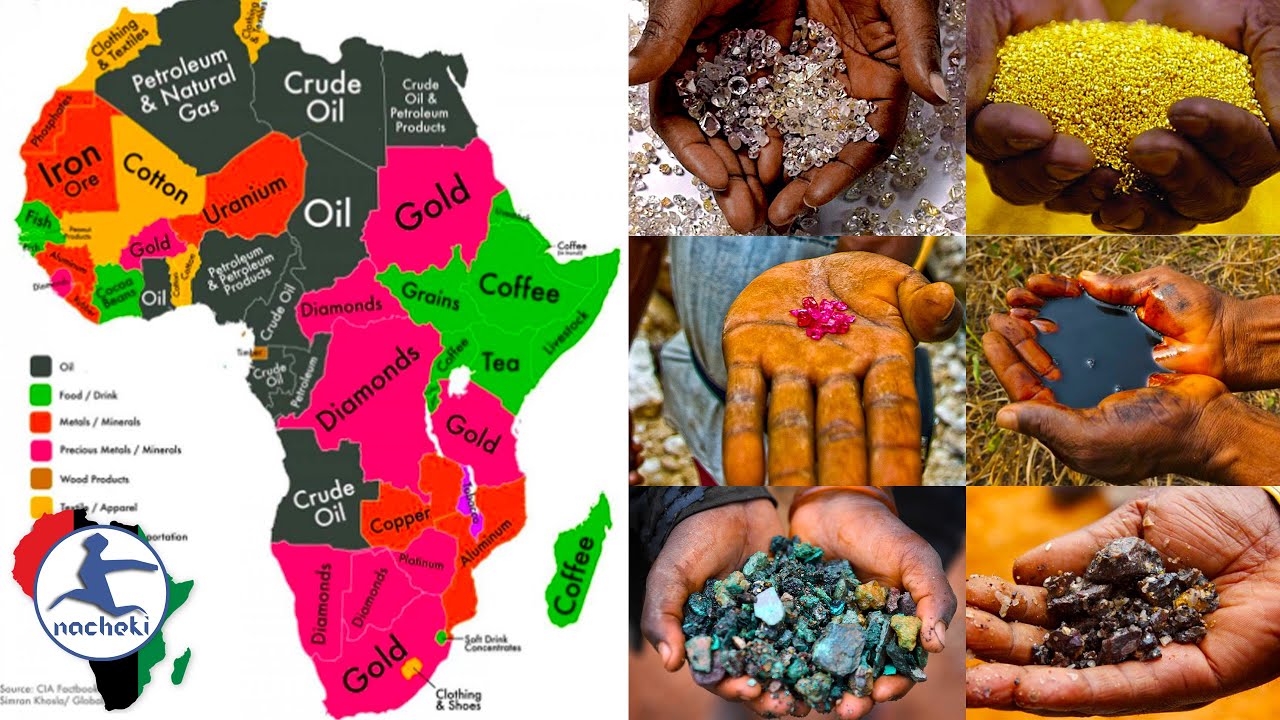
Mineral Riches: A Foundation for Industrial Growth
Africa possesses a significant share of the world’s mineral resources, playing a vital role in global supply chains. From the glittering gold mines of South Africa to the vast copper deposits of the Democratic Republic of Congo, the continent boasts a diverse mineral landscape.
Key Minerals and Their Locations:
- Gold: South Africa, Ghana, Mali, Burkina Faso, Zimbabwe
- Diamonds: Botswana, South Africa, Democratic Republic of Congo, Angola
- Copper: Democratic Republic of Congo, Zambia, South Africa, Namibia
- Cobalt: Democratic Republic of Congo, Zambia, Madagascar
- Platinum Group Metals (PGMs): South Africa, Zimbabwe
- Iron Ore: South Africa, Mauritania, Algeria, Liberia
- Bauxite: Guinea, Ghana, Cameroon
- Uranium: Niger, Namibia, South Africa, Gabon
- Phosphates: Morocco, Senegal, Togo, Tunisia
These mineral resources are fundamental to various industries, from construction and manufacturing to electronics and energy production. Their extraction and processing can drive economic growth, generate employment, and foster technological advancement. However, it is crucial to ensure sustainable mining practices that minimize environmental damage and promote community development.
Energy Potential: Powering Africa’s Future
Africa holds vast reserves of energy resources, both traditional and renewable, offering the potential to power its development and contribute to global energy security.
Traditional Energy Sources:
- Oil and Gas: Nigeria, Algeria, Libya, Angola, Egypt
- Coal: South Africa, Mozambique, Zimbabwe
While fossil fuels remain significant contributors to Africa’s energy mix, the continent is increasingly turning towards renewable sources to address energy poverty and climate change concerns.
Renewable Energy Potential:
- Hydropower: Ethiopia, Democratic Republic of Congo, Zambia, Tanzania
- Solar Power: North Africa, particularly Morocco, Egypt, and Tunisia
- Wind Power: South Africa, Kenya, Ethiopia
- Geothermal Power: Ethiopia, Kenya, Rwanda
Developing these renewable energy sources can not only provide clean and reliable energy for millions of Africans but also create new industries and attract foreign investment.
Agricultural Bounty: Feeding the Continent and Beyond
Africa boasts vast arable land, ideal for agricultural production. The continent’s diverse climate and soil types support a wide range of crops, from staple foods like maize and rice to cash crops like coffee, cocoa, and cotton.
Key Agricultural Products:
- Maize: South Africa, Nigeria, Ethiopia, Kenya
- Rice: Nigeria, Egypt, Madagascar, Senegal
- Wheat: Egypt, Morocco, Algeria
- Cassava: Nigeria, Ghana, Tanzania
- Coffee: Ethiopia, Uganda, Kenya, Côte d’Ivoire
- Cocoa: Côte d’Ivoire, Ghana, Nigeria
- Cotton: Egypt, Sudan, Benin, Burkina Faso
Developing sustainable agricultural practices is crucial for ensuring food security, increasing rural incomes, and promoting economic growth.
Biodiversity: A Natural Treasure Trove
Africa is home to a remarkable array of biodiversity, boasting a vast array of plant and animal species. This biodiversity holds immense value for scientific research, medicine, and tourism.
Key Biodiversity Hotspots:
- The Congo Basin: The world’s second-largest rainforest, teeming with biodiversity.
- The Eastern Afromontane: A region of diverse mountains and forests, home to unique flora and fauna.
- The Guinean Forests of West Africa: A region of rich rainforests and diverse wildlife.
- The Madagascar Biodiversity Hotspot: A unique island ecosystem with a high concentration of endemic species.
Protecting Africa’s biodiversity is crucial for maintaining ecosystem services, preserving cultural heritage, and fostering sustainable development.
Challenges and Opportunities: Navigating the Resource Landscape
While Africa’s resource wealth presents significant opportunities for development, it also faces a number of challenges:
- Resource Curse: In some cases, mineral wealth has led to conflict, corruption, and inequality, rather than sustainable development.
- Infrastructure Deficiencies: Limited infrastructure, particularly in transportation and energy, hinders resource extraction and processing.
- Lack of Investment: Insufficient investment in research and development, technology, and human capital hinders the full exploitation of resource potential.
- Environmental Sustainability: Balancing resource extraction with environmental protection is essential to ensure long-term sustainability.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach:
- Good Governance: Promoting transparency, accountability, and inclusive development to ensure resource wealth benefits all citizens.
- Investment in Infrastructure: Developing robust infrastructure to facilitate resource extraction, processing, and transportation.
- Human Capital Development: Investing in education, training, and skills development to create a skilled workforce.
- Sustainable Resource Management: Implementing responsible resource extraction practices and environmental regulations to protect ecosystems and communities.
FAQs about Africa’s Resource Map
Q: What are the major resource-rich countries in Africa?
A: South Africa, Nigeria, Algeria, Democratic Republic of Congo, Egypt, Angola, and Ghana are among the countries with the most significant resource endowments.
Q: How can Africa’s resources contribute to economic development?
A: Resource extraction can generate revenue, create jobs, and stimulate industrial growth. Diversification of economies, value addition through processing, and investment in human capital are crucial to maximizing benefits.
Q: What are the environmental impacts of resource extraction in Africa?
A: Resource extraction can lead to deforestation, pollution, habitat loss, and climate change. Sustainable practices, including responsible mining and environmental regulations, are vital to minimize these impacts.
Q: What are the challenges of managing Africa’s resources?
A: Challenges include corruption, conflict, lack of infrastructure, limited technological capacity, and environmental degradation.
Q: What are the opportunities for sustainable development in Africa’s resource sector?
A: Opportunities include diversification of economies, value addition through processing, green energy development, sustainable mining practices, and investment in human capital.
Tips for Understanding Africa’s Resource Map
- Consult reliable sources: Utilize reputable organizations like the African Development Bank, the World Bank, and the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa for accurate data and analysis.
- Consider the context: Understand the historical, political, and social factors that influence resource management in Africa.
- Focus on sustainability: Recognize the importance of balancing resource extraction with environmental protection and community development.
- Engage with stakeholders: Listen to the voices of local communities, governments, and businesses to ensure inclusive and equitable resource management.
Conclusion
Africa’s resource map is a complex tapestry of opportunities and challenges. Understanding this map is crucial for unlocking the continent’s potential for sustainable development. By promoting good governance, investing in infrastructure, developing human capital, and embracing sustainable practices, Africa can harness its resource wealth to create a more prosperous and equitable future for all.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Resources: Understanding Africa’s Natural Wealth. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!