Decoding The Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Look At The French Political Map
By admin / August 19, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Decoding the Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the French Political Map
Related Articles: Decoding the Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the French Political Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Decoding the Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the French Political Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Decoding the Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the French Political Map
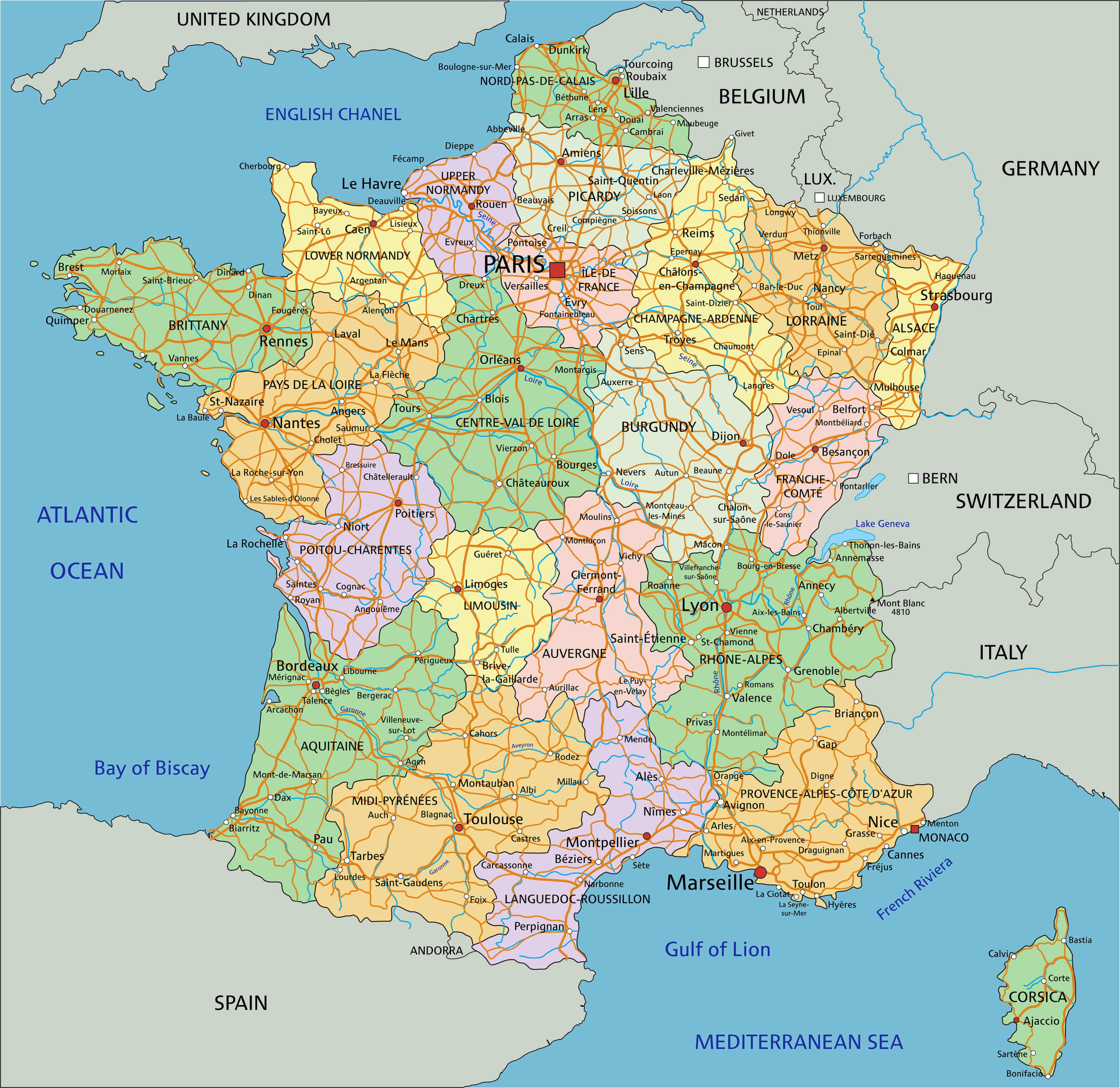
The political map of France is a complex tapestry woven with historical threads, regional identities, and contemporary political realities. It goes beyond a mere visual representation of administrative boundaries, offering a deeper understanding of the country’s intricate political dynamics. This article delves into the intricacies of this map, exploring its key components, their significance, and the impact they have on the nation’s political landscape.
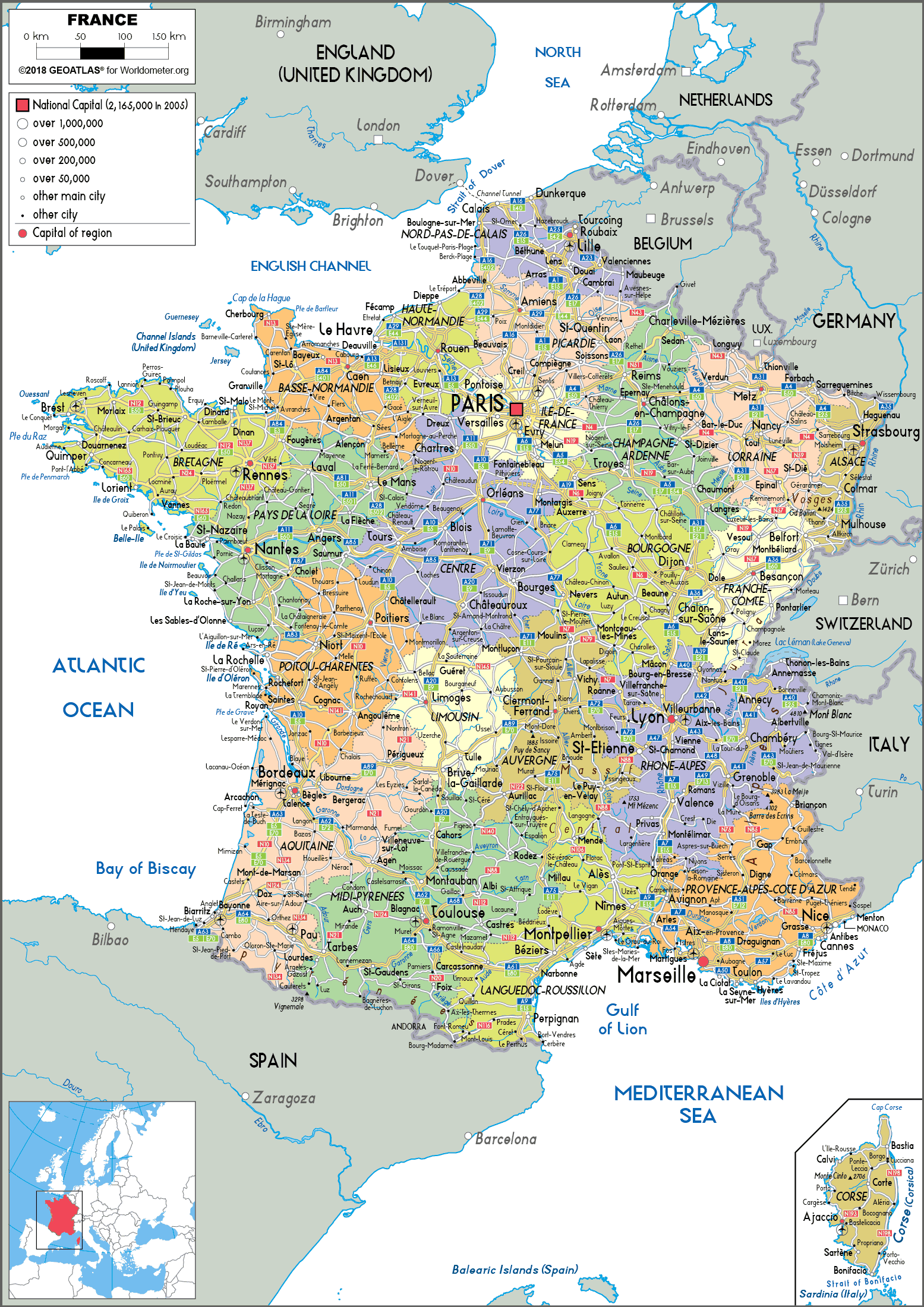
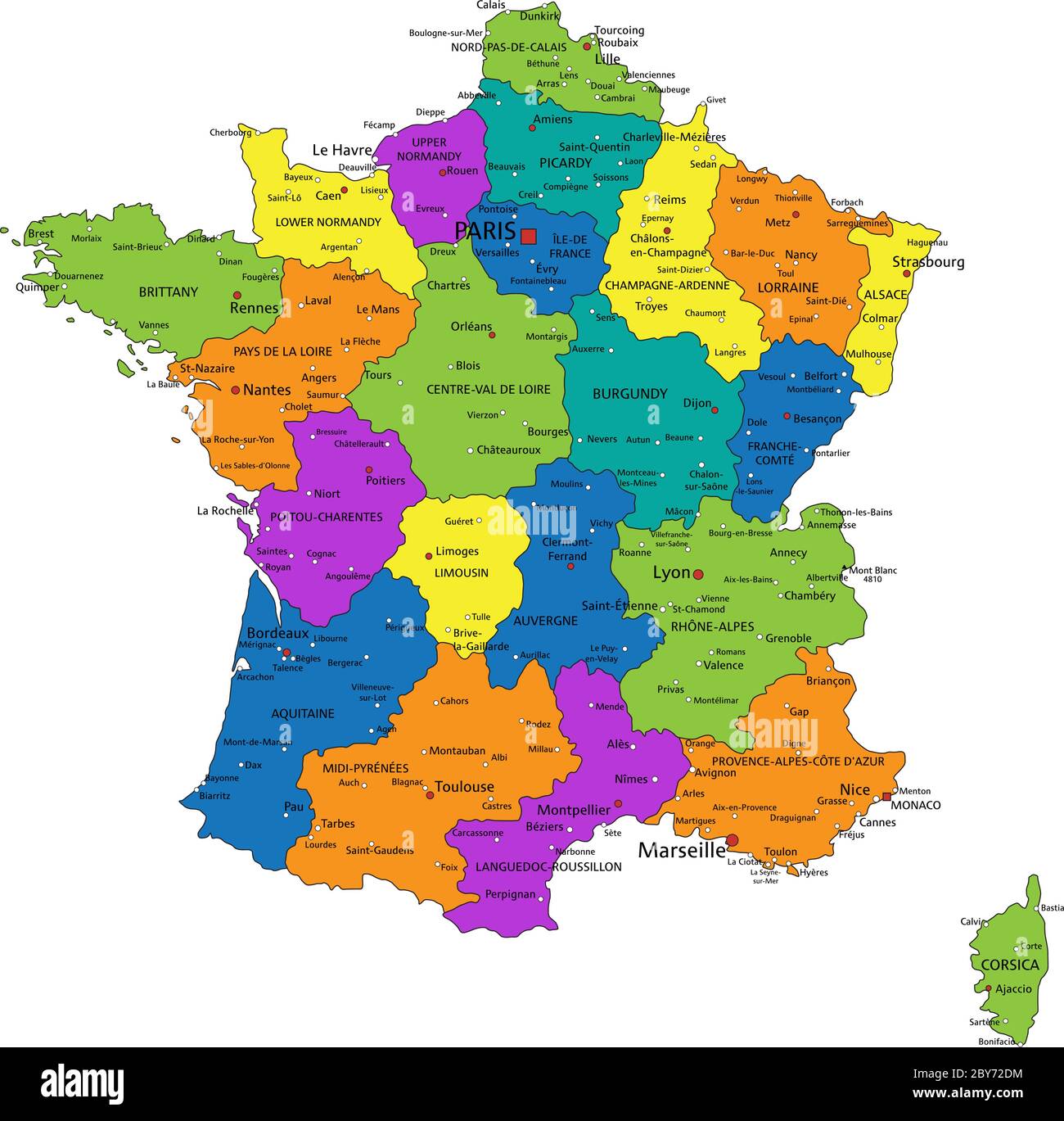
The Foundation: Administrative Divisions
France is divided into 18 regions, each with a distinct identity and varying levels of autonomy. These regions, further subdivided into 101 departments, form the bedrock of the French administrative structure. Each region possesses a Regional Council, responsible for managing local affairs like education, transportation, and environmental policies. This decentralized system fosters a sense of regional identity and allows for tailored solutions to local challenges.
Beyond Boundaries: The Political Spectrum
While the administrative map lays the groundwork, the political map is shaped by the diverse spectrum of political ideologies represented across the country. The French political landscape is characterized by a dynamic interplay of left-leaning, right-leaning, and centrist parties.
- Left-leaning parties typically emphasize social justice, economic equality, and government intervention in the economy. They often advocate for stronger social welfare programs and environmental protection.
- Right-leaning parties generally favor individual liberty, free-market principles, and limited government intervention. They often prioritize fiscal responsibility and a strong national defense.
- Centrist parties seek to find common ground between the left and right, emphasizing pragmatism and compromise. They often prioritize economic growth and social stability.
The distribution of these political ideologies across the regions reveals fascinating patterns. For example, the historically industrial regions of northern France tend to lean left, while the more rural and agricultural regions of the south often favor right-leaning parties. This regional variation in political sentiment plays a significant role in national elections and policy debates.
A Closer Look: Key Regional Differences
1. Île-de-France: Home to Paris, the capital, Île-de-France is the most populous region and a center of economic and political power. It consistently votes for parties on the left of the political spectrum.
2. Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur: This region in the south of France is known for its Mediterranean climate and tourist industry. It has a strong right-wing presence, often electing candidates from the Republican Party.
3. Brittany: Located in the northwest of France, Brittany has a distinct cultural identity and a strong regionalist movement. It often votes for parties that advocate for greater regional autonomy.
4. Alsace: Situated in the east of France, Alsace has a unique history and a strong sense of regional identity. It has a history of voting for both left- and right-leaning parties, depending on the political climate.
5. Corsica: An island with a distinct culture and language, Corsica has a strong regionalist movement that advocates for greater autonomy from mainland France. It often votes for parties that prioritize regional interests.
The Importance of the Political Map
Understanding the political map of France is crucial for several reasons:
- Predicting Election Outcomes: The distribution of political ideologies across the regions provides valuable insights into the likely outcome of national elections.
- Shaping Policy Decisions: Regional differences in political sentiment influence the formation of national policies. For example, the strong environmental movement in Brittany has led to the adoption of policies aimed at protecting the region’s natural resources.
- Promoting Regional Development: The regional councils, elected by the people, play a crucial role in shaping the development of their respective regions. They prioritize local needs and allocate resources to address regional challenges.
- Fostering National Unity: While regional differences exist, the political map also highlights the shared values and aspirations that unite the French people.
FAQs about the Political Map of France:
1. What is the most politically diverse region in France?
The Rhône-Alpes region is known for its diverse political landscape, with a significant presence of both left- and right-leaning parties.
2. How has the political map of France changed over time?
The political map of France has evolved significantly over time, reflecting changes in demographics, economic trends, and social attitudes. For example, the rise of regionalist movements has led to a greater emphasis on regional identities and political autonomy.
3. How does the political map of France compare to those of other European countries?
Compared to other European countries, the political map of France exhibits a relatively high level of regional diversity. However, it is important to note that the political landscape is constantly evolving, and these comparisons can change over time.
Tips for Understanding the Political Map of France:
- Consult reliable sources: Stay informed about the latest political developments and regional trends by consulting reputable news sources and academic journals.
- Engage in discussions: Participate in conversations about French politics with people from different backgrounds and regions. This will help you gain a more nuanced understanding of the country’s political landscape.
- Travel to different regions: Experiencing the diverse cultures and perspectives of different regions firsthand can provide invaluable insights into the political map of France.
Conclusion
The political map of France is a dynamic and ever-evolving representation of the country’s complex political reality. It provides a framework for understanding the interplay of regional identities, political ideologies, and national priorities. By recognizing the regional variations and the forces shaping the political landscape, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the richness and diversity of French politics.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Decoding the Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the French Political Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!