Navigating The Flooded Landscape: Understanding Flood Risks In West Virginia
By admin / July 31, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Navigating the Flooded Landscape: Understanding Flood Risks in West Virginia
Related Articles: Navigating the Flooded Landscape: Understanding Flood Risks in West Virginia
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Flooded Landscape: Understanding Flood Risks in West Virginia. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Flooded Landscape: Understanding Flood Risks in West Virginia

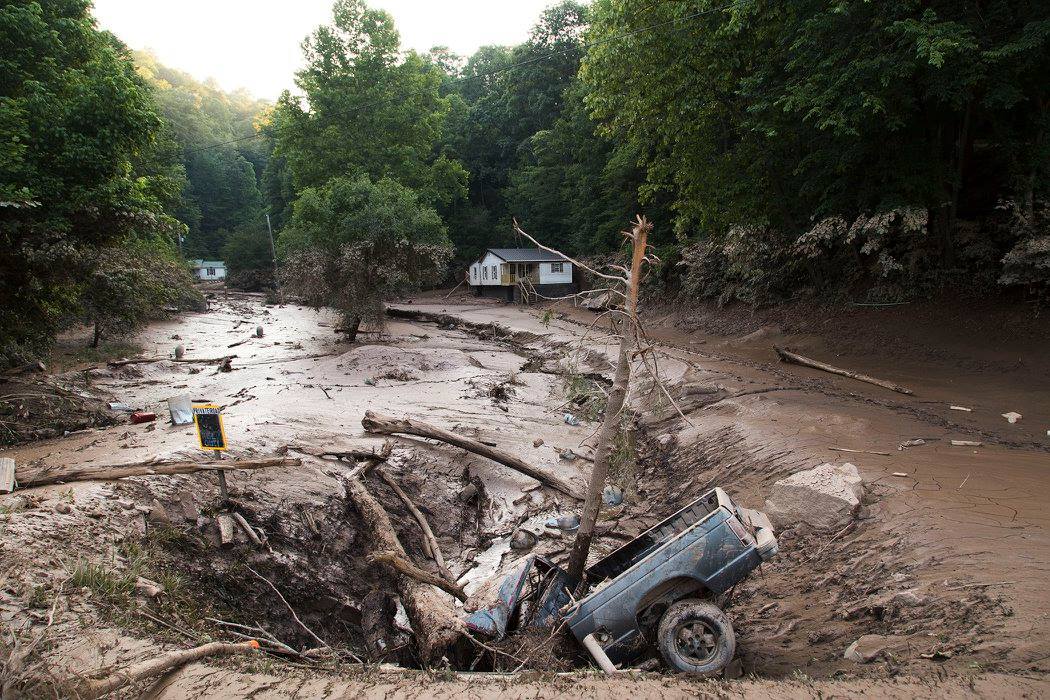
West Virginia, known for its rugged beauty and Appalachian heritage, also bears the burden of significant flood risk. The state’s topography, characterized by steep mountains, narrow valleys, and numerous rivers and streams, makes it particularly susceptible to flooding. This susceptibility is exacerbated by factors like heavy rainfall, rapid snowmelt, and deforestation, contributing to a complex interplay of natural and human-induced vulnerabilities.
Understanding the Geography of Flooding in West Virginia
The state’s topography plays a crucial role in flood patterns. The Appalachian Mountains, which dominate the state’s landscape, create a series of narrow valleys and steep slopes. When heavy rainfall occurs, water rushes down these slopes, accumulating rapidly in the valleys, leading to flash floods. The numerous rivers and streams, often originating in the mountains, further amplify the risk.
The Role of Rainfall and Snowmelt
West Virginia experiences significant rainfall, particularly during the spring and summer months. These periods often coincide with snowmelt, further increasing the volume of water flowing into rivers and streams. The combination of heavy rainfall and snowmelt can overwhelm the capacity of waterways, leading to widespread flooding.
The Impact of Human Activities
Human activities, such as deforestation and urbanization, can significantly exacerbate flood risks. Deforestation removes the natural barriers that slow down water flow, accelerating runoff and increasing flood severity. Urbanization, with its impervious surfaces like concrete and asphalt, prevents water absorption into the ground, further contributing to rapid runoff and flooding.
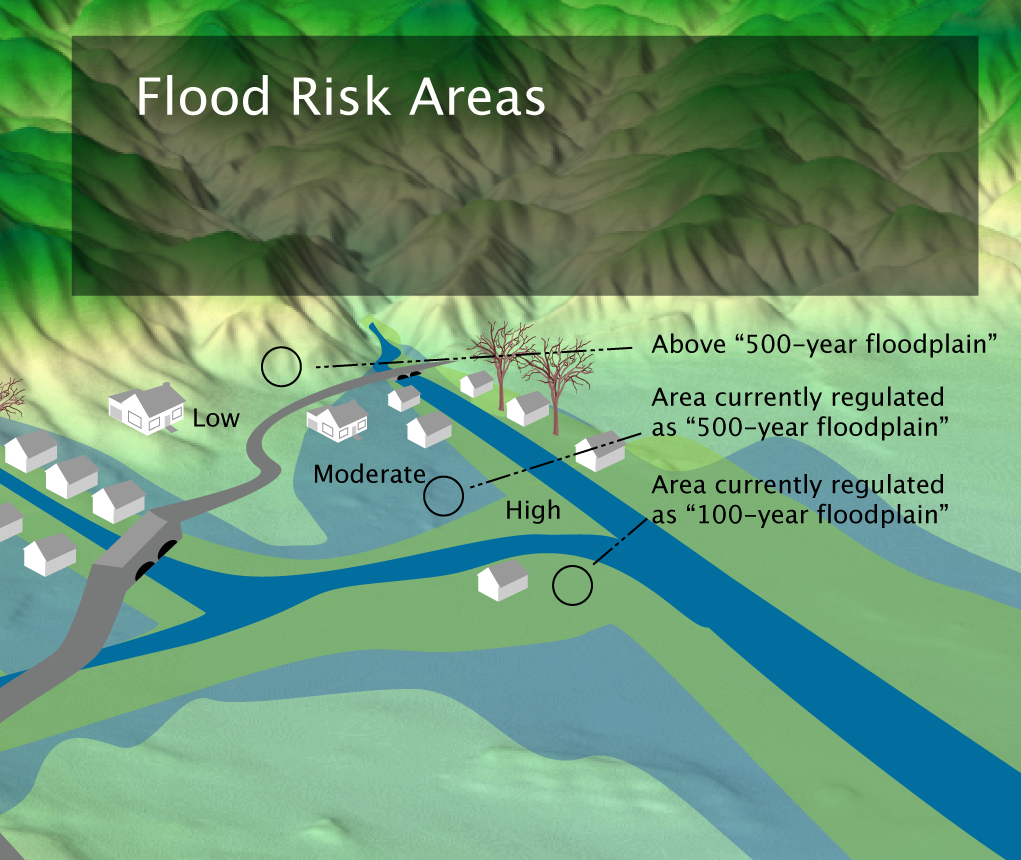
Mapping the Flood Risk
Visualizing flood risk is crucial for understanding the potential impact of flooding and developing effective mitigation strategies. Flood risk maps, created using geographic information systems (GIS) and historical flood data, provide a valuable tool for identifying areas prone to flooding. These maps can be used to:
- Identify high-risk areas: By highlighting areas with a high probability of flooding, maps can help residents and communities understand their vulnerability.
- Guide infrastructure development: Planning infrastructure projects like roads, bridges, and buildings in areas less prone to flooding can minimize potential damage.
- Inform emergency response: Maps can assist emergency responders in identifying affected areas and allocating resources efficiently during flood events.
Understanding the Types of Floods in West Virginia
West Virginia experiences various types of floods, each with unique characteristics and impacts:
- Flash floods: These rapid and intense floods occur within a few hours of heavy rainfall or rapid snowmelt. They are particularly dangerous due to their sudden onset and the limited time for evacuation.
- Riverine floods: These floods occur when rivers and streams overflow their banks due to prolonged rainfall or snowmelt. They often affect wider areas and can last for days or weeks.
- Coastal floods: While less common than other types, coastal flooding can occur in West Virginia due to rising sea levels and storm surges.
The Impact of Flooding on West Virginia
Flooding in West Virginia has significant impacts on the state’s economy, infrastructure, and environment:
- Economic impact: Flooding can disrupt businesses, damage property, and lead to job losses. The agricultural sector is particularly vulnerable, with crops and livestock often being destroyed by floodwaters.
- Infrastructure damage: Roads, bridges, and other infrastructure can be damaged or destroyed by flooding, disrupting transportation and communication.
- Environmental impact: Flooding can pollute waterways with debris and sewage, harming aquatic life and water quality. It can also erode soil, leading to sedimentation and habitat loss.
FAQs about Flooding in West Virginia
Q: What are the most flood-prone areas in West Virginia?
A: The most flood-prone areas in West Virginia are typically located in narrow valleys, along rivers and streams, and in areas with steep slopes. These areas are particularly vulnerable to flash floods and riverine floods.
Q: What can I do to prepare for a flood?
A: You can prepare for a flood by:
- Identifying flood risks in your area: Consult flood risk maps and be aware of potential flood sources.
- Developing a flood plan: Determine evacuation routes, gather emergency supplies, and communicate your plan with family members.
- Elevating valuables: Store important documents and belongings in waterproof containers or on higher floors.
Q: What are the signs of an impending flood?
A: Signs of an impending flood include:
- Rapidly rising water levels: Observe rivers and streams for sudden changes in water levels.
- Increased water flow: Pay attention to increased water flow and the sound of rushing water.
- Heavy rainfall or snowmelt: Be aware of weather forecasts and potential for heavy rainfall or snowmelt.
Tips for Staying Safe During a Flood
- Evacuate immediately: If you are advised to evacuate, do so immediately. Do not attempt to drive through flooded areas.
- Stay informed: Monitor weather reports and official announcements for updates on flood conditions.
- Be aware of potential hazards: Be cautious of downed power lines, debris, and contaminated water.
- Help your neighbors: If you are able, assist those in need, but prioritize your own safety.
Conclusion
Understanding flood risks in West Virginia is crucial for protecting lives, property, and the environment. By recognizing the factors contributing to flooding, utilizing flood risk maps, and implementing mitigation strategies, communities can reduce vulnerability and build resilience to these natural hazards. While flooding poses significant challenges, it also highlights the importance of responsible land management, proactive planning, and community preparedness. By working together, West Virginia can effectively navigate the challenges posed by flooding and ensure the well-being of its residents and the preservation of its unique landscape.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Flooded Landscape: Understanding Flood Risks in West Virginia. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!