The Azov Sea: A Vital Waterway In A Complex Region
By admin / April 12, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
The Azov Sea: A Vital Waterway in a Complex Region
Related Articles: The Azov Sea: A Vital Waterway in a Complex Region
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Azov Sea: A Vital Waterway in a Complex Region. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Azov Sea: A Vital Waterway in a Complex Region

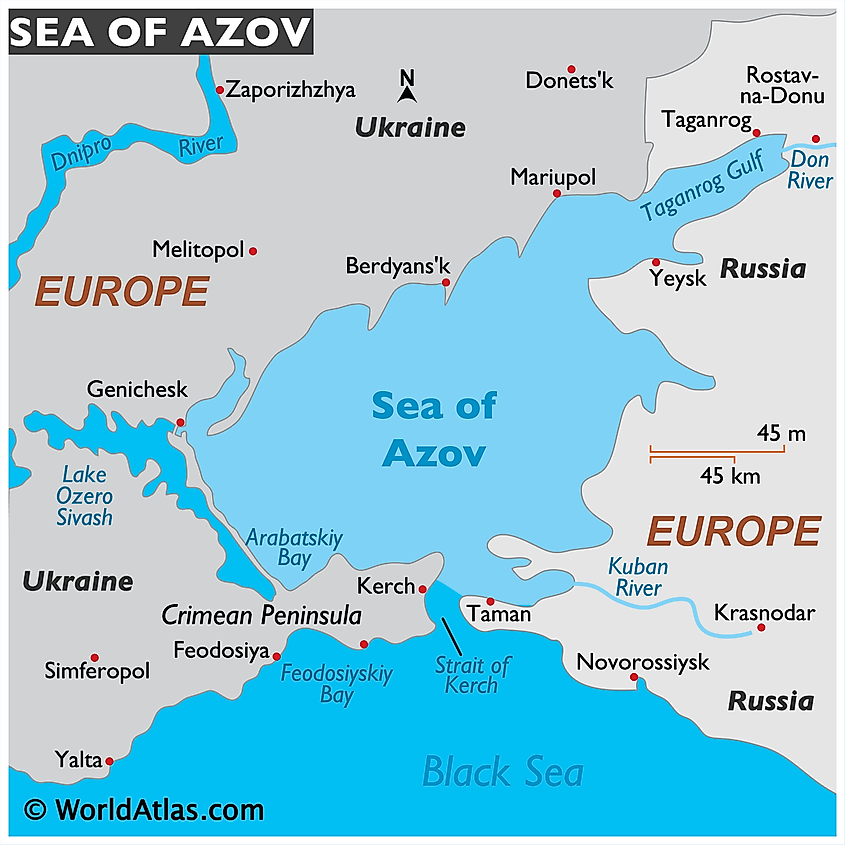
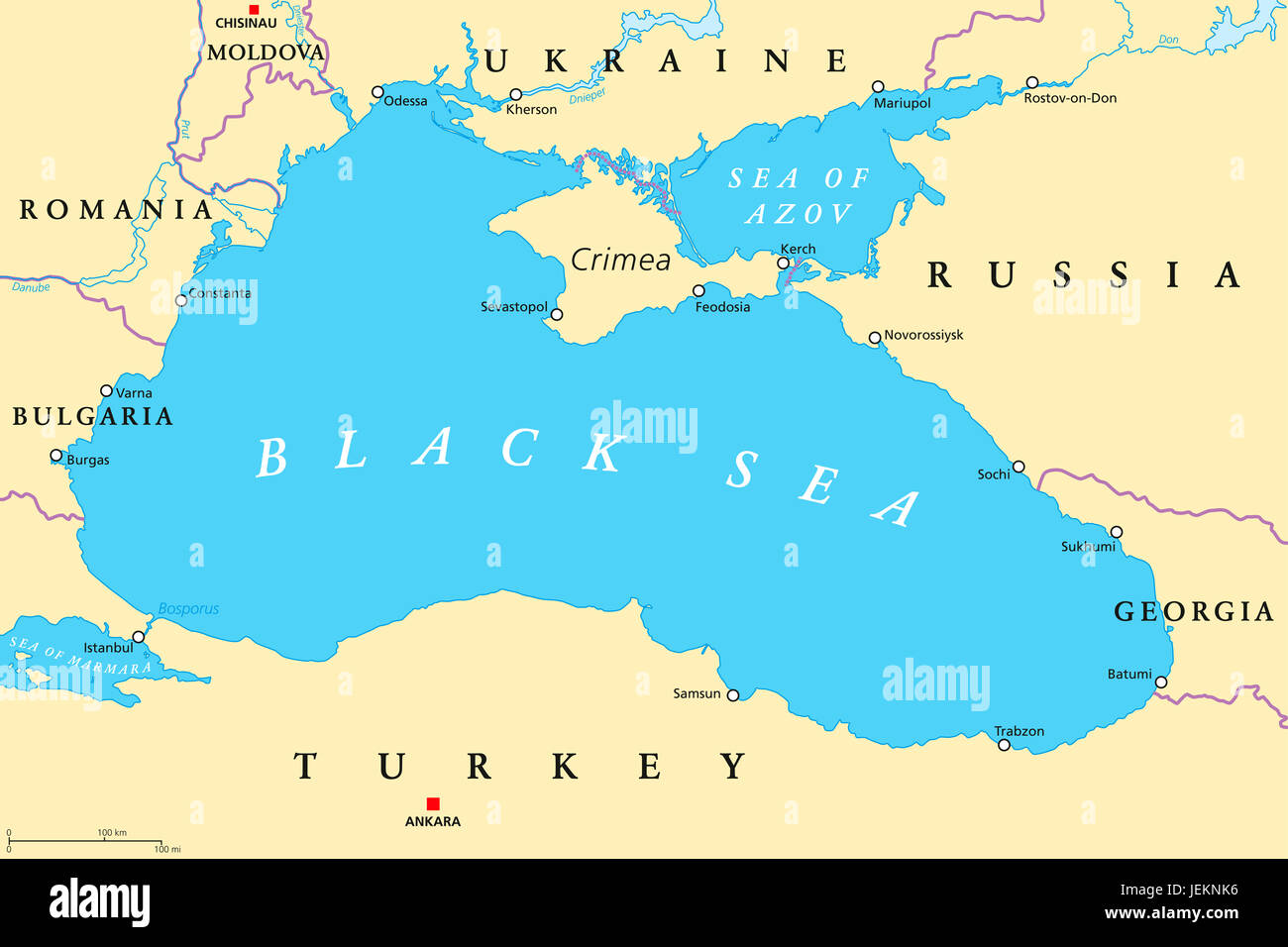
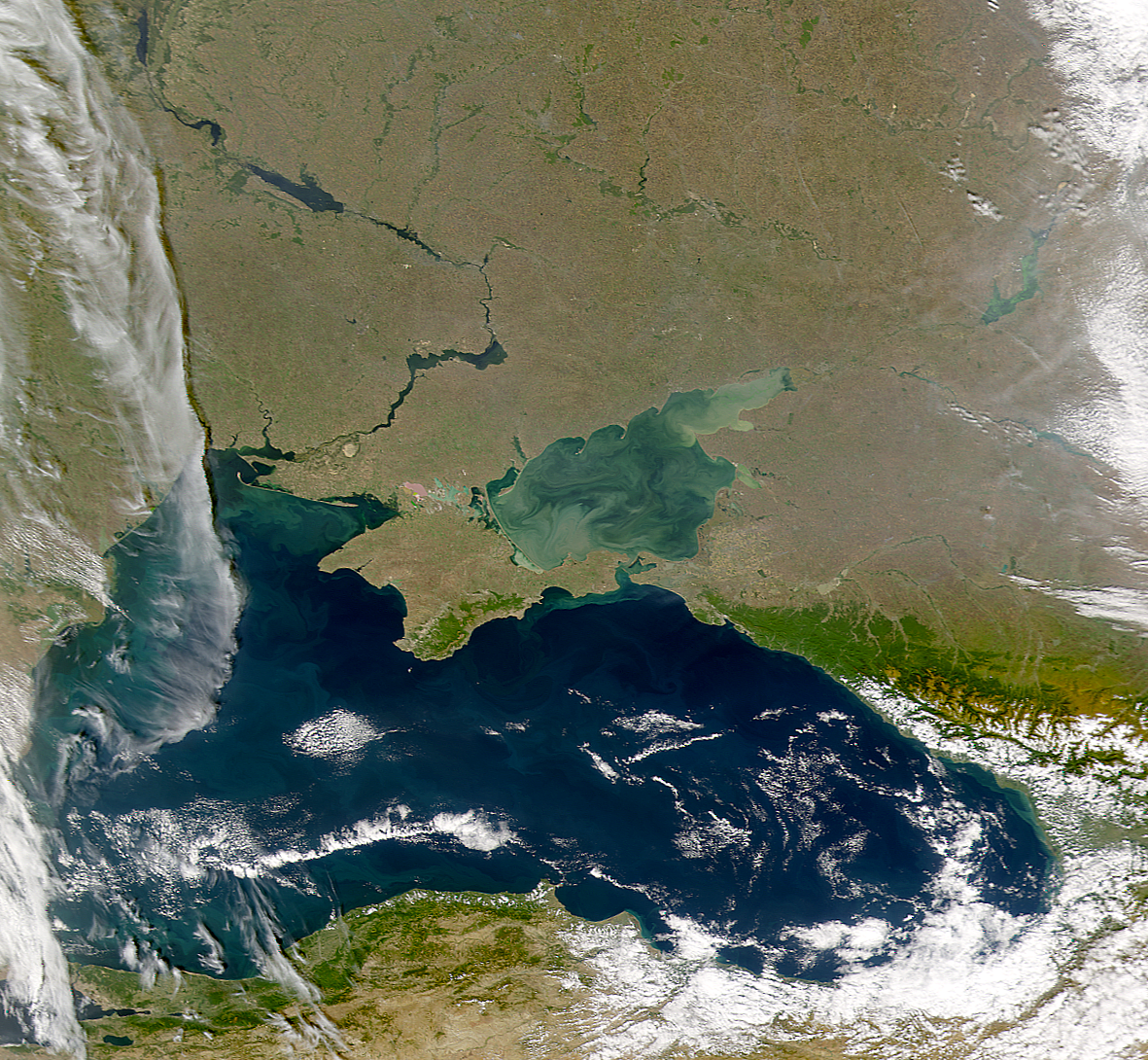
The Azov Sea, a shallow inland sea nestled between Ukraine and Russia, is a vital waterway with a rich history and a complex present. It is the smallest sea in the world by surface area, yet its significance extends far beyond its size. Its strategic location, abundant resources, and unique ecosystem make it a crucial player in regional politics, economics, and environmental concerns. Understanding the Azov Sea’s geography, history, and current challenges is essential for grasping the complexities of the Black Sea region and its impact on international relations.
Geographical Overview:
The Azov Sea is connected to the Black Sea through the narrow Strait of Kerch, which acts as a gateway between the two bodies of water. Its relatively small size, covering approximately 39,000 square kilometers, belies its importance as a critical transportation route and a vital source of resources. The sea is shallow, with an average depth of just 7 meters, and its waters are characterized by low salinity due to the influx of freshwater from numerous rivers, most notably the Don and Kuban.
A History of Conflict and Cooperation:
The Azov Sea has been a focal point of historical conflicts and cooperation for centuries. Its strategic location, connecting the Black Sea to the Don River and beyond, has made it a coveted waterway for both trade and military control. Throughout history, various empires, including the Scythians, Greeks, Romans, Byzantines, and Ottomans, have sought to control its waters and the surrounding lands.
The 17th and 18th centuries saw the Azov Sea become a battleground between Russia and the Ottoman Empire, with control shifting back and forth. The region was eventually incorporated into the Russian Empire, and the sea became a vital economic hub for the Russian Empire, facilitating trade and transportation.
The 20th Century and Beyond:
The 20th century brought new challenges and opportunities for the Azov Sea. The establishment of the Soviet Union led to the development of extensive infrastructure, including ports, canals, and industrial complexes, along its shores. The sea became a major center for fishing, shipping, and resource extraction. However, the intense industrialization and agricultural development also led to environmental degradation, including pollution and overfishing.
The collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 marked a significant turning point for the Azov Sea. The region became divided between Ukraine and Russia, with both countries claiming ownership of the sea’s waters and resources. This division led to disputes over resource allocation, fishing quotas, and navigation rights, further complicating the region’s political landscape.
Current Challenges and Concerns:
The Azov Sea currently faces a multitude of challenges, stemming from both human activities and natural phenomena. The most pressing issue is the impact of industrialization and pollution. Decades of intensive resource extraction and industrial activity have resulted in significant environmental damage, including:
- Pollution: The Azov Sea is heavily polluted by industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and sewage discharge. This pollution has led to a decline in water quality, affecting marine life and impacting the health of coastal communities.
- Overfishing: Overfishing has depleted fish stocks, threatening the livelihoods of local fishermen and disrupting the delicate balance of the marine ecosystem.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures and changing weather patterns are affecting the Azov Sea’s ecosystem, leading to increased salinity, algal blooms, and habitat loss.
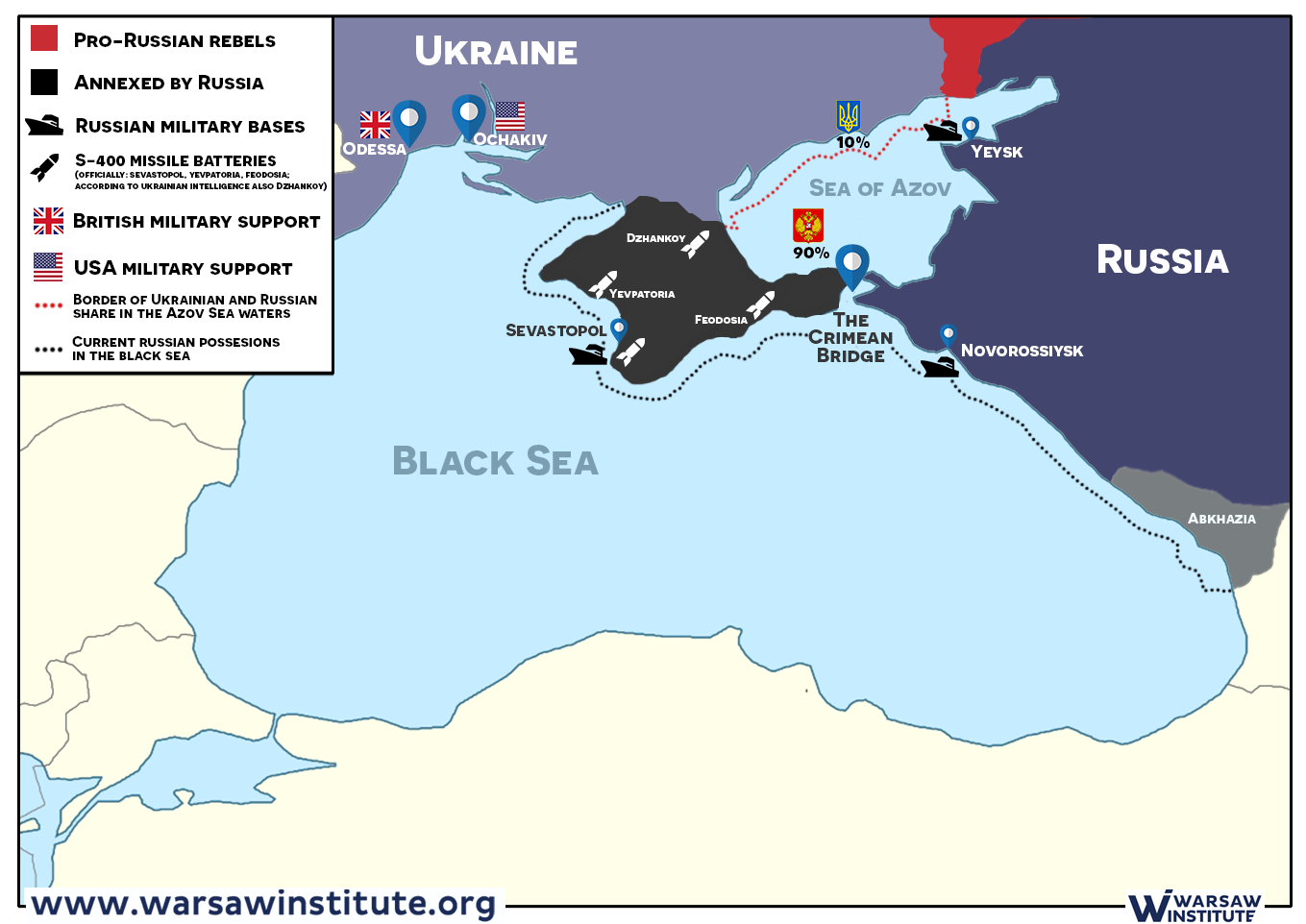
These challenges are further exacerbated by the ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine. The annexation of Crimea by Russia in 2014, which includes the strategically important Strait of Kerch, has significantly impacted navigation and resource access. The ongoing conflict has also led to increased military activity and the deployment of naval forces in the region, raising concerns about potential escalation and environmental damage.
Economic Importance and Resources:
Despite the challenges, the Azov Sea remains a vital economic resource for both Ukraine and Russia. Its waters are rich in fish, including sturgeon, herring, and sprat, and the seafloor holds significant reserves of oil and natural gas. The region is also a major center for agriculture, with vast fields producing wheat, corn, and sunflowers.
The Azov Sea is also a crucial transportation route, connecting the Black Sea to the Don River and providing access to the inland regions of Russia and Ukraine. The ports of Mariupol, Rostov-on-Don, and Taganrog are major centers for shipping and trade, facilitating the movement of goods and people throughout the region.
The Future of the Azov Sea:
The future of the Azov Sea is uncertain, but its importance as a vital waterway and economic resource remains undeniable. Addressing the environmental challenges, promoting sustainable resource management, and fostering cooperation between Ukraine and Russia are crucial for ensuring the sea’s long-term health and prosperity.
FAQs about the Azov Sea:
1. What is the Azov Sea’s significance in the Black Sea region?
The Azov Sea is a vital waterway connecting the Black Sea to the Don River, facilitating trade and transportation throughout the region. Its rich resources, including fish and potential oil and gas reserves, contribute significantly to the local economies of Ukraine and Russia.
2. What are the main environmental challenges facing the Azov Sea?
The Azov Sea is facing severe environmental challenges, including pollution from industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and sewage discharge; overfishing; and the impacts of climate change. These factors threaten the sea’s ecosystem, impacting marine life and coastal communities.
3. How does the ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine affect the Azov Sea?
The conflict has exacerbated existing tensions over resource allocation, navigation rights, and environmental protection. The annexation of Crimea and the deployment of naval forces in the region have raised concerns about potential escalation and environmental damage.
4. What measures can be taken to protect the Azov Sea?
Protecting the Azov Sea requires a multifaceted approach, including:
- Reducing pollution: Implementing stricter regulations on industrial emissions, agricultural runoff, and sewage discharge.
- Sustainable fishing practices: Establishing quotas and enforcing fishing regulations to prevent overfishing.
- Climate change mitigation: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions to mitigate the impacts of climate change on the sea’s ecosystem.
- Cooperation between Ukraine and Russia: Fostering dialogue and collaboration on resource management, navigation rights, and environmental protection.
5. What is the future outlook for the Azov Sea?
The future of the Azov Sea depends on the ability of Ukraine and Russia to address the challenges facing the sea. Sustainable resource management, environmental protection, and cooperation are crucial for ensuring the sea’s long-term health and prosperity.
Tips for Understanding the Azov Sea:
- Explore maps and satellite imagery: Visualizing the sea’s location, its connection to the Black Sea, and its surrounding landmasses helps to grasp its strategic importance.
- Read historical accounts: Studying the Azov Sea’s history reveals its role in shaping the region’s political and economic landscape.
- Follow news and research: Staying informed about current events, scientific studies, and environmental initiatives provides insights into the challenges and opportunities facing the sea.
- Engage in discussions: Participating in discussions about the Azov Sea’s future helps to raise awareness and promote solutions for its protection.
Conclusion:
The Azov Sea, despite its small size, plays a significant role in the Black Sea region. Its strategic location, abundant resources, and unique ecosystem make it a vital waterway with a complex history and a challenging present. Addressing the environmental challenges, promoting sustainable resource management, and fostering cooperation between Ukraine and Russia are essential for ensuring the sea’s long-term health and prosperity. As a shared resource with significant economic and geopolitical importance, the Azov Sea requires a collaborative approach to ensure its future sustainability.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Azov Sea: A Vital Waterway in a Complex Region. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!