The Mosaic Of Iran: Understanding The Country’s Ethnic Diversity
By admin / August 22, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
The Mosaic of Iran: Understanding the Country’s Ethnic Diversity
Related Articles: The Mosaic of Iran: Understanding the Country’s Ethnic Diversity
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Mosaic of Iran: Understanding the Country’s Ethnic Diversity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Mosaic of Iran: Understanding the Country’s Ethnic Diversity

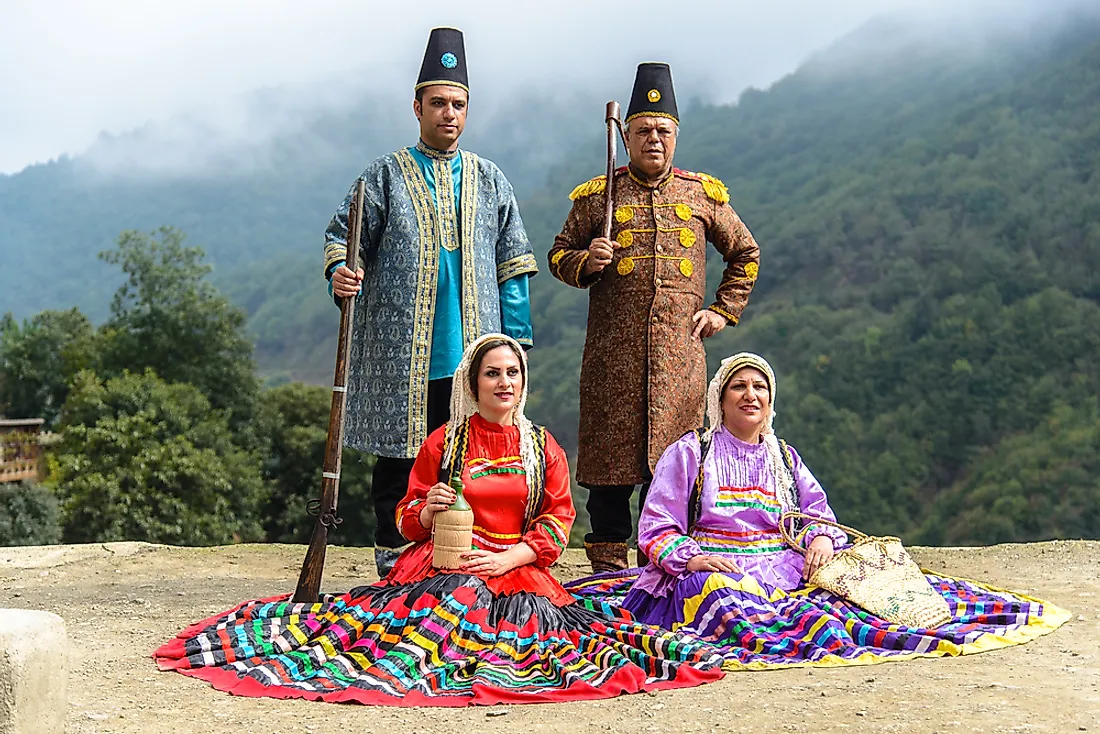
Iran, a nation nestled in the heart of the Middle East, is often perceived through the lens of its rich history, ancient culture, and vibrant landscapes. However, a deeper understanding of Iran necessitates acknowledging its multifaceted ethnic tapestry. The country is home to a remarkable array of ethnic groups, each with its unique language, traditions, and cultural heritage. This diversity, interwoven into the fabric of Iranian society, shapes the country’s identity and fosters a dynamic interplay of cultural influences.
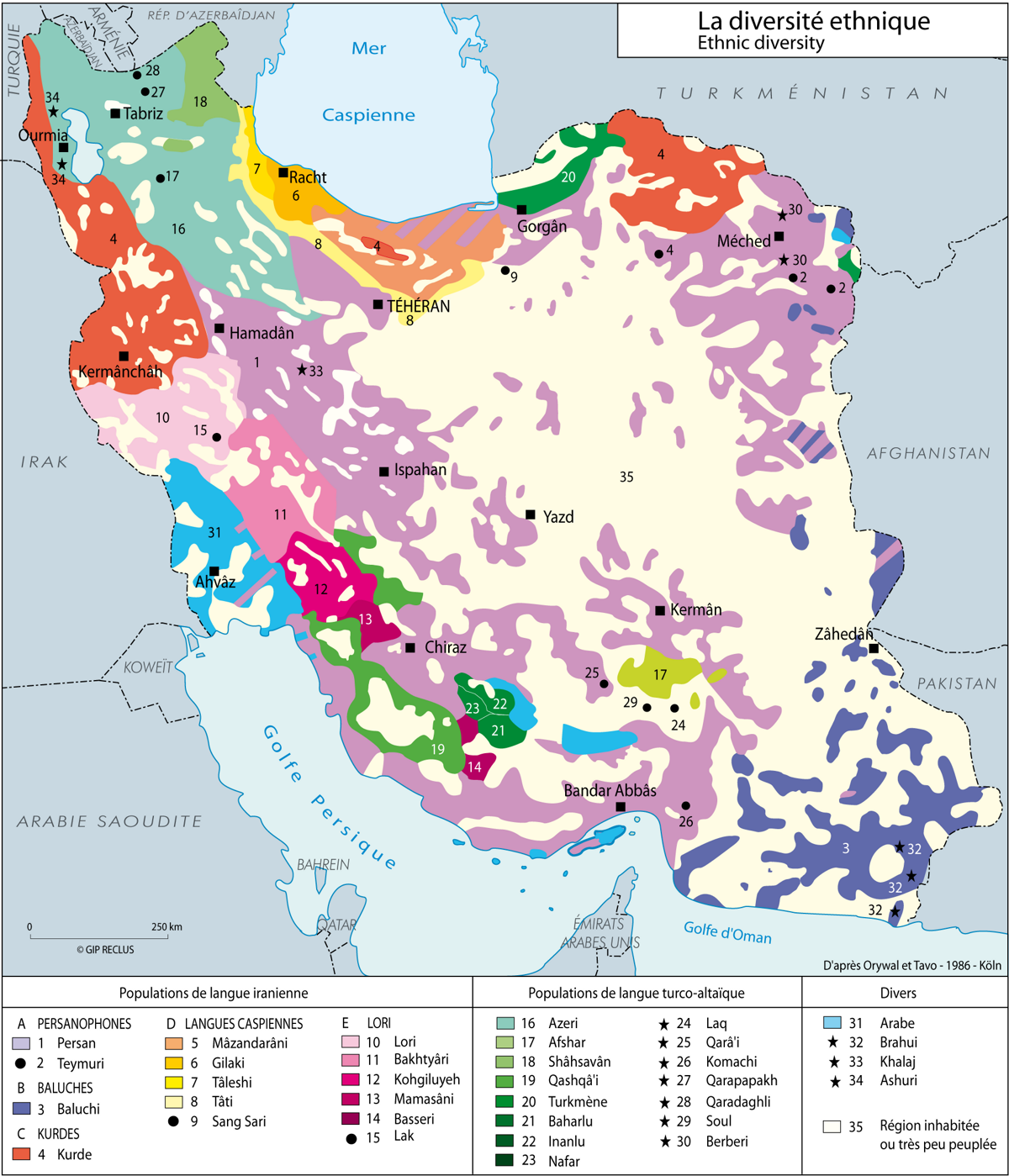
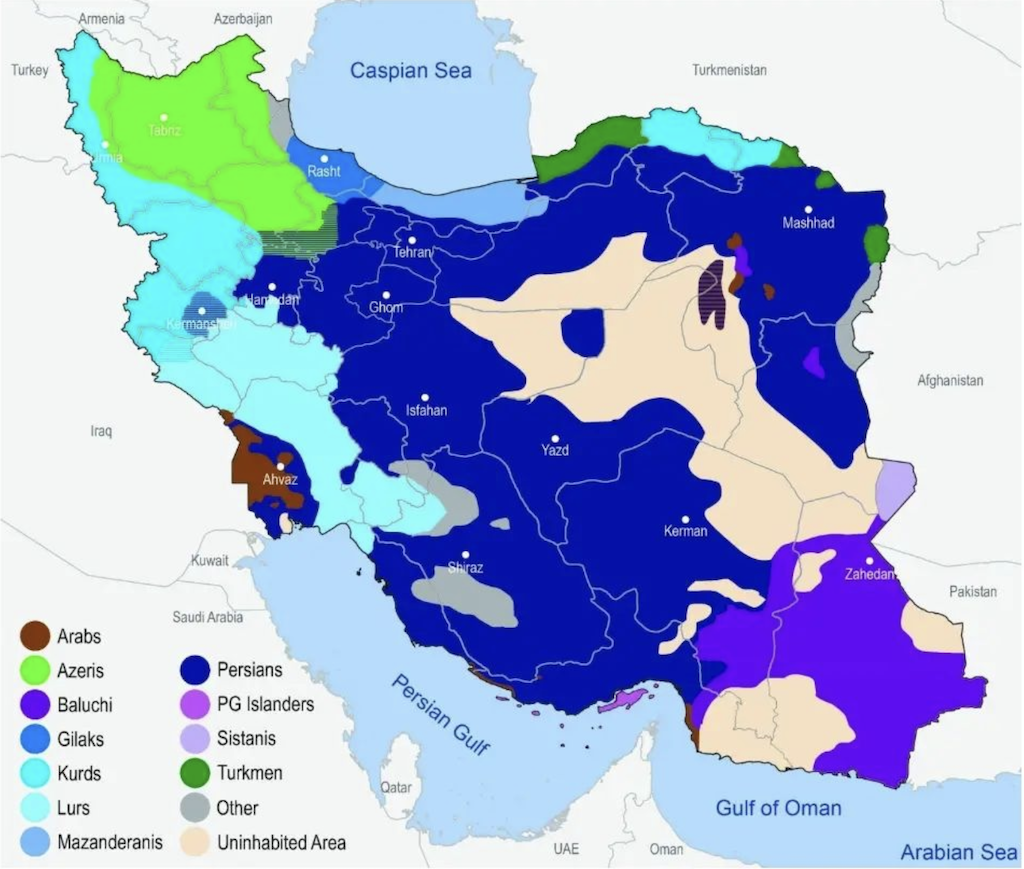
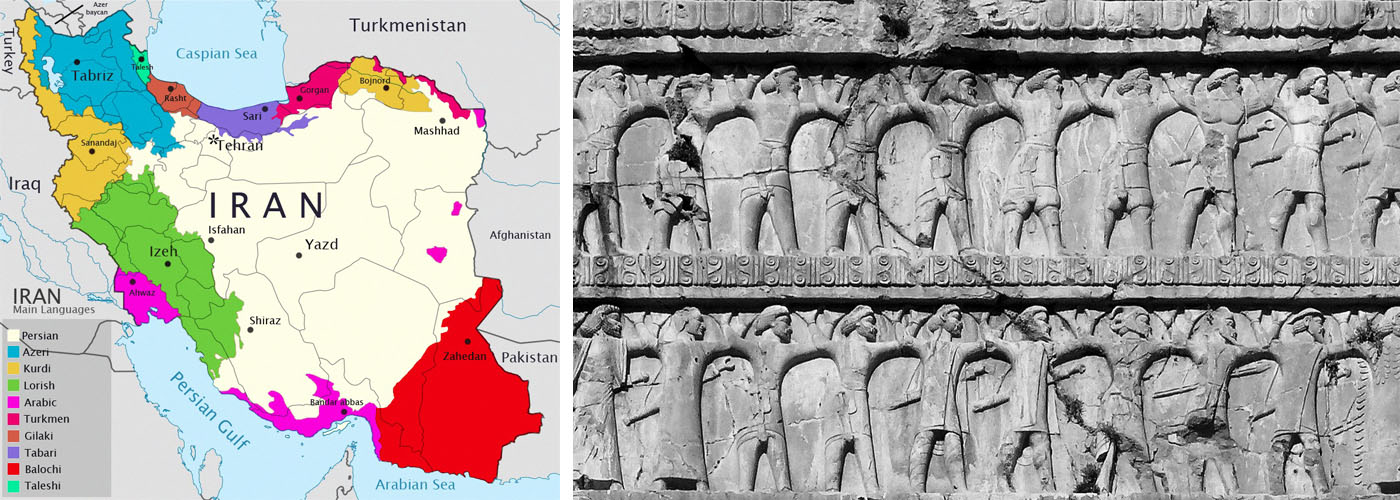
A Complex Mosaic: Decoding the Ethnic Map
The ethnic map of Iran, while complex, offers a fascinating glimpse into the country’s diverse population. The majority of Iranians identify as Persian (around 60%), with the Persian language serving as the official language. However, a significant number of other ethnic groups contribute to the country’s rich cultural mosaic.
1. The Azeri Population:
The largest non-Persian ethnic group in Iran is the Azeri, with an estimated population of around 16-25%. Primarily located in the northwestern region of the country, they share a common linguistic and cultural heritage with Azerbaijan, the independent nation to Iran’s north. The Azeri language, a Turkic language, is widely spoken in the region, and their cultural traditions are deeply rooted in Turkic culture, including music, dance, and cuisine.
2. The Kurds:
The Kurds, with an estimated population of around 10%, reside primarily in the western and northwestern regions of Iran, bordering Turkey, Iraq, and Syria. They are a distinct ethnic group with their own language and rich cultural traditions. Kurdish culture is deeply intertwined with nomadic traditions, emphasizing hospitality, poetry, and music.
3. The Lurs:
The Lurs, estimated to comprise around 2-3% of Iran’s population, are primarily located in the Zagros Mountains in western and southwestern Iran. Their language, Luri, is closely related to Persian, and their culture is deeply intertwined with the nomadic traditions of the region. They are known for their skilled craftsmanship, particularly in rug weaving and metalwork.
4. The Baluch:
The Baluch, with an estimated population of around 2%, reside in the southeastern regions of Iran, bordering Pakistan and Afghanistan. They speak the Baluchi language, a member of the Indo-Iranian language family, and their culture is heavily influenced by their nomadic past. They are renowned for their craftsmanship in textiles and handicrafts.
5. The Turkmen:
The Turkmen, with an estimated population of around 1%, are primarily located in the northeastern regions of Iran, bordering Turkmenistan. They speak the Turkmen language, a Turkic language, and their cultural traditions are closely tied to nomadic life and equestrian culture.
6. The Arabs:
The Arab population in Iran, estimated to be around 2%, primarily resides in the southwestern region of Khuzestan, bordering Iraq. They speak Arabic, and their culture is influenced by their proximity to the Arabian Peninsula.
7. Other Ethnic Groups:
Besides these major ethnic groups, Iran is home to a diverse array of smaller ethnic communities, including the Assyrians, Armenians, Gilaki, Mazandarani, and Qashqai. Each group contributes to the richness and complexity of Iranian culture, adding unique threads to the national tapestry.
The Importance of Ethnic Diversity in Iran
The ethnic map of Iran is not merely a geographical representation; it reflects the vibrant and dynamic nature of Iranian society. The presence of these diverse ethnic groups contributes to the following aspects:
-
Cultural Enrichment: Each ethnic group brings its unique traditions, languages, and cultural practices, enriching the cultural landscape of Iran. From the vibrant music and dance of the Azeris to the intricate rug weaving of the Lurs, the diverse cultural expressions add depth and vibrancy to Iranian society.
-
Linguistic Diversity: The presence of multiple languages, including Persian, Azeri, Kurdish, Luri, Baluchi, Turkmen, and Arabic, creates a rich linguistic landscape. This diversity fosters a dynamic exchange of ideas and expressions, enriching the communication and cultural experiences within Iran.
-
Historical Significance: The ethnic diversity of Iran reflects its long and complex history. The presence of these groups is a testament to the various migrations, conquests, and cultural interactions that have shaped the country’s identity.
-
Economic Impact: The ethnic diversity in Iran is also reflected in its economic activities. Each group has its own skills and traditions, contributing to the diverse economic landscape of the country. For example, the nomadic traditions of the Kurds and Baluch have influenced their skills in livestock herding and agriculture, while the Azeri community has a strong presence in trade and commerce.
-
Social Cohesion: While acknowledging the potential for cultural tensions, the diverse ethnic communities in Iran have generally coexisted peacefully for centuries. This coexistence has fostered a sense of shared identity and national unity, despite the differences in language, culture, and traditions.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
1. What is the official language of Iran?
The official language of Iran is Persian, also known as Farsi.
2. Are there any official languages besides Persian?
While Persian is the official language, other languages are spoken in various regions, particularly Azeri, Kurdish, Luri, Baluchi, and Turkmen. These languages have regional recognition and are used in education, government, and media in their respective areas.
3. How does the government of Iran address the diverse ethnic groups within the country?
The government of Iran has a policy of recognizing the cultural and linguistic rights of its diverse ethnic groups. It has established cultural institutions and organizations to promote the preservation and development of these ethnic cultures. However, the extent to which these policies are implemented in practice remains a subject of debate.
4. Are there any tensions between different ethnic groups in Iran?
While generally coexisting peacefully, there have been instances of tensions between different ethnic groups in Iran. These tensions are often related to issues of language, cultural recognition, and economic opportunities. However, it is important to note that these tensions are not widespread and do not represent the overall relationship between different ethnic groups.
5. What are some of the challenges facing the diverse ethnic groups in Iran?
Some of the challenges facing diverse ethnic groups in Iran include:
- Economic Inequality: There are economic disparities between different ethnic groups, with some groups facing greater challenges in accessing education, employment, and resources.
- Cultural Assimilation: There have been concerns about the potential for cultural assimilation, where the dominant Persian culture might overshadow the cultural identities of other groups.
- Political Representation: Some groups argue that they lack adequate representation in government and decision-making processes.
Tips for Understanding the Ethnic Map of Iran
- Embrace the diversity: When exploring Iran, be open to experiencing the rich cultural tapestry that the country offers. Engage with different ethnic communities, learn about their traditions, and appreciate their unique contributions to Iranian society.
- Respect cultural differences: Be mindful of the diverse cultural practices and customs that exist within Iran. Respect the traditions and beliefs of different ethnic groups, and avoid making generalizations or assumptions.
- Engage in meaningful dialogue: Seek opportunities to engage in meaningful conversations with people from different ethnic backgrounds. Listen to their perspectives, share your own experiences, and foster understanding and respect.
Conclusion: A Tapestry of Diversity
The ethnic map of Iran is not just a geographical representation; it is a vibrant tapestry woven with threads of history, culture, and language. Each ethnic group contributes to the richness and complexity of Iranian society, shaping the country’s identity and fostering a dynamic interplay of cultural influences. Understanding this diverse mosaic is crucial for appreciating the depth and breadth of Iranian culture and for recognizing the importance of inclusivity and cultural understanding in building a cohesive and vibrant nation.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Mosaic of Iran: Understanding the Country’s Ethnic Diversity. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!