The Shifting Lines: A Comprehensive Look At France In World War II
By admin / May 24, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
The Shifting Lines: A Comprehensive Look at France in World War II
Related Articles: The Shifting Lines: A Comprehensive Look at France in World War II
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Shifting Lines: A Comprehensive Look at France in World War II. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Shifting Lines: A Comprehensive Look at France in World War II
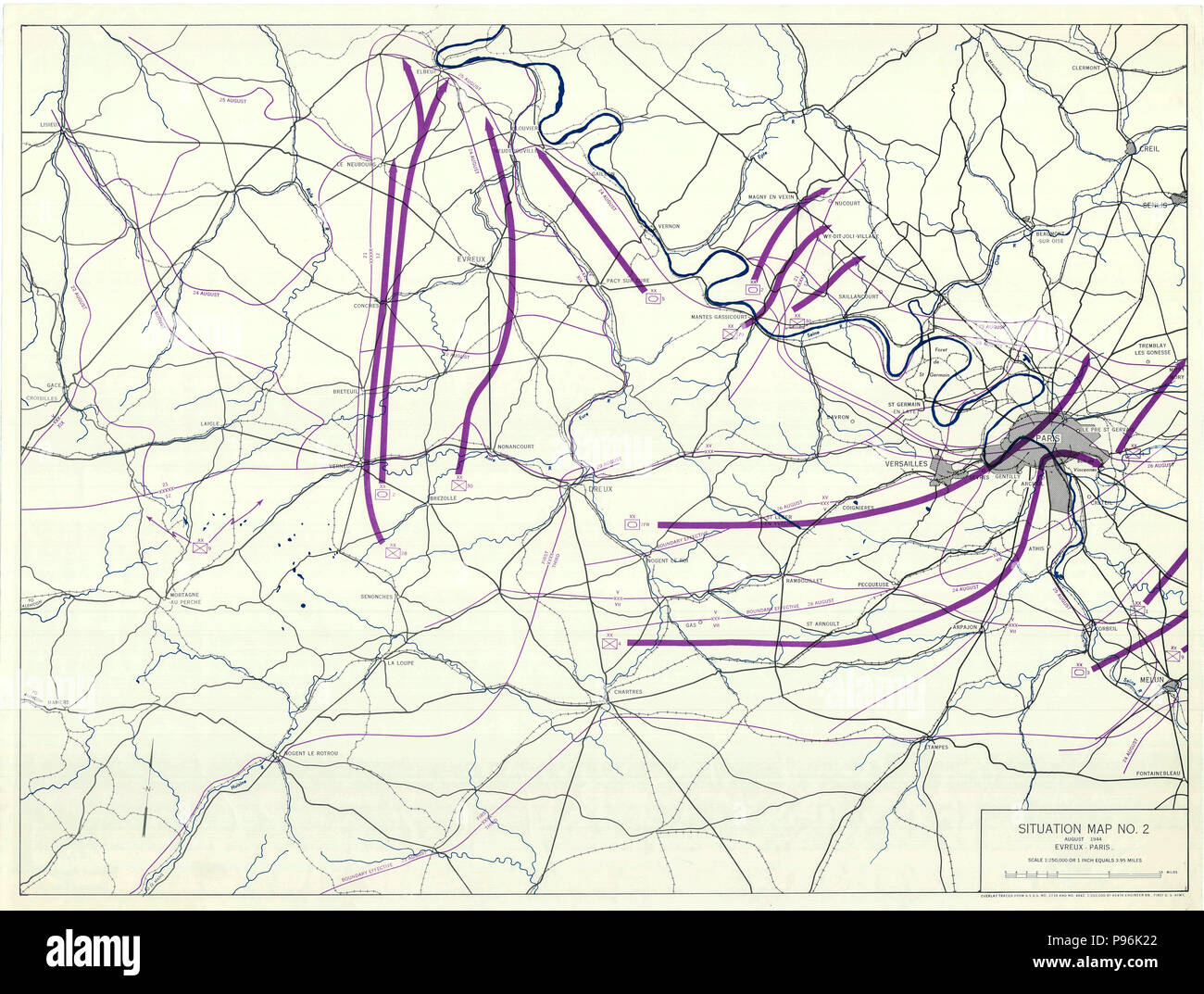
The Second World War, a global conflict of unprecedented scale and devastation, saw France, a nation historically associated with power and influence, become a battleground, a pawn in a complex geopolitical game. Understanding the shifting lines of control in France during the war, as depicted on maps, reveals a narrative of resilience, collaboration, and ultimately, liberation.
The Fall of France: 1940
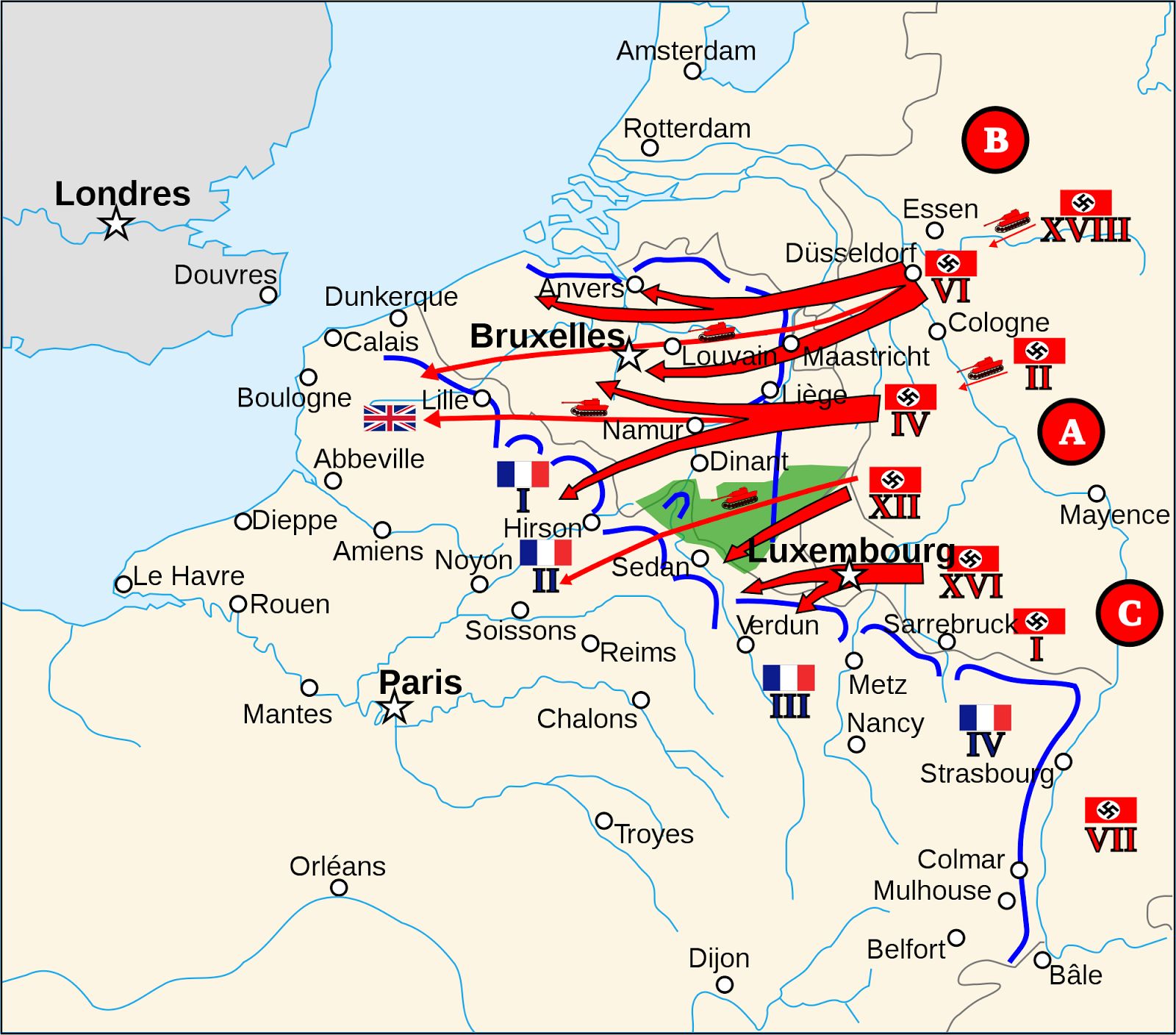
In the initial stages of the war, Germany’s blitzkrieg strategy, employing a combination of overwhelming force and technological superiority, proved devastatingly effective. The French Maginot Line, a series of fortifications along the Franco-German border, designed to protect against a conventional invasion, proved ineffective against the German armored divisions that bypassed it through Belgium and the Netherlands.
The Map Reveals:
- The swiftness of the German advance: The maps of May and June 1940 illustrate the rapid German encirclement of French forces, pushing deep into the country. The Battle of France, lasting just six weeks, ended with the German occupation of Paris on June 14th.
- The impact of the Battle of Dunkirk: The evacuation of British and French troops from Dunkirk, depicted on maps as a narrow strip of coastline, highlights the desperate measures taken to salvage what was left of Allied forces. While a strategic victory for Germany, it also allowed the British to regroup and continue the war.
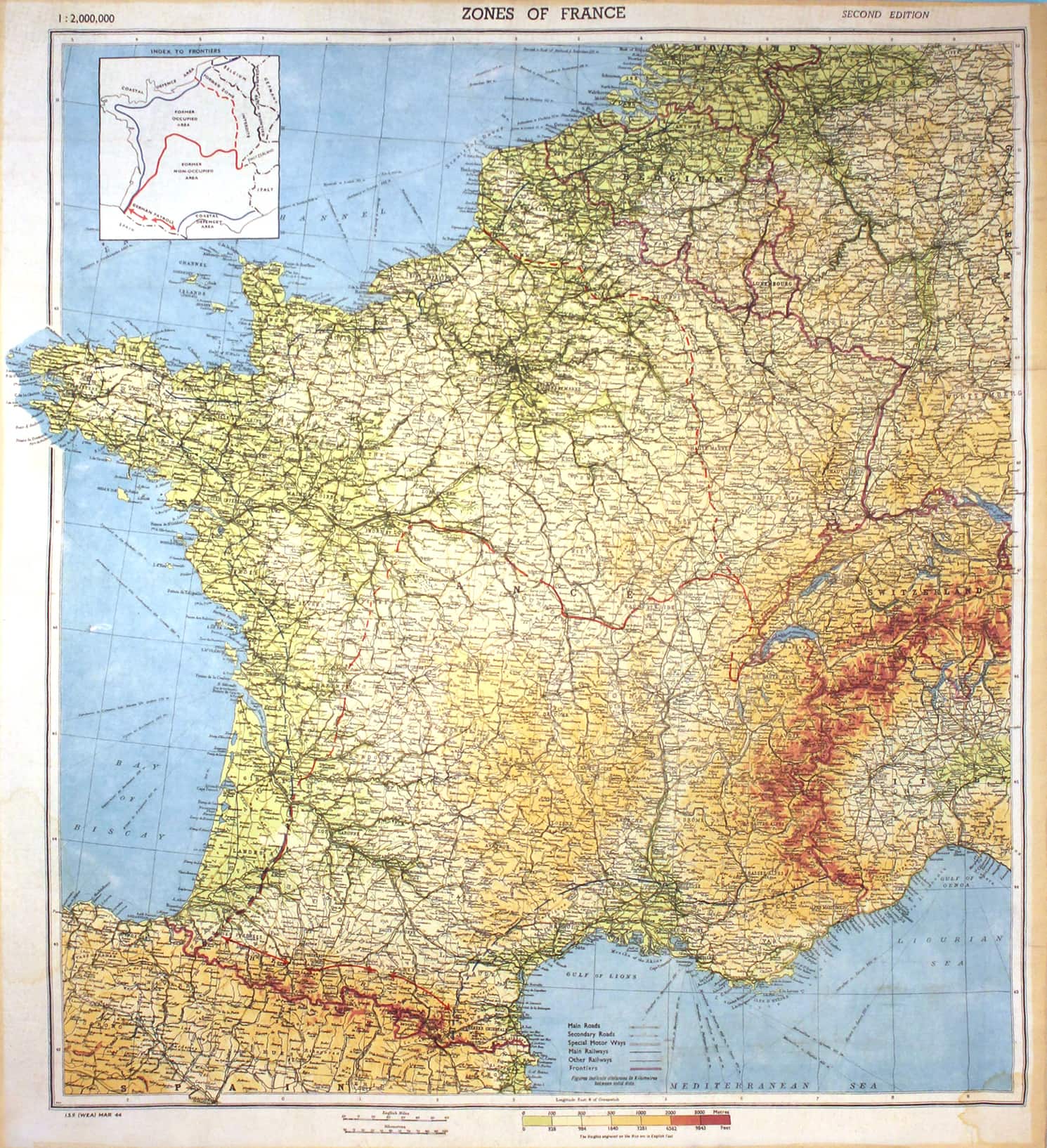
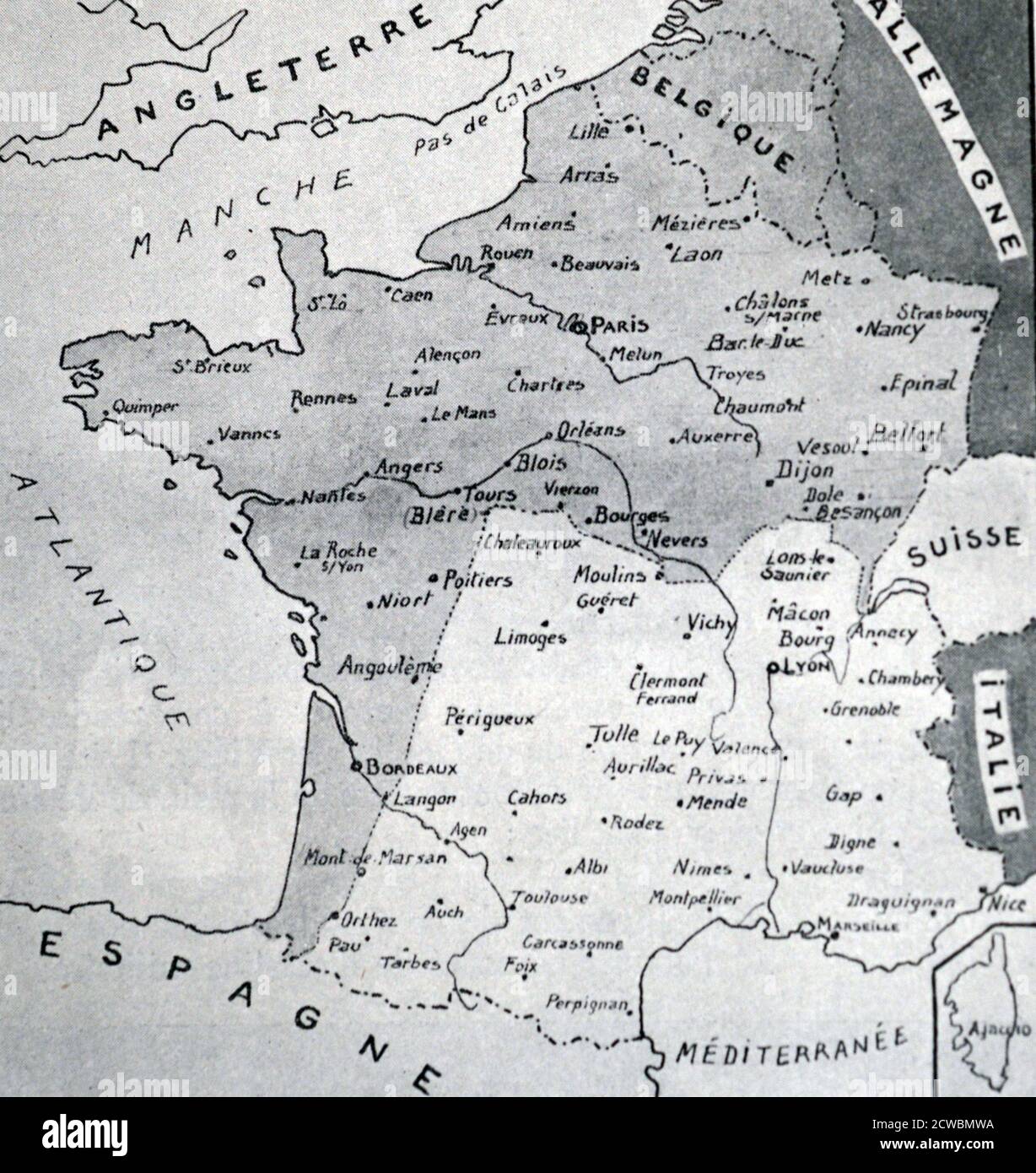
- The division of France: The Armistice of June 22nd, 1940, split France into two zones. The northern and western regions were occupied by Germany, while the southern part, known as Vichy France, remained nominally independent under the control of the collaborationist regime led by Marshal Philippe Pétain. This division, clearly visible on maps, symbolized the tragic reality of a nation fractured by war.
Resistance and Collaboration: 1940-1944
The occupation years saw France become a battleground not just between the Allied and Axis powers, but also within its own population. While some collaborated with the Germans, others joined the Resistance, actively working to undermine the Nazi regime.
The Map Reveals:
- The Resistance network: Maps highlighting the locations of Resistance groups, their networks of communication and safe houses, reveal the intricate web of resistance against the occupation. These groups, operating in secret, provided vital intelligence to the Allies, sabotaged German operations, and offered aid to Allied airmen and escaped prisoners.
- The collaborationist regime: The map of Vichy France, with its capital in the city of Vichy, shows the extent of the collaborationist government’s control. This regime, while ostensibly independent, became deeply entangled with the German war effort, providing resources and manpower to the Axis.
- The Allied air campaign: Maps depicting the air raids on French cities, notably Paris, showcase the Allied strategy of targeting German infrastructure and weakening their hold on occupied territories. These raids, while often causing civilian casualties, contributed to the weakening of the German war effort.
The Liberation: 1944-1945
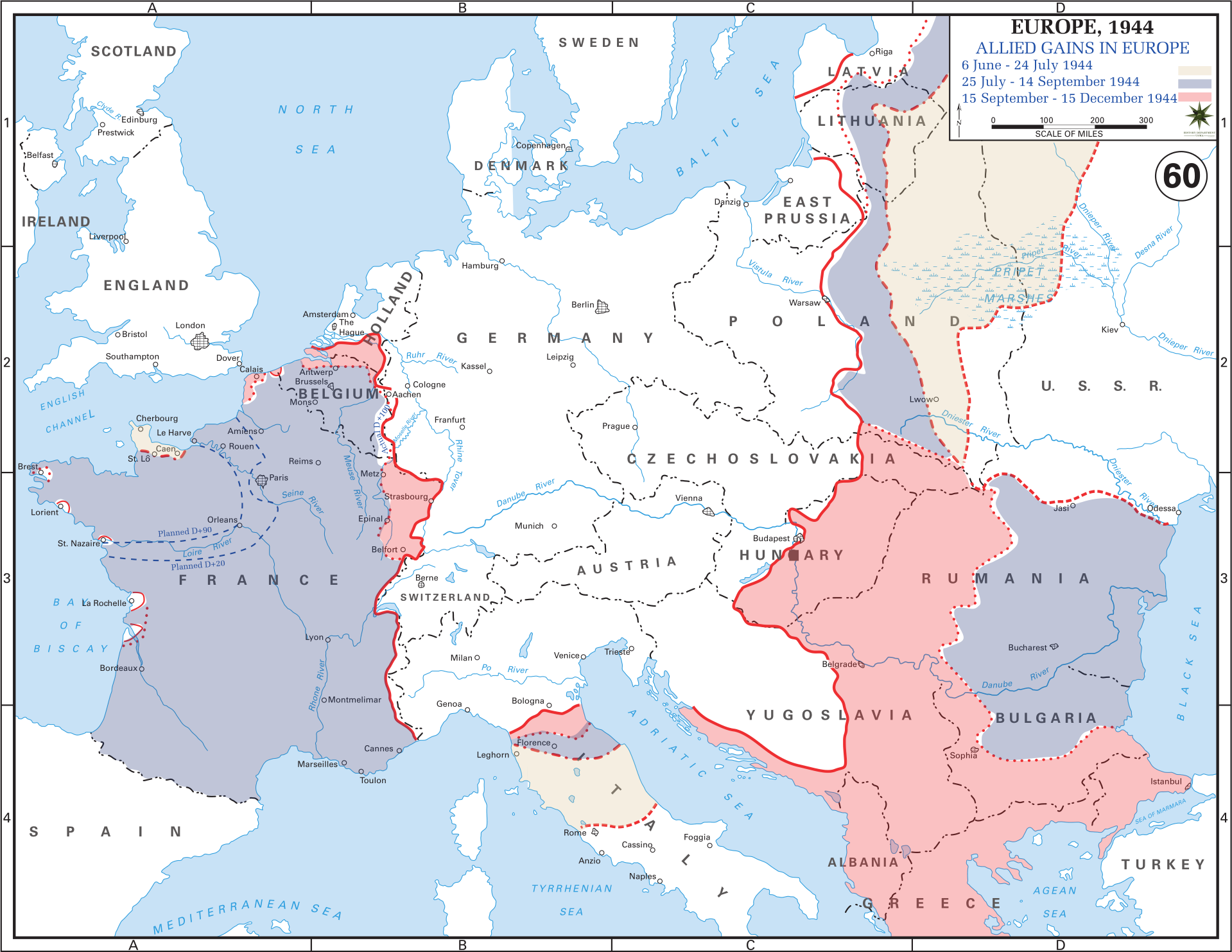
The tide of war began to turn in 1944 with the Allied landings in Normandy on June 6th, known as D-Day. The liberation of France was a long and arduous process, involving fierce battles and heavy casualties.
The Map Reveals:
- The Allied advance: Maps tracing the path of the Allied forces, from Normandy to Paris, show the gradual liberation of French territories. The map also highlights the role of the Resistance in supporting the Allied advance, providing vital intelligence and aiding in the disruption of German supply lines.
- The liberation of Paris: The map of August 1944 depicts the liberation of Paris, a pivotal moment in the war, symbolizing the end of Nazi occupation. The liberation of the capital, achieved through a combination of Allied military action and Parisian resistance, marked a significant turning point in the war.
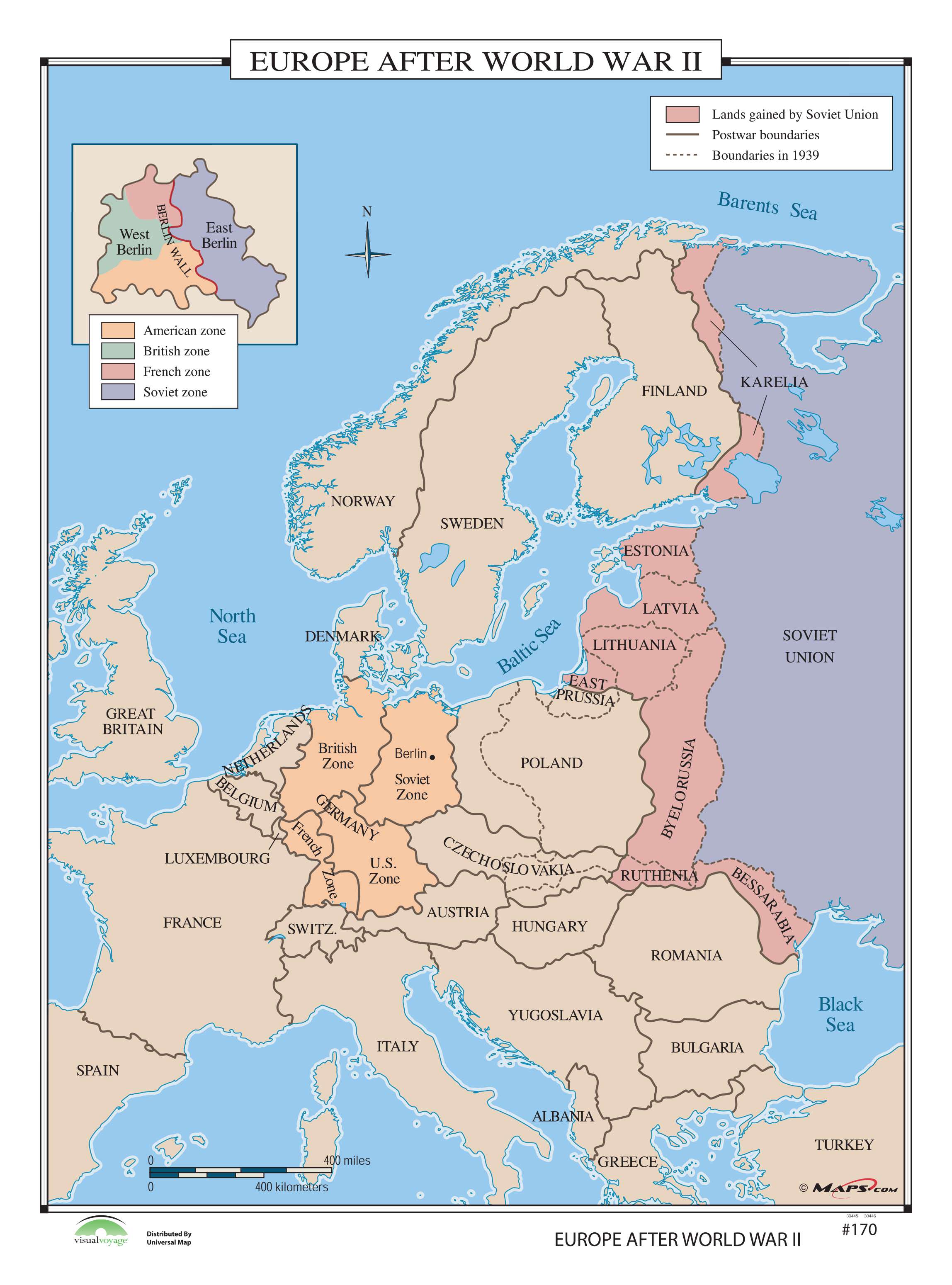
- The final push to victory: The map of 1945 reveals the final stages of the war, with Allied forces pushing eastward, ultimately leading to the surrender of Germany in May 1945. The liberation of France marked the end of a dark chapter in the nation’s history and the beginning of a long process of rebuilding and reconciliation.
Beyond the Battlefield: The Impact of War on French Society
The maps of World War II in France are not merely illustrations of military movements. They also offer a window into the profound impact of the conflict on French society. The war, with its devastation, division, and occupation, left an indelible mark on the nation’s collective memory.
The Map Reveals:
- The scars of war: Maps showcasing the destruction of French cities, infrastructure, and cultural heritage, reveal the extent of the physical and emotional devastation inflicted by the war. The loss of lives, the displacement of populations, and the disruption of normal life left a lasting impact on French society.
- The legacy of collaboration: The maps of Vichy France highlight the complexities of the war, revealing the internal divisions and the difficult questions surrounding collaboration with the enemy. The legacy of this period continues to be debated and analyzed, revealing the moral dilemmas faced by individuals and the nation as a whole.
- The rise of the Resistance: The maps of Resistance activity highlight the courage and resilience of the French people who actively fought against the Nazi occupation. The Resistance movement, born out of a desire for freedom and a rejection of oppression, became a symbol of hope and resistance, inspiring generations to come.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of the France WWII Map
Q: Why is the Maginot Line depicted as a failure on the map?
A: The Maginot Line, designed to protect against a conventional invasion, failed to account for the German blitzkrieg strategy of bypassing fortifications through Belgium and the Netherlands. The map demonstrates the German armored divisions’ ability to outmaneuver the static defenses, highlighting the limitations of a defensive strategy in the face of technological advancements.
Q: How did the Resistance operate in a heavily occupied France?
A: The map reveals the Resistance’s intricate network of communication and safe houses, highlighting their ability to operate in secrecy. They relied on local knowledge, coded messages, and clandestine meetings to evade German surveillance. The map also illustrates the Resistance’s strategic use of sabotage, intelligence gathering, and aid to Allied forces, showcasing their vital role in undermining the Nazi occupation.
Q: What is the significance of the liberation of Paris?
A: The liberation of Paris, depicted on the map as a pivotal moment in the war, symbolizes the end of Nazi occupation and the restoration of French freedom. The city, a symbol of French culture and history, became a focal point of the liberation struggle, showcasing the collective effort of Allied forces and the Parisian resistance.
Tips: Interpreting the France WWII Map
- Focus on key dates: The map’s timeline helps to understand the progression of the war and the changing lines of control. Key dates, such as the fall of France, the liberation of Paris, and the end of the war, provide context for the events depicted on the map.
- Analyze the symbols: The map uses various symbols to represent different aspects of the war, such as military units, battle lines, and cities. Understanding these symbols is crucial for interpreting the map’s message and understanding the complexities of the conflict.
- Consider the context: The map should be viewed within the broader historical context of World War II, taking into account the political, social, and economic factors that shaped the conflict. This contextual understanding helps to interpret the map’s significance and its impact on French society.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Resilience and Transformation
The maps of France during World War II offer a powerful visual narrative of a nation grappling with unprecedented challenges. They depict the swiftness of the German advance, the resilience of the Resistance, the complexities of collaboration, and the long and arduous process of liberation. Ultimately, the maps reveal the profound impact of the war on French society, leaving a legacy of resilience, transformation, and a renewed sense of national identity.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Shifting Lines: A Comprehensive Look at France in World War II. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!