The Silk Road: A Map Of Connectivity And Exchange
By admin / September 28, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
The Silk Road: A Map of Connectivity and Exchange
Related Articles: The Silk Road: A Map of Connectivity and Exchange
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Silk Road: A Map of Connectivity and Exchange. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Silk Road: A Map of Connectivity and Exchange
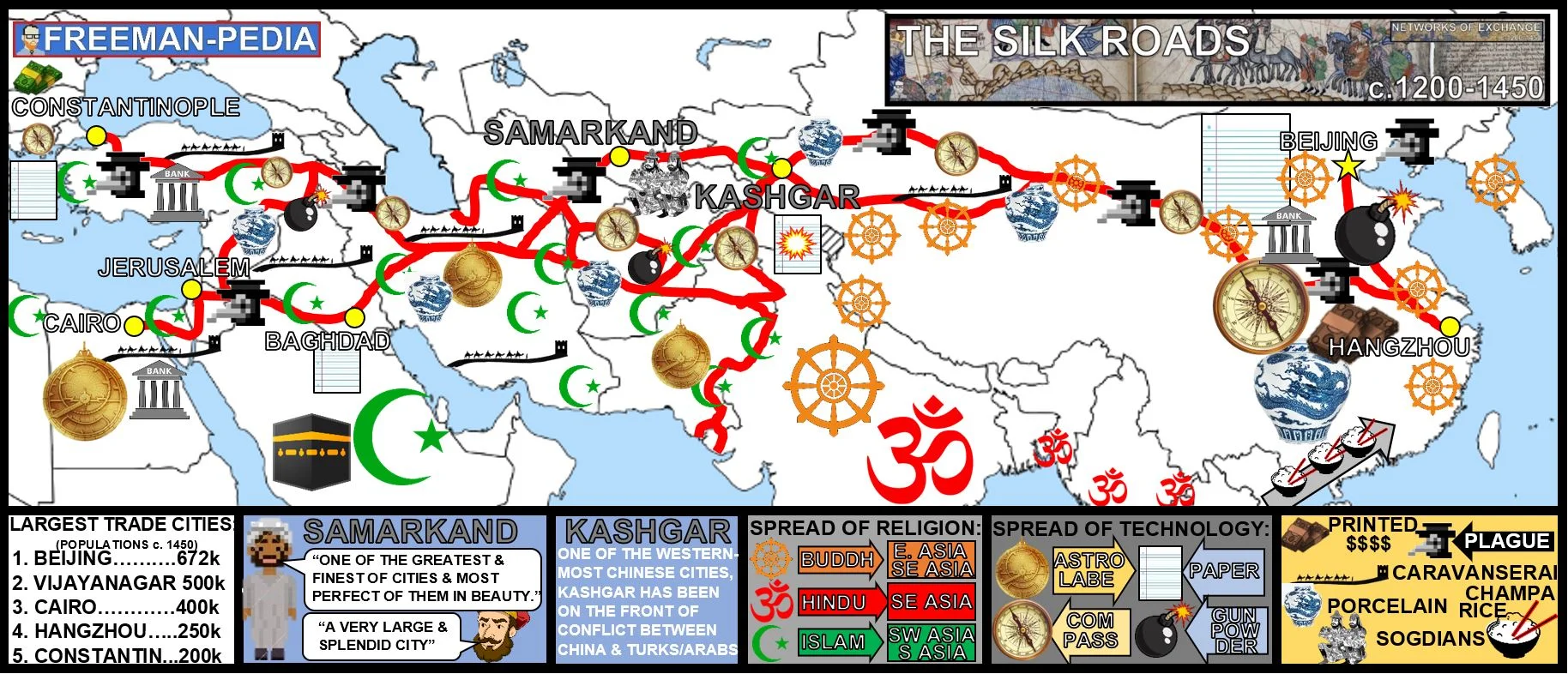
The Silk Road, a network of trade routes spanning millennia, has left an indelible mark on history, shaping civilizations and economies across continents. While the term "Silk Road" evokes images of luxurious fabrics traversing vast distances, the reality is far more complex and multifaceted. This article delves into the intricate tapestry of the Silk Road, examining its historical significance, economic impact, and lasting legacy.
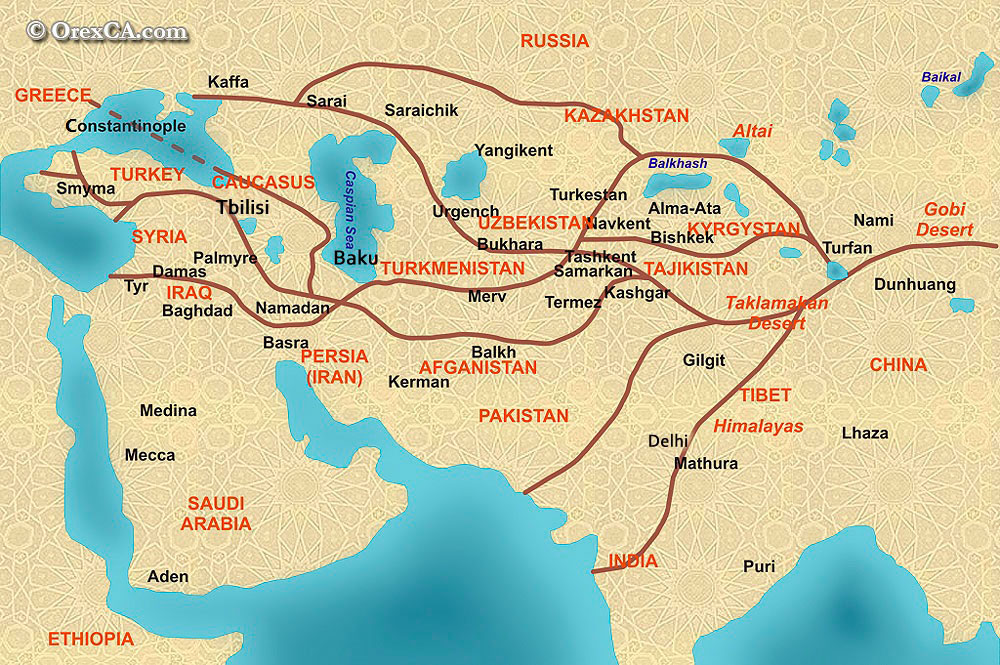
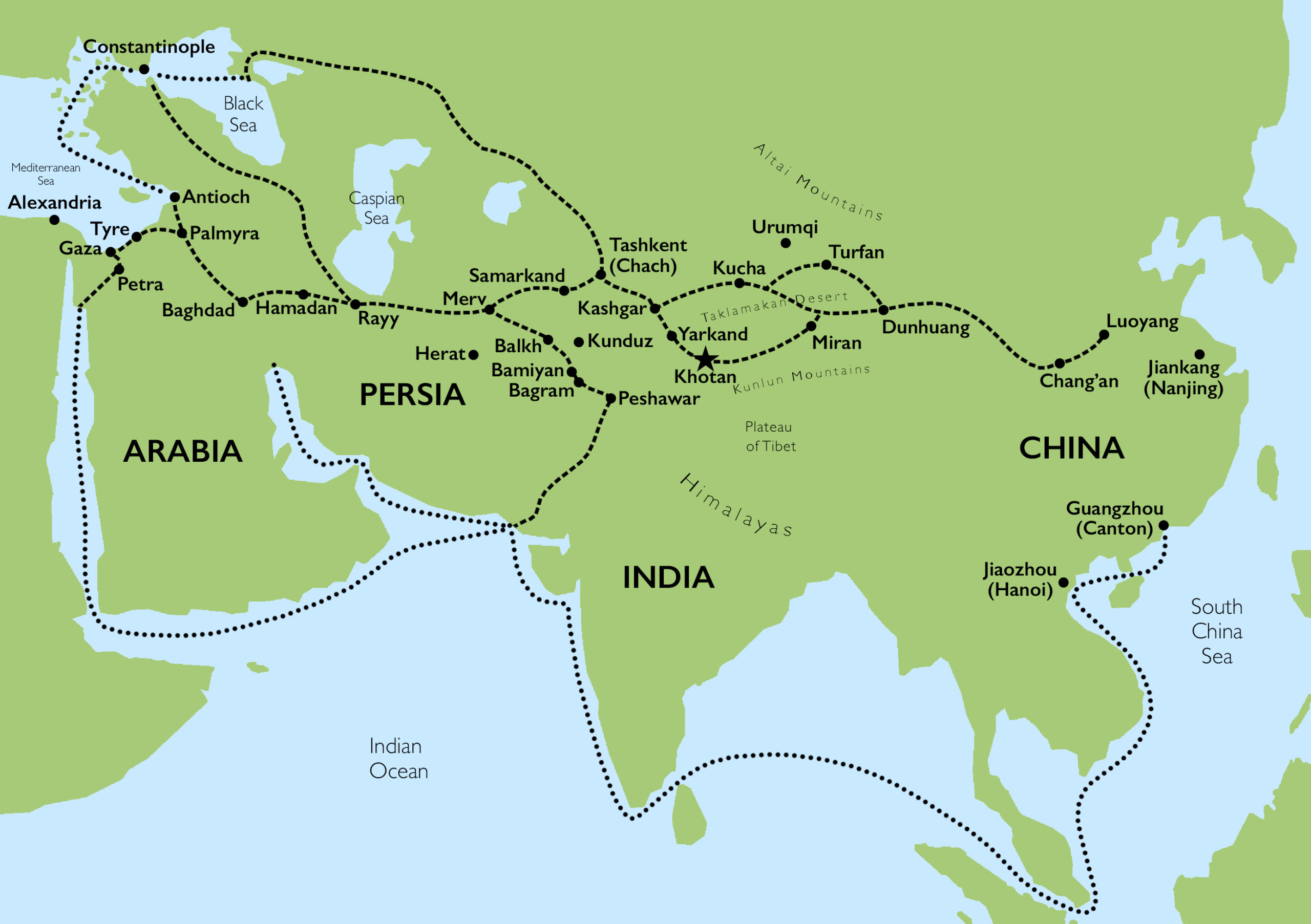
A Network of Routes, Not a Single Path:
The Silk Road was not a single, well-defined path but a network of routes that evolved over centuries. Its origins can be traced back to the Han Dynasty in China (206 BCE – 220 CE), when trade with the West flourished. This initial network primarily connected China to Central Asia and the Mediterranean, facilitated by the expansion of the Roman Empire.
The Silk Road’s geography varied greatly, traversing diverse landscapes, from the arid deserts of Central Asia to the lush valleys of the Himalayas. The routes were not solely land-based; maritime routes played a crucial role, connecting ports in the Indian Ocean and the Red Sea, facilitating trade between the East and West.
Beyond Silk: A Symphony of Trade:
While silk was undoubtedly a valuable commodity, the Silk Road was not solely a conduit for luxury goods. A vibrant exchange of ideas, cultures, and goods occurred along these routes. From the East, China exported silk, porcelain, tea, and spices, while the West brought back glass, textiles, precious metals, and horses.
The Silk Road also facilitated the transmission of knowledge and technology. Buddhism, originating in India, spread eastward along the Silk Road, influencing Chinese culture and philosophy. Scientific innovations, such as papermaking and gunpowder, were also shared, contributing to the advancement of knowledge across Eurasia.
A Catalyst for Economic Growth:
The Silk Road’s economic impact was profound. It stimulated trade, fostered urbanization, and spurred economic growth in regions along the routes. Cities like Samarkand, Bukhara, and Xi’an flourished as centers of commerce and cultural exchange.
The Silk Road also played a crucial role in the development of international trade networks. It facilitated the exchange of goods and services, connecting diverse economies and fostering interregional cooperation.
Challenges and Disruptions:
Despite its immense success, the Silk Road was not without its challenges. The long distances, harsh conditions, and security concerns posed significant obstacles to trade. The routes were often subject to political instability, banditry, and natural disasters, disrupting trade and threatening the flow of goods.
The decline of the Roman Empire in the 5th century CE and the rise of the Mongol Empire in the 13th century CE significantly impacted the Silk Road. The Mongol conquest led to a period of renewed prosperity, but it also brought about changes in trade patterns and political control.
The Enduring Legacy:
Although the Silk Road as a network of trade routes eventually faded, its legacy continues to resonate today. It serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness of human societies and the power of trade to foster cultural exchange and economic growth.
The Silk Road’s influence can be seen in the languages, religions, and cultures of the regions it traversed. It left behind a rich tapestry of archaeological sites, architectural wonders, and cultural traditions, offering insights into the past and shaping the present.
The Modern Silk Road: A Vision for the Future:
In recent years, the concept of a "New Silk Road" has emerged, reflecting China’s ambitious vision for global connectivity and economic cooperation. This initiative, known as the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), aims to revitalize trade and infrastructure along the ancient Silk Road routes, connecting China to Asia, Europe, and Africa.
The BRI encompasses a wide range of projects, including infrastructure development, trade agreements, and cultural exchange programs. Its proponents argue that it will foster economic growth, promote regional integration, and strengthen global cooperation.
FAQs about the Silk Road:
1. When did the Silk Road exist?
The Silk Road existed for over 1,500 years, from the Han Dynasty in China (206 BCE – 220 CE) to the 15th century CE.
2. What was the main purpose of the Silk Road?
The Silk Road served as a network of trade routes, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures between the East and West.
3. What were some of the key goods traded along the Silk Road?
Silk, porcelain, tea, spices, textiles, glass, precious metals, and horses were among the key goods traded along the Silk Road.
4. What were some of the major challenges faced by travelers on the Silk Road?
Travelers faced challenges such as long distances, harsh conditions, security concerns, political instability, banditry, and natural disasters.
5. What is the legacy of the Silk Road?
The Silk Road left a lasting legacy, shaping languages, religions, cultures, and economies across Eurasia. Its influence can be seen in archaeological sites, architectural wonders, and cultural traditions.
Tips for Exploring the Silk Road:
- Research thoroughly: Learn about the history, culture, and geography of the regions you plan to visit.
- Plan your itinerary carefully: Consider the distances, transportation options, and time required for travel.
- Respect local customs and traditions: Be mindful of cultural differences and dress appropriately.
- Pack for the weather: The Silk Road traverses diverse landscapes, so be prepared for varying temperatures and conditions.
- Learn some basic phrases in the local language: This will enhance your interactions with locals and make your trip more enriching.
Conclusion:
The Silk Road stands as a testament to the interconnectedness of human societies and the power of trade to shape civilizations and economies. Its legacy continues to resonate today, reminding us of the importance of cultural exchange, economic cooperation, and the enduring human spirit of exploration and connection. As we look to the future, the concept of a "New Silk Road" offers a vision for renewed global connectivity and cooperation, drawing inspiration from the ancient routes that once connected the world.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Silk Road: A Map of Connectivity and Exchange. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!