The Silk Road: A Map Of Trade, Culture, And Connection In China
By admin / March 19, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
The Silk Road: A Map of Trade, Culture, and Connection in China
Related Articles: The Silk Road: A Map of Trade, Culture, and Connection in China
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Silk Road: A Map of Trade, Culture, and Connection in China. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Silk Road: A Map of Trade, Culture, and Connection in China
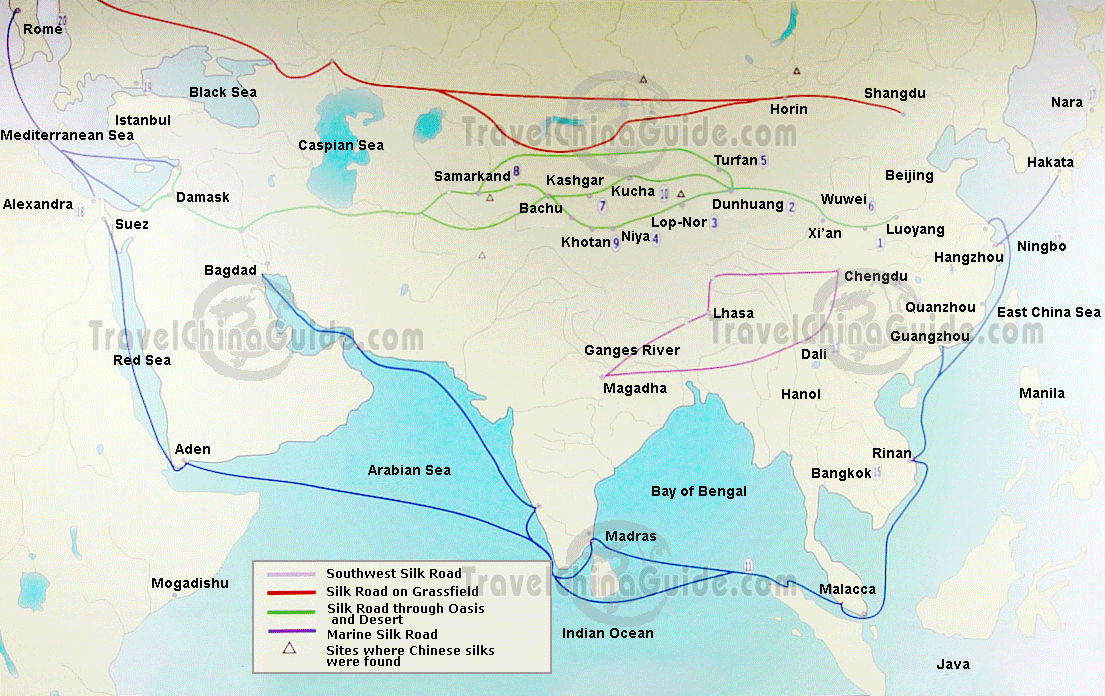
The Silk Road, a network of ancient trade routes spanning millennia, holds a captivating place in history. While the name evokes images of silken fabrics traversing vast distances, the Silk Road was far more than a singular path for luxury goods. It was a dynamic tapestry of interactions, exchanges, and movements, weaving together diverse cultures, economies, and ideas across Eurasia.
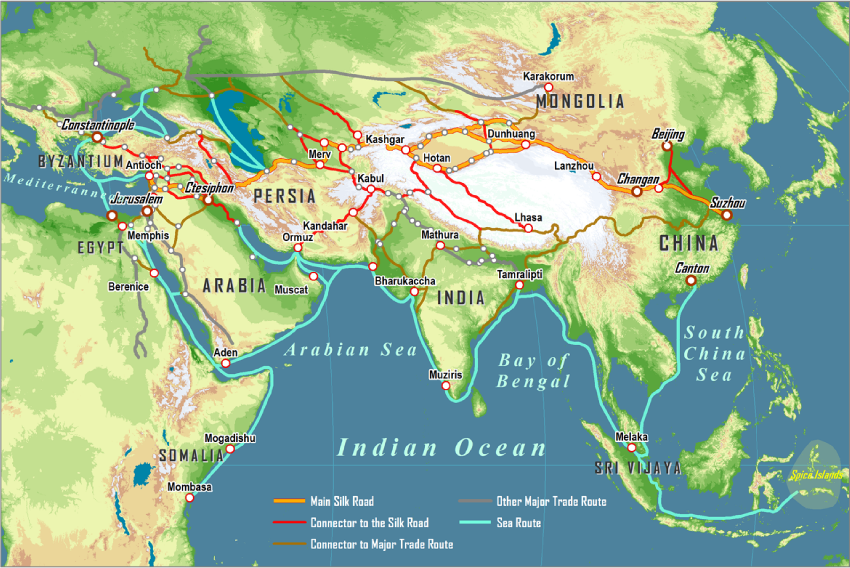
A Network, Not a Road:
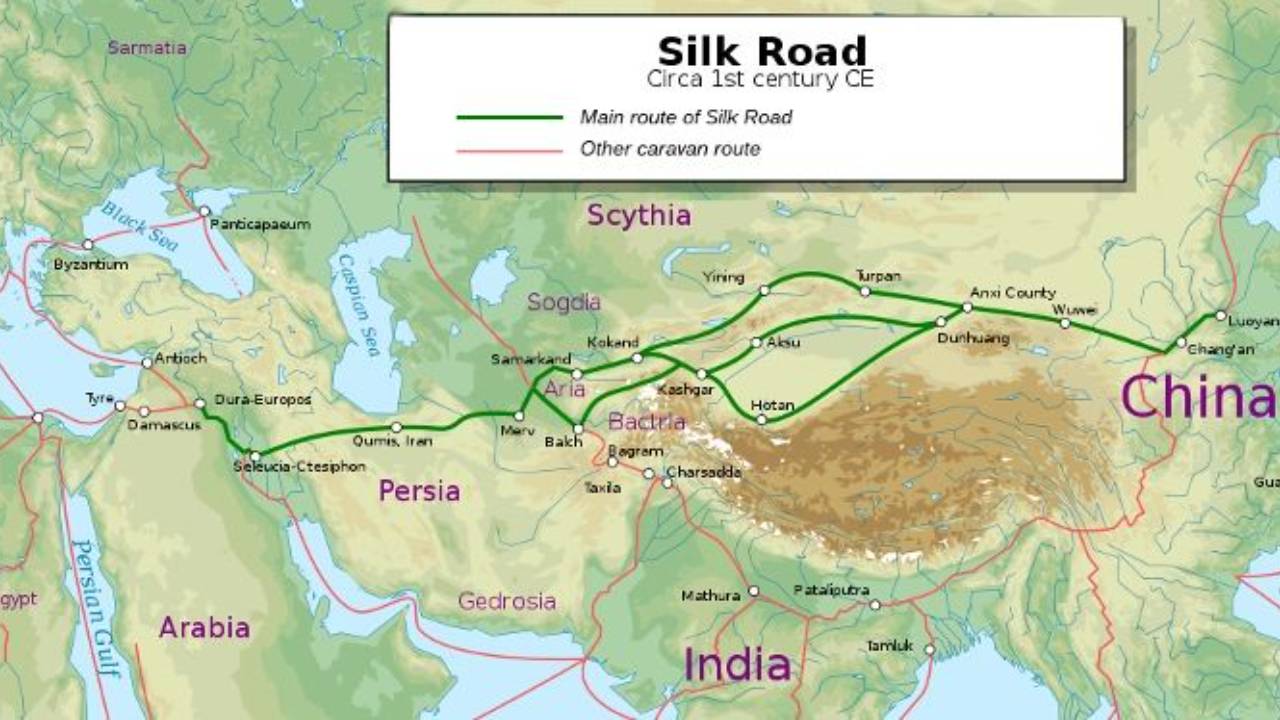
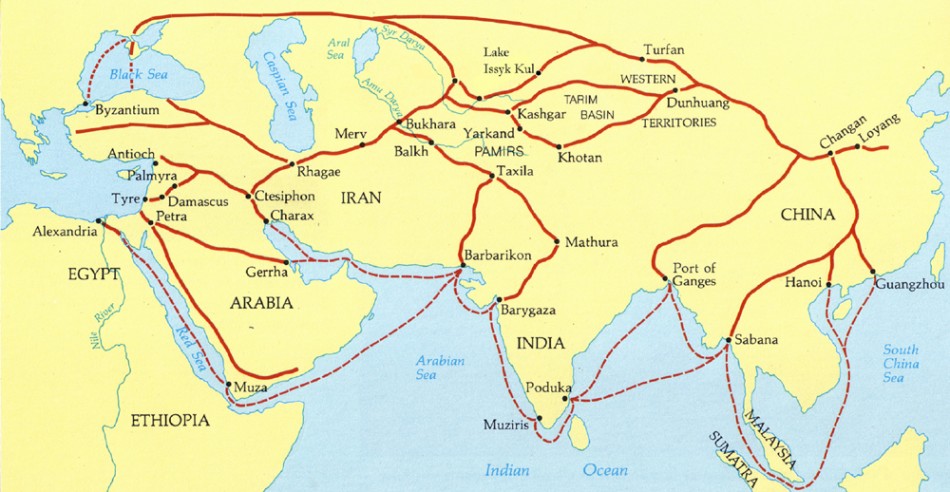
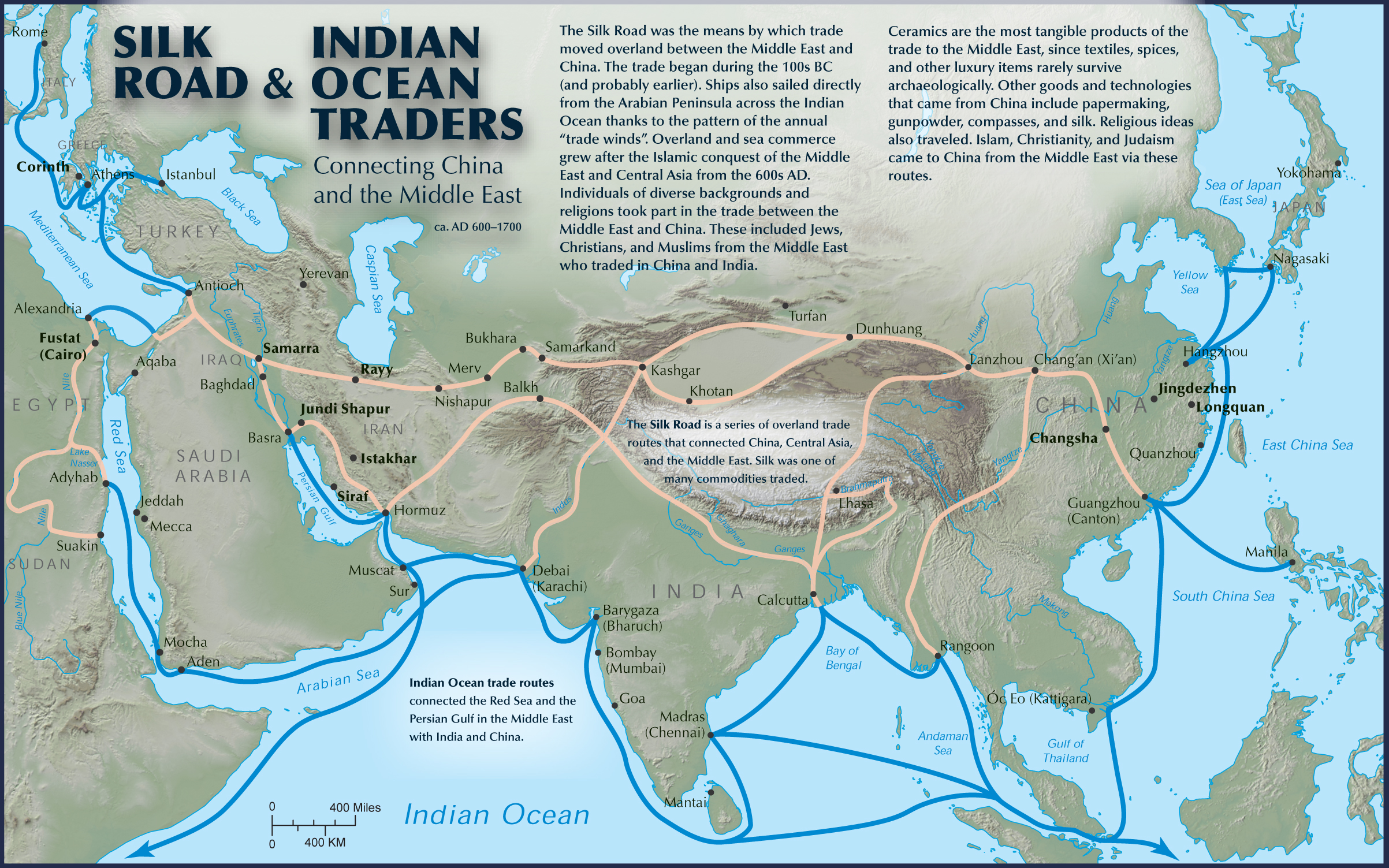
The Silk Road was not a single, well-defined road but rather a complex web of interconnected routes. Its origins can be traced back to the 2nd century BCE, during the Han Dynasty in China. It stretched westward from China, traversing Central Asia, the Middle East, and eventually reaching Europe. This network facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies, playing a pivotal role in shaping the world as we know it.
Trade and Exchange:
The Silk Road, as its name suggests, was instrumental in the trade of silk, a prized commodity originating in China. However, the exchange went far beyond luxury fabrics. Spices, precious metals, textiles, ceramics, glassware, and even religious artifacts traveled along these routes. The flow of goods created thriving economies and bustling cities, fostering economic development and cultural exchange.
Cultural Crossroads:
The Silk Road was more than just a trade route; it was a conduit for cultural diffusion. The movement of people along these routes led to the exchange of ideas, philosophies, religions, and artistic expressions. Buddhism, originating in India, spread eastward along the Silk Road, finding fertile ground in China and influencing its cultural landscape. Similarly, Islamic influences reached China, enriching its art, architecture, and intellectual traditions.
A Legacy of Connection:
The Silk Road’s influence extended beyond the tangible exchange of goods and ideas. It fostered a sense of connection between civilizations, bridging geographical and cultural divides. The network facilitated the development of diplomatic relations, fostering understanding and cooperation between different societies.
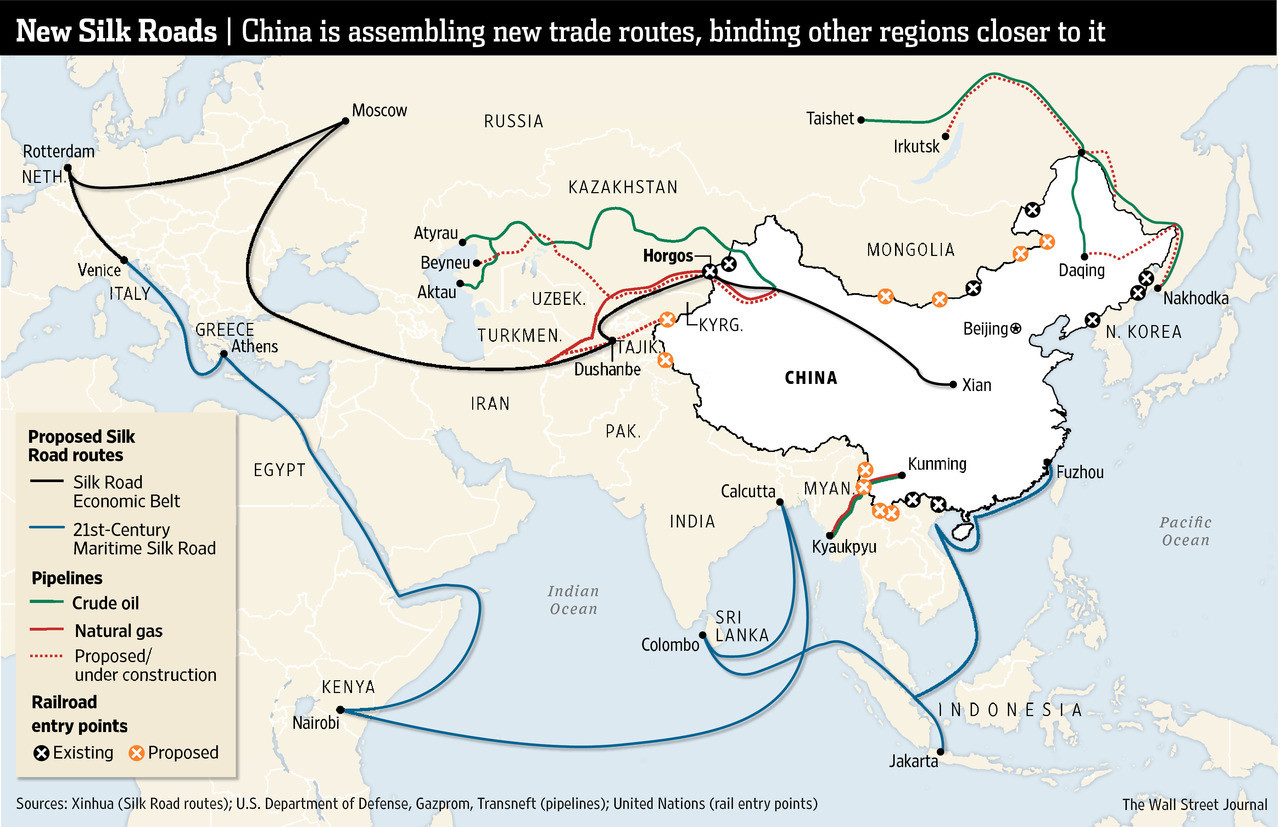
The Modern Silk Road:
The concept of the Silk Road has experienced a resurgence in the 21st century with the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), a modern-day vision for economic cooperation and infrastructure development. This initiative, launched by China in 2013, aims to revive the spirit of the ancient Silk Road by fostering trade, investment, and connectivity across Eurasia and beyond. The BRI seeks to build modern infrastructure, including roads, railways, and ports, to facilitate the flow of goods, services, and people, promoting economic growth and regional integration.
FAQs about the Silk Road:
1. What were the main goods traded along the Silk Road?
The Silk Road facilitated the trade of a wide range of goods, including silk, spices, precious metals, textiles, ceramics, glassware, and religious artifacts.
2. How did the Silk Road influence the development of China?
The Silk Road played a crucial role in China’s economic development, facilitating trade and cultural exchange. It also introduced new ideas and technologies, contributing to the country’s cultural and intellectual evolution.
3. What are the main benefits of the Belt and Road Initiative?
The BRI aims to promote economic growth, infrastructure development, and regional integration by fostering trade, investment, and connectivity across Eurasia and beyond.
4. What are some of the challenges associated with the Belt and Road Initiative?
The BRI has faced criticism regarding its environmental impact, debt sustainability, and potential for geopolitical influence.
5. How does the Silk Road continue to influence the world today?
The legacy of the Silk Road lives on through the enduring influence of its cultural exchanges and the contemporary revival of its spirit through initiatives like the BRI.
Tips for Understanding the Silk Road:
- Explore historical maps: Visualizing the network of routes helps grasp the scale and complexity of the Silk Road.
- Learn about the key cities: Understanding the significance of cities like Xi’an, Samarkand, and Constantinople sheds light on the diverse cultures and economies that thrived along the Silk Road.
- Read accounts of travelers: Accounts by travelers like Marco Polo offer firsthand insights into the experiences and challenges of traversing the Silk Road.
- Investigate the cultural exchange: Examining the spread of Buddhism, Islamic influences, and other cultural exchanges highlights the Silk Road’s role in shaping global civilizations.
- Consider the modern context: Understanding the Belt and Road Initiative and its implications provides a contemporary perspective on the Silk Road’s legacy and its potential for future development.
Conclusion:
The Silk Road, a testament to human ingenuity and the power of connection, continues to captivate and inspire. From its ancient origins as a network of trade routes to its modern revival through the Belt and Road Initiative, the Silk Road remains a powerful symbol of the interconnectedness of our world. As we navigate the complexities of globalization and strive for greater understanding and cooperation, the lessons learned from the Silk Road offer valuable insights into the enduring power of cultural exchange, economic collaboration, and the pursuit of a shared future.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Silk Road: A Map of Trade, Culture, and Connection in China. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!