Understanding Flood Risk In West Virginia: A Guide To Flood Maps
By admin / June 5, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Understanding Flood Risk in West Virginia: A Guide to Flood Maps
Related Articles: Understanding Flood Risk in West Virginia: A Guide to Flood Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Flood Risk in West Virginia: A Guide to Flood Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Flood Risk in West Virginia: A Guide to Flood Maps
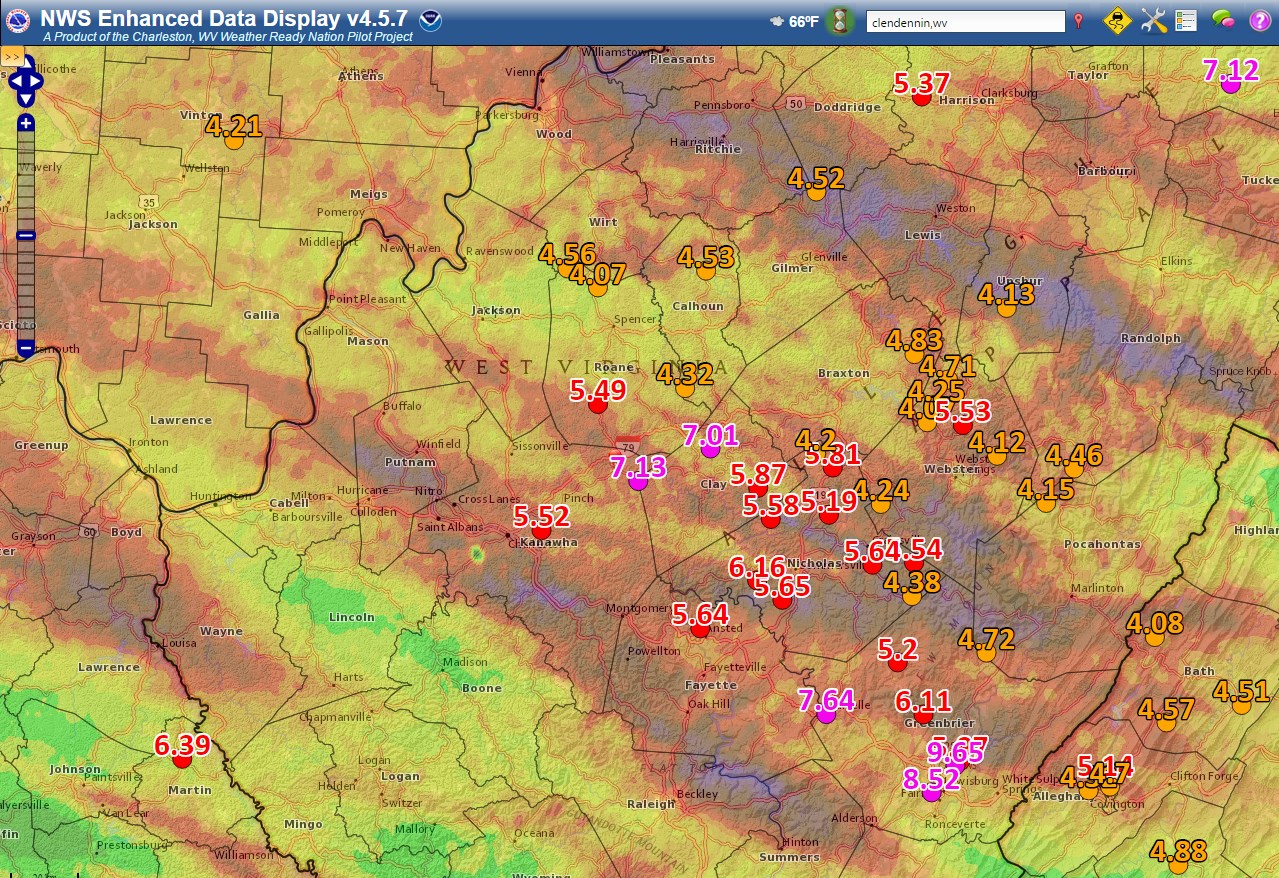
West Virginia, with its mountainous terrain and numerous rivers and streams, is inherently susceptible to flooding. Understanding flood risk is crucial for individuals, communities, and policymakers alike. Flood maps, produced by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), provide a vital tool for visualizing and assessing this risk.
What are Flood Maps?
Flood maps, also known as Flood Insurance Rate Maps (FIRMs), are detailed graphical representations of areas that have been identified as being at risk of flooding. They depict flood zones, which are areas where the probability of flooding is statistically significant. These maps are based on historical flood data, hydrological modeling, and other scientific data.
Types of Flood Zones:
Flood maps categorize areas into different flood zones, each representing a specific level of flood risk. The most common flood zones include:
- Special Flood Hazard Area (SFHA): These areas have a 1% chance of experiencing a flood in any given year, commonly referred to as the "100-year flood." Properties located within SFHAs are typically required to purchase flood insurance.
- Zone X: These areas are considered to be outside of the 100-year floodplain and have a lower risk of flooding. However, they may still be subject to flooding from other sources, such as dam failures or storm surge.
- Zone A: These areas are considered to be within the 100-year floodplain but have not been specifically studied in detail.
- Zone AE: These areas have been studied and have a 1% annual chance of flooding.
- Zone AO: These areas are subject to flooding from mudslides or debris flows.
- Zone AH: These areas are subject to flooding from high tides or storm surge.
Importance of Flood Maps:
Flood maps serve as a vital resource for various stakeholders:
- Homeowners and Businesses: They provide essential information to assess flood risk and make informed decisions about property purchase, construction, and insurance.
- Community Planners: They help in identifying areas that are vulnerable to flooding and guide the development of flood mitigation measures.
- Emergency Responders: They provide critical information for planning evacuation routes and coordinating emergency response efforts.
- Insurance Companies: They use flood maps to determine flood insurance premiums.
Accessing Flood Maps:
Flood maps are readily available online through the FEMA website. Users can search by address, zip code, or county. The FEMA website also offers interactive map viewers and downloadable data for further analysis.
Benefits of Using Flood Maps:
- Improved Flood Preparedness: By understanding flood risk, individuals and communities can take proactive steps to mitigate potential damage, such as elevating structures, installing flood barriers, and developing evacuation plans.
- Informed Decision-Making: Flood maps provide valuable data for property owners, developers, and policymakers to make informed decisions about land use, construction, and infrastructure investments.
- Reduced Flood Losses: By identifying and mitigating high-risk areas, flood maps contribute to reducing property damage and economic losses caused by flooding.
- Increased Resilience: Understanding flood risk and implementing appropriate mitigation measures can enhance community resilience and minimize the impacts of future flooding events.
FAQs about Flood Maps:
1. What does it mean if my property is in a flood zone?
If your property is located within a flood zone, it indicates that there is a statistically significant risk of flooding. This means that your property has a higher probability of being affected by a flood compared to properties outside of flood zones.
2. Does being in a flood zone mean my property will definitely flood?
No, being in a flood zone does not guarantee that your property will flood. However, it does indicate a higher likelihood of flooding than properties outside of flood zones.
3. Do I need flood insurance if my property is in a flood zone?
If your property is located within a Special Flood Hazard Area (SFHA), you are typically required to purchase flood insurance if you have a mortgage from a federally regulated lender. Even if you are not required to purchase flood insurance, it is highly recommended, as standard homeowner’s insurance policies typically do not cover flood damage.
4. How often are flood maps updated?
Flood maps are typically updated every five years. However, FEMA may update them more frequently if significant changes occur, such as major flood events, changes in land use, or new scientific data.
5. Can I appeal a flood map determination?
Yes, property owners can appeal a flood map determination if they believe it is inaccurate. FEMA has a formal appeals process that allows property owners to submit evidence and make their case.
Tips for Utilizing Flood Maps:
- Consult with a qualified professional: It is advisable to consult with a licensed engineer, surveyor, or flood risk specialist to interpret flood maps and assess the specific flood risks associated with your property.
- Understand the limitations: Flood maps are based on historical data and modeling, and they may not always accurately predict future flood events.
- Stay informed: Stay updated on flood warnings and advisories issued by local authorities and the National Weather Service.
- Consider flood mitigation measures: Implement flood mitigation measures, such as elevating structures, installing flood barriers, or landscaping to reduce flood risk.
- Purchase flood insurance: If your property is located within a flood zone, consider purchasing flood insurance to protect yourself from financial losses.
Conclusion:
Flood maps are essential tools for understanding and mitigating flood risk in West Virginia. By using these maps, individuals, communities, and policymakers can make informed decisions to enhance flood preparedness, reduce losses, and build resilience to future flooding events. Understanding flood risk is crucial for safeguarding lives, property, and the well-being of communities throughout the state.
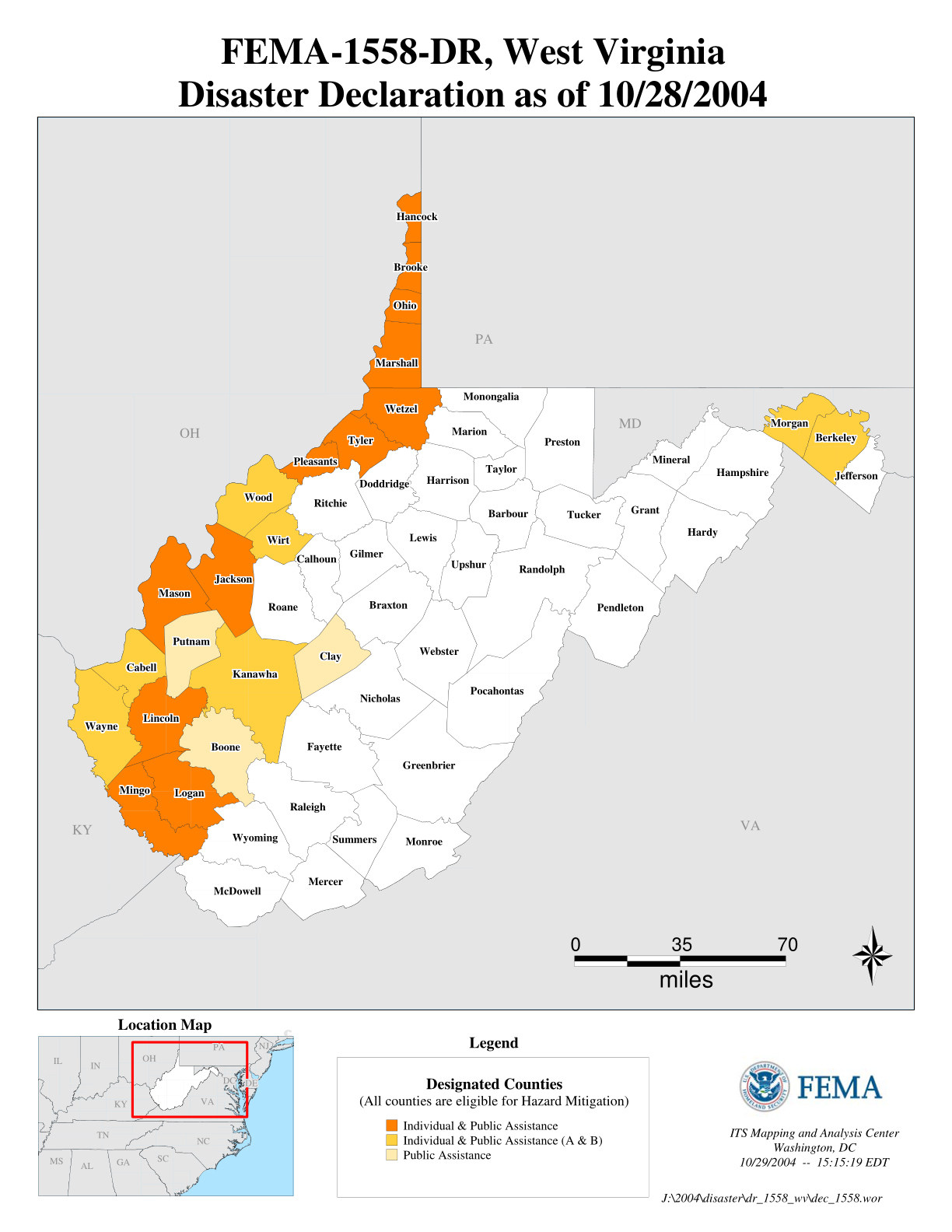

/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/gray/KGSNE4NSUFE6DHHJ6LNU72FKTY.png)

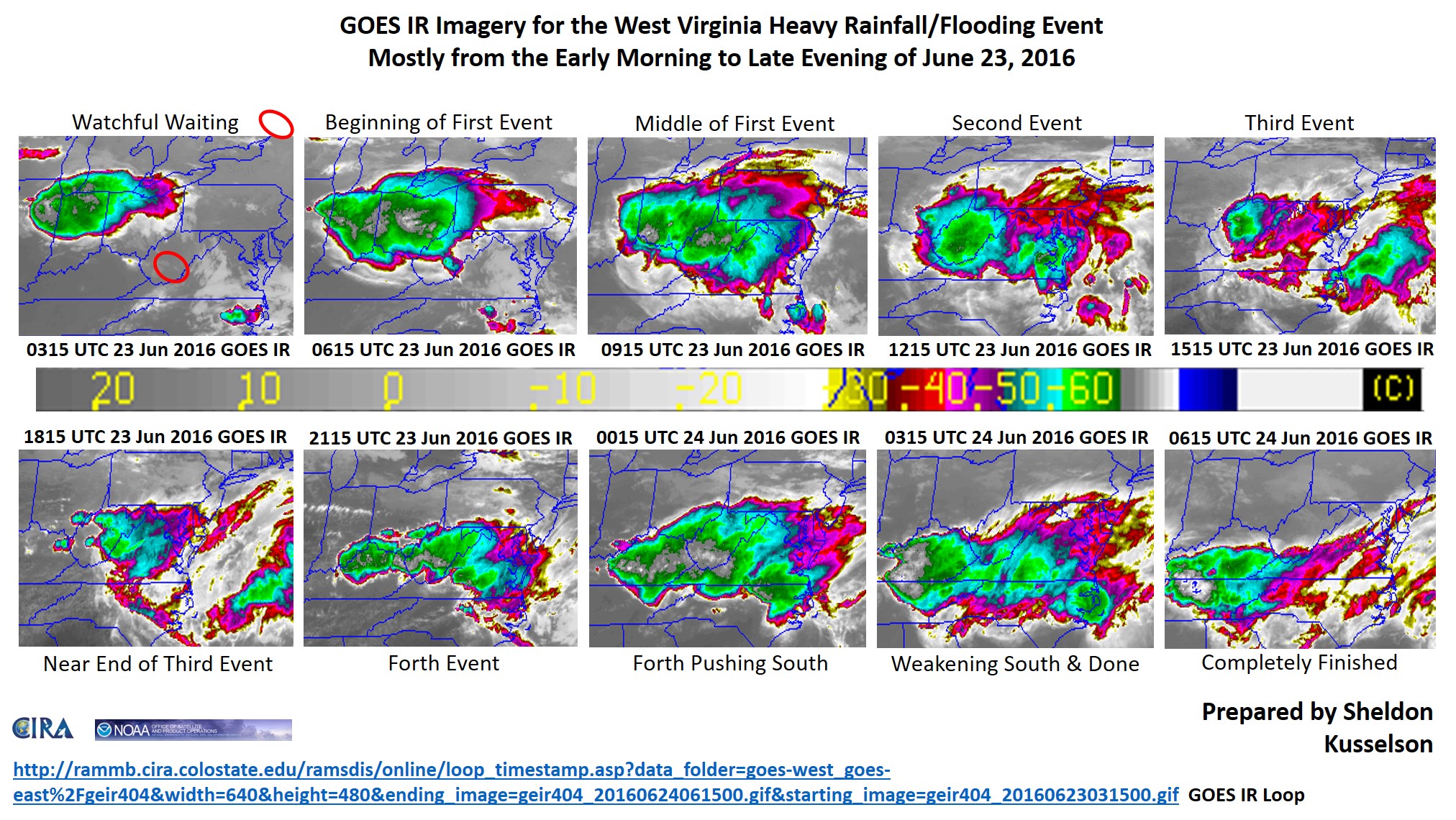
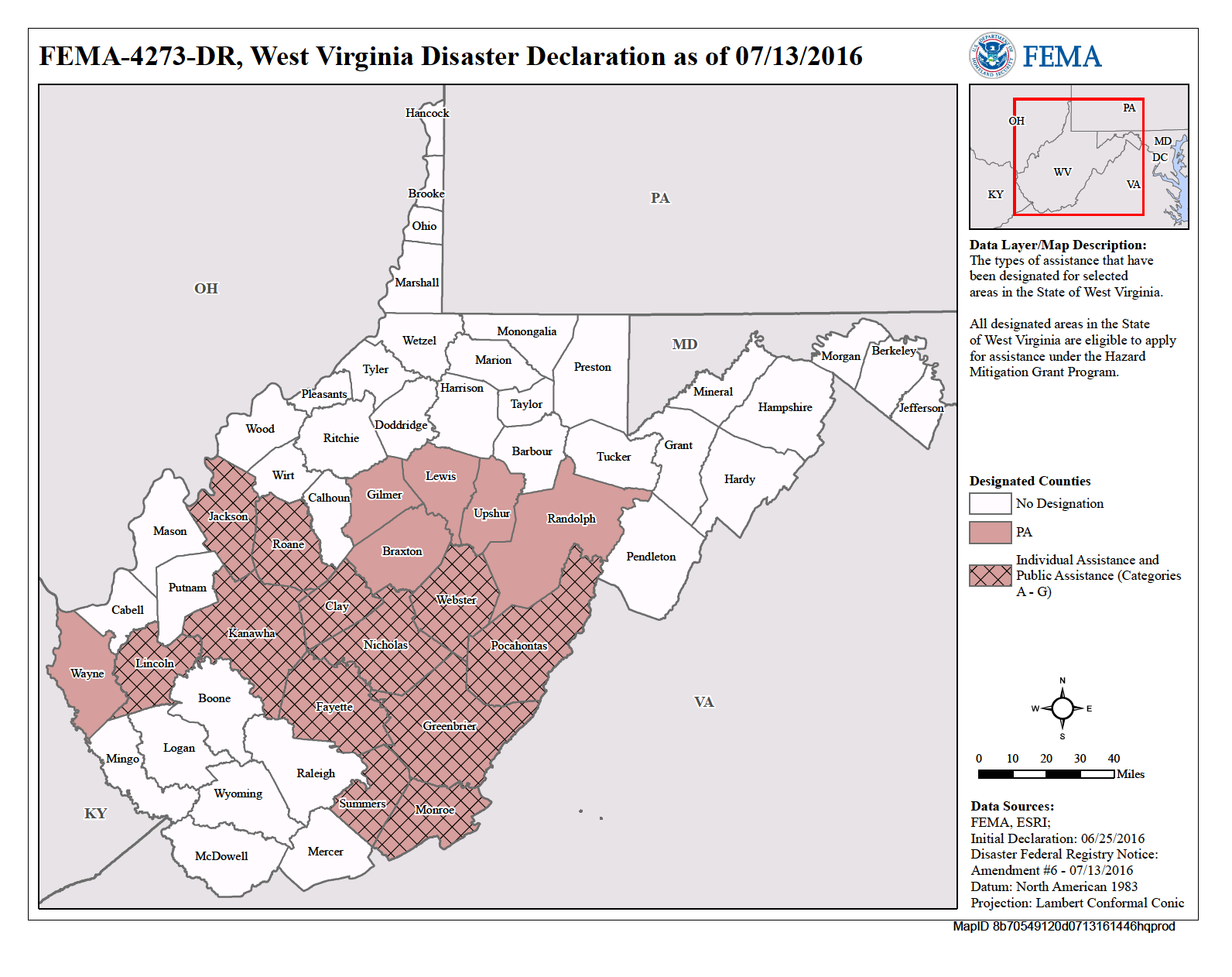


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Flood Risk in West Virginia: A Guide to Flood Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!