Unveiling The Complex World Of Organic Compounds: A Visual Guide
By admin / April 30, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Unveiling the Complex World of Organic Compounds: A Visual Guide
Related Articles: Unveiling the Complex World of Organic Compounds: A Visual Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Complex World of Organic Compounds: A Visual Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Complex World of Organic Compounds: A Visual Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Complex World of Organic Compounds: A Visual Guide
- 3.1 The Building Blocks of Organic Chemistry: A Conceptual Framework
- 3.2 The Benefits of a Visual Representation: A Deeper Understanding
- 3.3 Frequently Asked Questions about Organic Compounds Concept Maps
- 3.4 Tips for Creating and Using Organic Compounds Concept Maps
- 3.5 Conclusion: Navigating the Complex World of Organic Chemistry
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Complex World of Organic Compounds: A Visual Guide
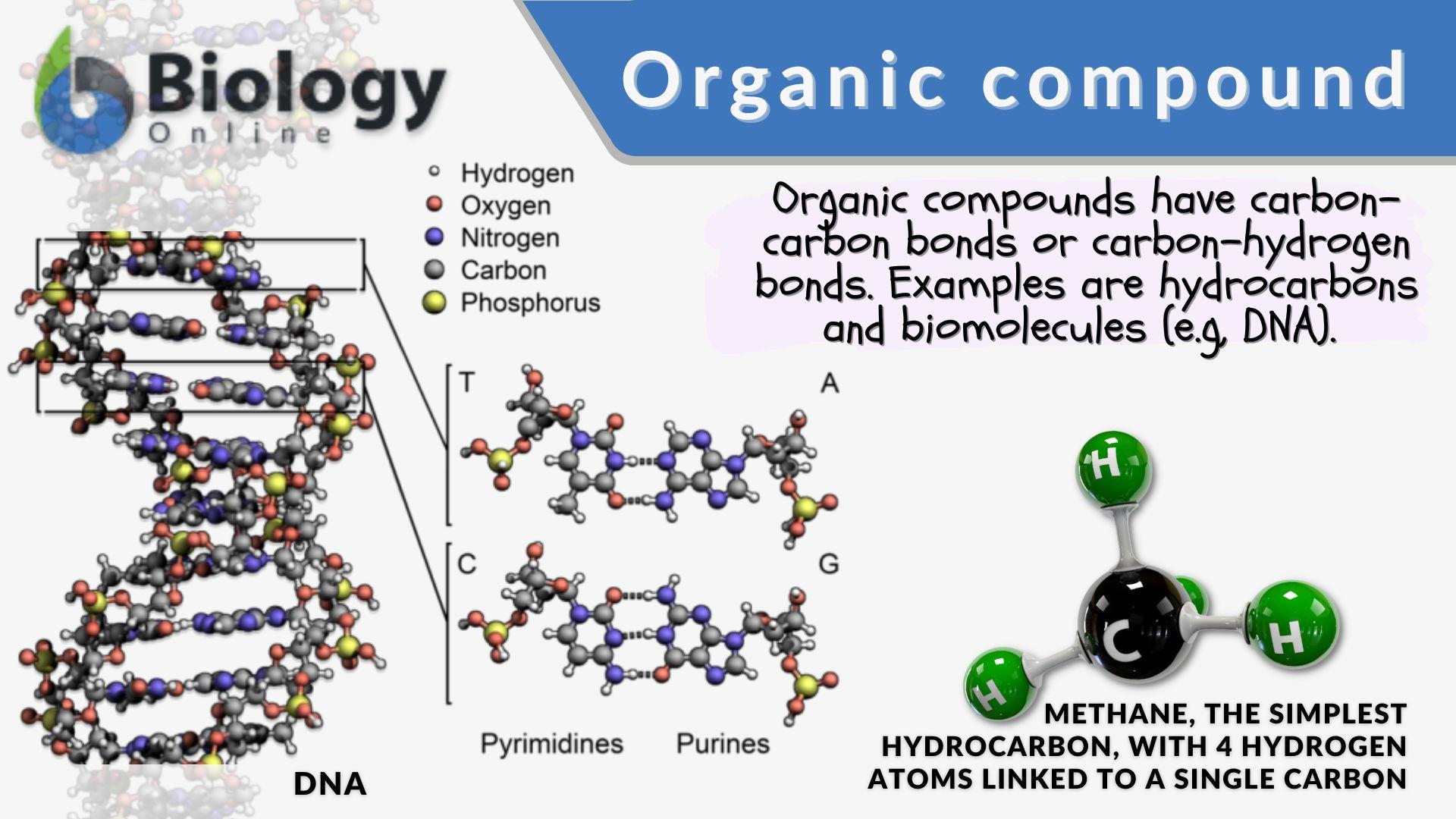
Organic chemistry, the study of carbon-containing compounds, is a vast and intricate field. Its scope encompasses everything from the simple molecules that form the basis of life to the complex polymers that make up our bodies and the world around us. Understanding the relationships between these diverse compounds and their properties is crucial for scientists, researchers, and anyone seeking a deeper understanding of the natural world. A concept map, a visual representation of interconnected ideas, can be a powerful tool for navigating this complex landscape.
The Building Blocks of Organic Chemistry: A Conceptual Framework
An organic compounds concept map effectively presents a hierarchical structure of knowledge, showcasing the relationships between different types of organic compounds and their key features. It serves as a visual roadmap, guiding learners through the diverse realm of organic chemistry. The map typically starts with the fundamental building blocks:
1. Carbon’s Unique Role:
- Carbon, with its ability to form four covalent bonds, serves as the backbone of all organic compounds.
- The tetrahedral geometry of carbon allows for the formation of a wide variety of complex molecules with diverse structures and properties.
2. Functional Groups: The Key to Reactivity:
- Functional groups are specific groups of atoms that dictate the chemical behavior of organic molecules.
- They introduce specific reactivity patterns and determine the compound’s physical and chemical properties.
- Examples include alcohols (OH), aldehydes (CHO), ketones (C=O), carboxylic acids (COOH), and amines (NH2).
3. Hydrocarbons: The Foundation of Organic Compounds:
- Hydrocarbons, composed solely of carbon and hydrogen, are the simplest organic compounds.
- They serve as the foundation for more complex organic molecules, providing the carbon skeleton upon which functional groups are added.
- Alkanes (single bonds), alkenes (double bonds), and alkynes (triple bonds) represent different types of hydrocarbons with varying reactivity.
4. Isomers: Molecules with the Same Formula, Different Structures:
- Isomers are molecules with the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms, leading to distinct properties.
- Structural isomers differ in the arrangement of atoms within the carbon chain, while stereoisomers differ in the spatial arrangement of atoms.
- Understanding isomerism is crucial for predicting and explaining the behavior of organic compounds.
5. Nomenclature and IUPAC Rules:
- A systematic naming system, based on IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) rules, provides a standardized way to name organic compounds.
- This system ensures clarity and unambiguous communication within the scientific community.
- The naming system reflects the structure and functional groups present in a molecule.
The Benefits of a Visual Representation: A Deeper Understanding
The organic compounds concept map offers several advantages for learning and understanding this complex field:
- Visual Organization: The map provides a clear and concise visual representation of the relationships between different types of organic compounds.
- Hierarchical Structure: It establishes a logical hierarchy, starting from fundamental concepts and progressing to more complex ideas.
- Interconnectedness: The map highlights the interconnectedness of different concepts, demonstrating how they build upon one another.
- Enhanced Memory: Visual representations aid in memory retention, making it easier to recall key concepts and relationships.
- Critical Thinking: The map encourages critical thinking by prompting learners to identify connections and analyze relationships between different elements of organic chemistry.
Frequently Asked Questions about Organic Compounds Concept Maps
Q1: What are the key elements to include in an organic compounds concept map?
A1: A comprehensive map should include:
- Central Theme: The concept of organic compounds and their diverse nature.
- Major Categories: Hydrocarbons, functional groups, isomers, and nomenclature.
- Key Subcategories: Alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, etc.
- Relationships: Connections between categories, subcategories, and specific examples.
- Visual Cues: Colors, shapes, and arrows to enhance clarity and visual appeal.
Q2: How can I create an effective organic compounds concept map?
A2: Creating an effective concept map involves:
- Defining Scope: Clearly define the scope of the map and the key concepts to be included.
- Hierarchical Organization: Arrange concepts in a logical hierarchy, starting from the most general and moving to specific details.
- Connections and Relationships: Use arrows, lines, and connecting phrases to illustrate relationships between concepts.
- Visual Clarity: Use clear and concise language, avoiding technical jargon.
- Visual Appeal: Employ colors, shapes, and other visual cues to enhance clarity and interest.
Q3: How can I use an organic compounds concept map effectively?
A3: Effective use of a concept map involves:
- Active Learning: Actively participate in creating or reviewing the map, rather than passively observing it.
- Review and Revision: Regularly revisit the map, adding new information and refining connections as understanding grows.
- Application: Apply the knowledge gained from the map to solve problems and understand real-world examples.
- Collaboration: Discuss the map with others, sharing insights and refining understanding through collaborative learning.
Tips for Creating and Using Organic Compounds Concept Maps
- Start with a central theme: Clearly define the core concept of the map, such as "organic compounds."
- Use clear and concise language: Avoid technical jargon and use simple, straightforward language.
- Emphasize key relationships: Use connecting lines, arrows, and phrases to highlight important relationships between concepts.
- Incorporate visual cues: Employ colors, shapes, and other visual elements to make the map more engaging and memorable.
- Review and revise regularly: Regularly revisit the map, adding new information and refining connections as your understanding grows.
- Use the map for active learning: Actively participate in creating or reviewing the map, rather than passively observing it.
- Apply the knowledge gained from the map to solve problems and understand real-world examples.
Conclusion: Navigating the Complex World of Organic Chemistry
An organic compounds concept map serves as a valuable tool for navigating the complex world of organic chemistry. It provides a visual framework for understanding the relationships between different types of organic compounds, their properties, and their reactions. By creating and using these maps, learners can develop a deeper understanding of this crucial field and its applications in various scientific disciplines. As with any visual aid, the effectiveness of a concept map depends on its clarity, organization, and the active engagement of the learner. By utilizing this powerful tool, individuals can unlock the secrets of organic chemistry and gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate world of carbon-containing compounds.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Complex World of Organic Compounds: A Visual Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!