Unveiling The Earth’s Surface: A Comprehensive Look At Topographic Maps
By admin / April 7, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Unveiling the Earth’s Surface: A Comprehensive Look at Topographic Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Earth’s Surface: A Comprehensive Look at Topographic Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Earth’s Surface: A Comprehensive Look at Topographic Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Earth’s Surface: A Comprehensive Look at Topographic Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Earth’s Surface: A Comprehensive Look at Topographic Maps
- 3.1 Defining Topographic Maps: A Visual Language of the Earth
- 3.2 The Importance of Topographic Maps: Navigating the World, Understanding its Complexity
- 3.3 Delving Deeper: Types of Topographic Maps and their Applications
- 3.4 Navigating the World of Topographic Maps: A Guide to Key Features and Interpretation
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Topographic Maps
- 3.6 Tips for Using Topographic Maps Effectively
- 3.7 Conclusion: Unveiling the Earth’s Complexity through Topographic Maps
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Earth’s Surface: A Comprehensive Look at Topographic Maps
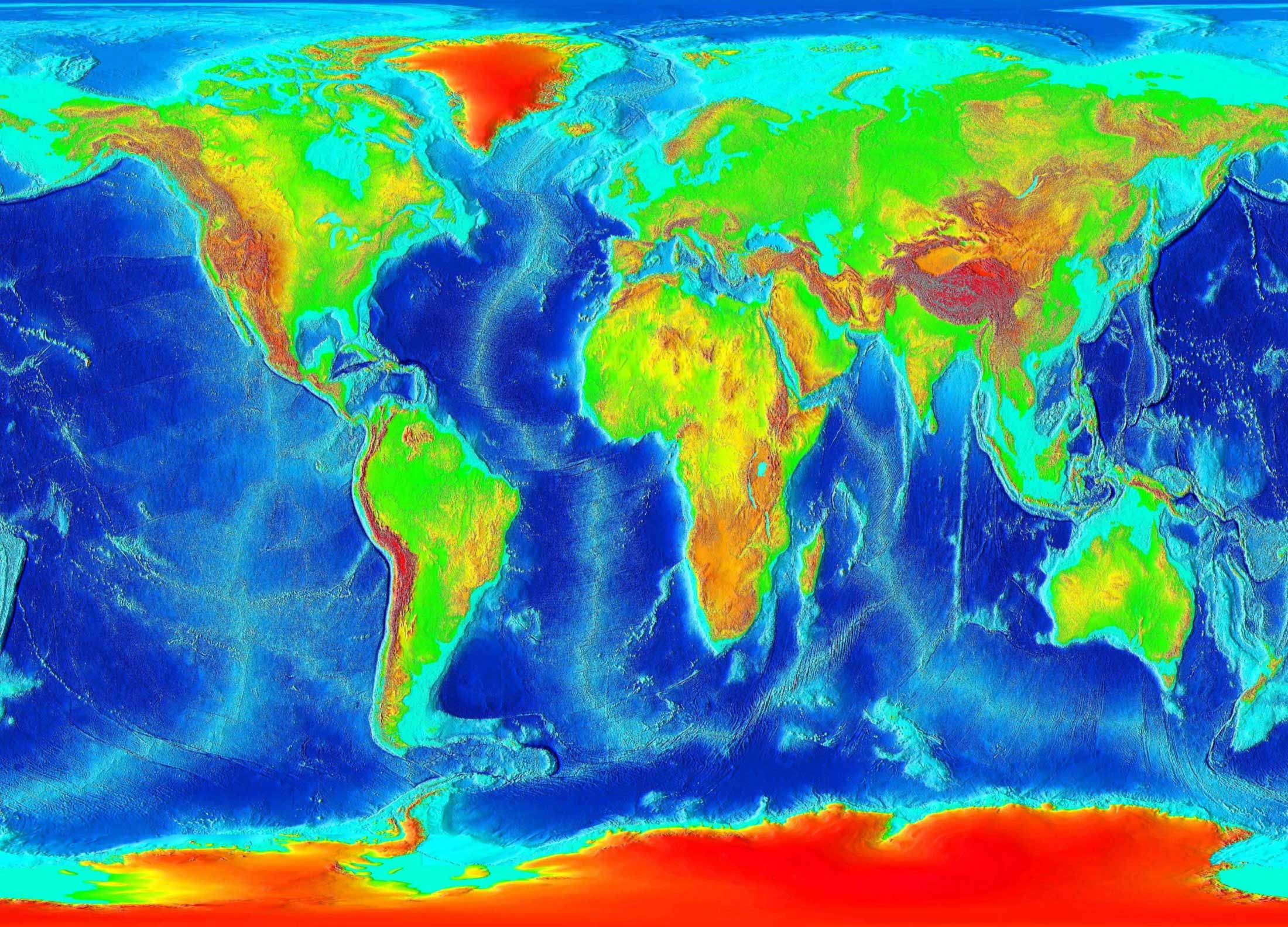
Our planet Earth, a dynamic sphere of land, water, and atmosphere, presents a complex and captivating surface. Understanding its intricate topography is crucial for numerous fields, from navigation and resource management to environmental studies and disaster preparedness. This is where topographic maps come into play, serving as visual representations of the Earth’s surface, revealing its contours, elevations, and features with remarkable detail.
Defining Topographic Maps: A Visual Language of the Earth
Topographic maps, unlike standard geographical maps, go beyond simple outlines and place names. They are specialized representations of the Earth’s surface, emphasizing its three-dimensional form. These maps utilize contour lines, a system of interconnected lines that connect points of equal elevation, providing a visual understanding of the terrain’s rise and fall.
Contour lines, the heart of topographic maps, offer a powerful tool for visualizing the landscape. Closely spaced lines indicate steep slopes, while widely spaced lines suggest gentle gradients. The density of these lines, therefore, becomes a visual indicator of the terrain’s ruggedness or smoothness.
Beyond contour lines, topographic maps incorporate a wealth of information, including:
- Elevation: Numerical values indicating the height of specific points, often referenced to a standard datum such as sea level.
- Landforms: Depiction of natural features like mountains, valleys, rivers, lakes, and coastlines.
- Cultural Features: Representation of human-made structures, including roads, railways, buildings, and other infrastructure.
- Symbols: Standardized symbols convey specific information about the terrain, such as vegetation types, soil composition, and hydrological features.
The Importance of Topographic Maps: Navigating the World, Understanding its Complexity
Topographic maps are essential tools for a diverse range of applications, impacting various aspects of our lives:
- Navigation: For hikers, mountaineers, and explorers, topographic maps are indispensable for safe and efficient navigation. They provide precise elevation information, allowing users to plan routes, estimate travel time, and identify potential hazards.
- Resource Management: Understanding the Earth’s topography is crucial for resource management. Topographic maps assist in identifying suitable locations for agriculture, mining, and infrastructure development, while also informing sustainable land use practices.
- Environmental Studies: These maps provide invaluable insights into the Earth’s natural processes. They reveal the distribution of vegetation, soil types, and water resources, aiding in environmental impact assessments, habitat conservation, and disaster risk management.
- Urban Planning: Topographic maps play a vital role in urban planning, informing decisions about infrastructure development, flood mitigation, and land use zoning. They provide a comprehensive understanding of the terrain, allowing for the design of efficient transportation networks and sustainable urban environments.
- Military Operations: In military operations, topographic maps are crucial for planning troop movements, identifying strategic locations, and assessing terrain suitability for various military activities.
Delving Deeper: Types of Topographic Maps and their Applications
The world of topographic maps encompasses a variety of types, each tailored for specific applications:
- Standard Topographic Maps: These are the most common type, produced by government agencies like the United States Geological Survey (USGS). They cover large areas with a focus on elevation, landforms, and cultural features.
- Contour Maps: These maps emphasize elevation, using contour lines to portray the terrain’s shape. They are commonly used in surveying, engineering, and land development.
- Relief Maps: These maps create a three-dimensional representation of the terrain, using shading, hachures, or other techniques to highlight the topography. They are often used for educational purposes and visual presentations.
- Digital Elevation Models (DEMs): These are computer-generated representations of the Earth’s surface, capturing elevation data in a digital format. DEMs are used in a wide range of applications, including 3D modeling, terrain analysis, and hydrological modeling.
Navigating the World of Topographic Maps: A Guide to Key Features and Interpretation
Understanding the key features of topographic maps is crucial for effective interpretation:
- Contour Lines: As mentioned earlier, these lines connect points of equal elevation, providing a visual representation of the terrain’s shape. The closer the lines, the steeper the slope.
- Elevation: Numerical values indicating the height of specific points, usually referenced to sea level.
- Scale: The ratio between the distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground. It is crucial for accurate measurement and understanding the map’s coverage.
- Symbols: Standardized symbols represent various features, including vegetation types, buildings, roads, and hydrological features. A legend accompanies the map, providing a key to understanding these symbols.
- Datum: A reference point used for determining elevations. Commonly used datums include the North American Vertical Datum of 1988 (NAVD88) and the World Geodetic System 1984 (WGS84).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Topographic Maps
1. What is the difference between a topographic map and a geographical map?
Topographic maps focus on the three-dimensional shape of the Earth’s surface, using contour lines to represent elevation changes. Geographical maps, on the other hand, primarily emphasize location, boundaries, and political features.
2. How are topographic maps created?
Topographic maps are created using various methods, including aerial photography, satellite imagery, and ground surveys. These techniques capture elevation data, which is then processed and used to generate contour lines and other map features.
3. How can I read a topographic map?
Reading a topographic map requires understanding the key features, including contour lines, elevation, scale, symbols, and the legend. Practice interpreting these features is essential for navigating and understanding the terrain depicted on the map.
4. Where can I find topographic maps?
Topographic maps are available from various sources, including government agencies like the USGS, online map services, and specialized map retailers.
5. What are some of the benefits of using topographic maps?
Topographic maps provide a detailed and accurate representation of the Earth’s surface, aiding in navigation, resource management, environmental studies, urban planning, and military operations.
Tips for Using Topographic Maps Effectively
- Familiarize yourself with the map’s key features: Understand contour lines, elevation, scale, symbols, and the legend before using the map.
- Practice interpreting the map: Start with simple maps and gradually work towards more complex ones.
- Use a compass and other navigation tools: Combine topographic maps with traditional navigation tools for accurate direction and location determination.
- Plan your route carefully: Study the map thoroughly before embarking on any trip, identifying potential hazards and choosing suitable routes.
- Always carry a map and compass: Even with modern technology, having a physical map and compass is essential for navigation and safety.
Conclusion: Unveiling the Earth’s Complexity through Topographic Maps
Topographic maps serve as powerful tools for understanding and navigating the Earth’s complex surface. By providing a visual representation of elevation, landforms, and other features, they offer valuable insights for diverse fields, from navigation and resource management to environmental studies and urban planning. As we continue to explore and interact with our planet, topographic maps will remain essential for revealing its intricate tapestry and guiding us towards a deeper understanding of its diverse landscapes.


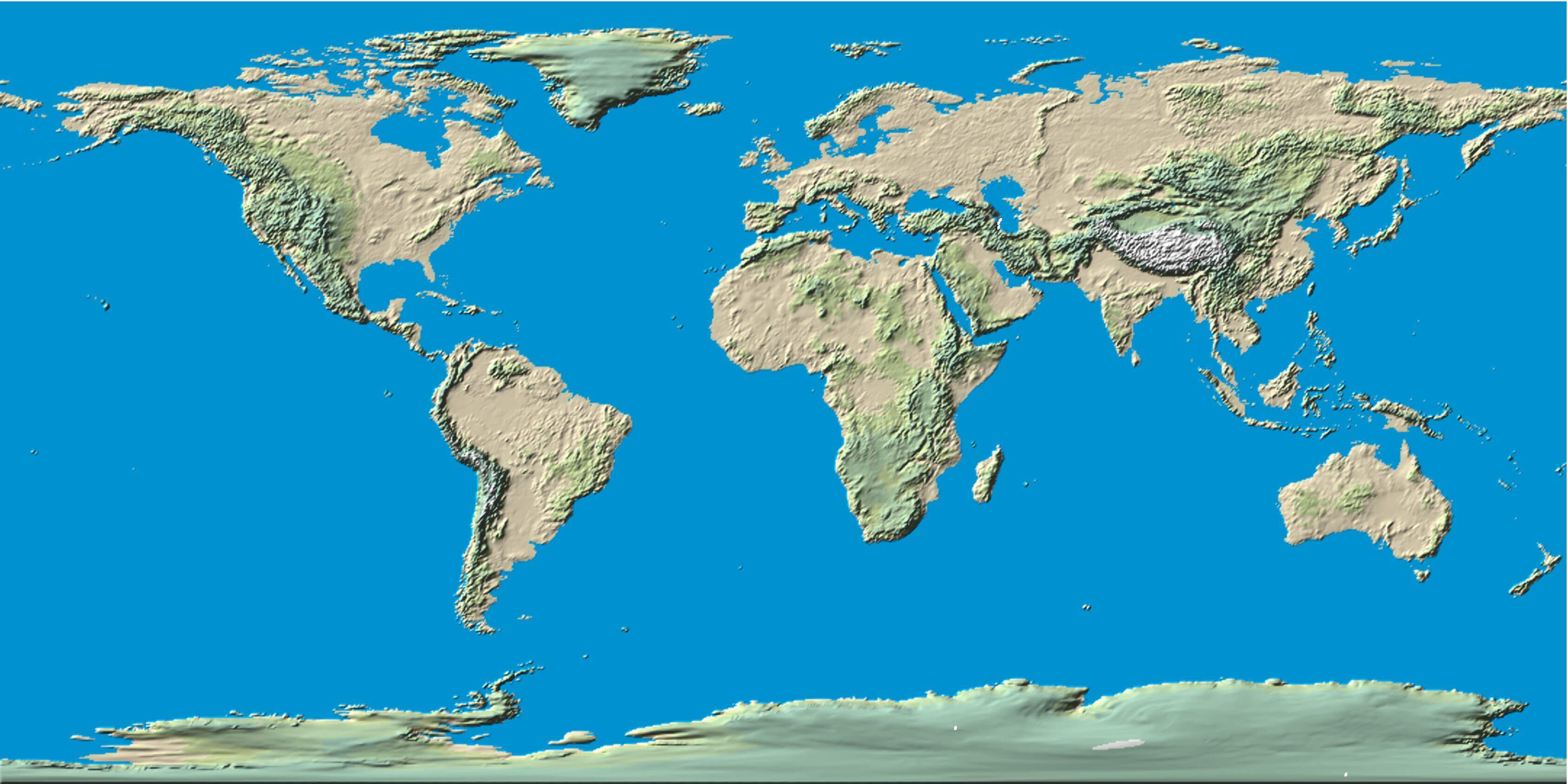
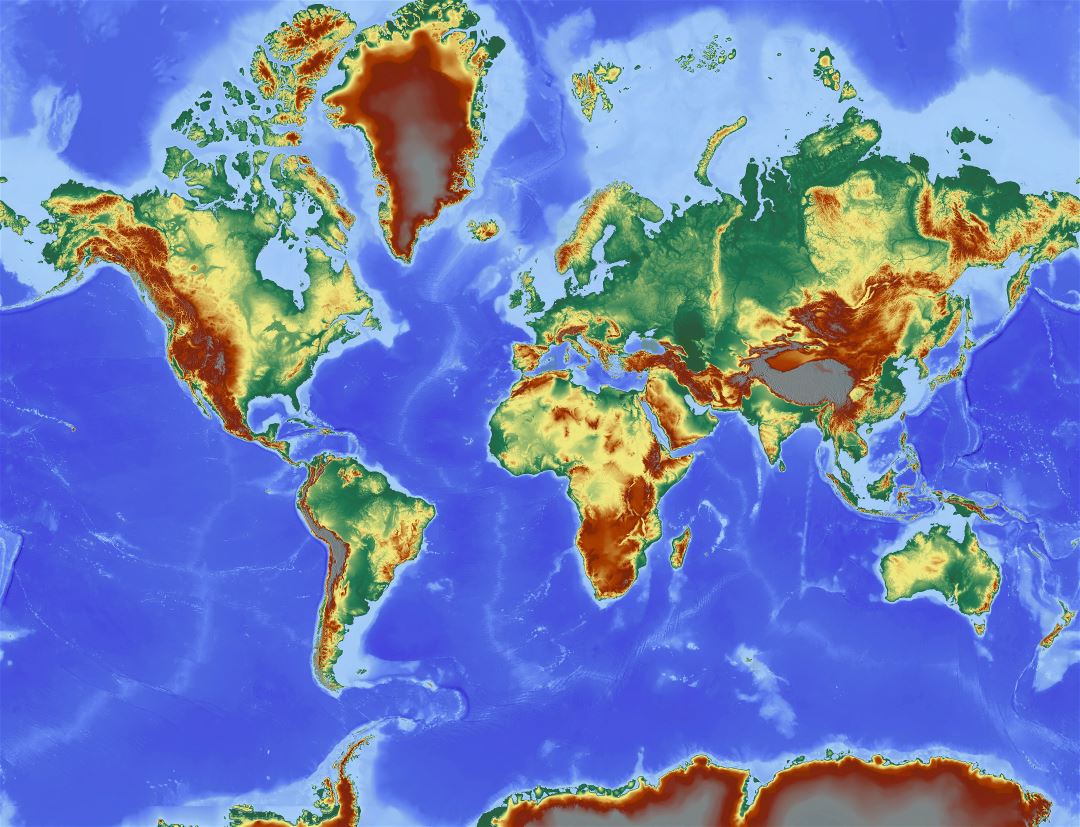

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Earth’s Surface: A Comprehensive Look at Topographic Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!