Unveiling The Network: A Comprehensive Guide To Optic Fiber Maps
By admin / October 15, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Unveiling the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to Optic Fiber Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to Optic Fiber Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to Optic Fiber Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to Optic Fiber Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to Optic Fiber Maps
- 3.1 Understanding the Essence of Optic Fiber Maps
- 3.2 The Importance of Optic Fiber Maps: A Multifaceted Perspective
- 3.3 Unveiling the Layers: Types of Optic Fiber Maps
- 3.4 Navigating the Network: FAQs on Optic Fiber Maps
- 3.5 Guiding the Network: Tips for Effective Optic Fiber Map Use
- 3.6 Conclusion: The Unseen Network, Now Visible
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to Optic Fiber Maps
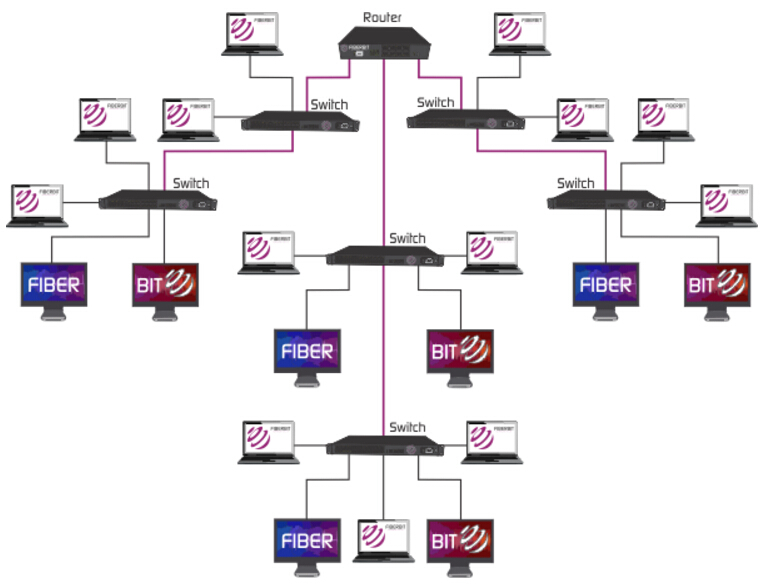
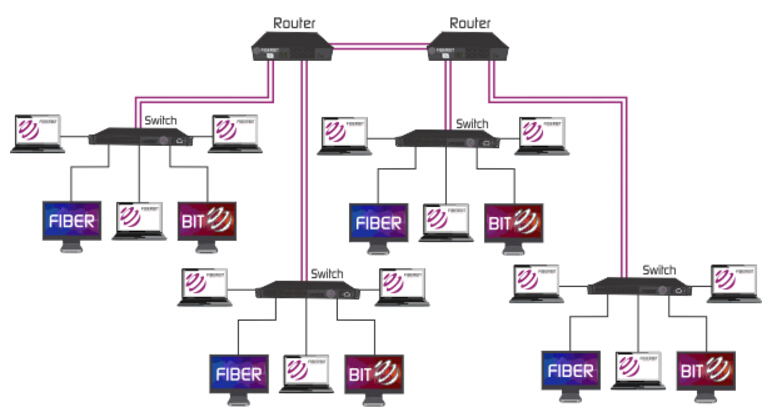
In the digital age, where information flows at lightning speed, understanding the intricate network that carries it is crucial. This network is not just a collection of wires; it’s a complex web of infrastructure, and one of its most vital components is the optic fiber cable. Optic fiber maps, visual representations of this network, provide a crucial insight into the physical structure of this high-speed data highway, offering valuable information for various stakeholders.
Understanding the Essence of Optic Fiber Maps
Optic fiber maps are essentially graphical representations of the optic fiber network, depicting the intricate pathways of these thin strands of glass that transmit data using light pulses. These maps serve as visual blueprints, outlining the location of cables, their connections, and the various points of access. They are not merely static diagrams; they are dynamic tools that evolve alongside the network itself, reflecting the ever-changing landscape of data flow.
The Importance of Optic Fiber Maps: A Multifaceted Perspective
The significance of optic fiber maps extends beyond mere visualization. They offer a range of benefits, making them indispensable tools for various entities involved in the digital ecosystem:
1. Network Planning and Deployment:
- Strategic Planning: Optic fiber maps serve as the foundation for strategic planning, allowing network operators to identify areas with high demand, optimize cable routes, and ensure efficient network expansion.
- Efficient Deployment: By understanding the existing infrastructure, operators can minimize disruptions and optimize resource allocation during new cable installations.
2. Network Management and Troubleshooting:
- Fault Identification: When network outages occur, optic fiber maps pinpoint the location of the fault, enabling swift troubleshooting and restoration of service.
- Maintenance and Repair: Maps facilitate efficient maintenance and repair by providing a clear understanding of the network’s layout, allowing technicians to quickly access the affected areas.
3. Business Development and Investment:
- Market Analysis: Optic fiber maps provide valuable data for market analysis, allowing businesses to identify areas with high internet penetration and potential growth opportunities.
- Investment Decisions: Potential investors can leverage these maps to assess the viability of projects, understand the existing infrastructure, and make informed investment decisions.
4. Public Safety and Emergency Response:
- Disaster Preparedness: Optic fiber maps play a critical role in disaster preparedness, enabling emergency response teams to assess network vulnerabilities and ensure communication channels remain operational.
- Critical Infrastructure Protection: These maps contribute to the protection of critical infrastructure by providing a detailed understanding of the network’s structure and potential vulnerabilities.
5. Research and Development:
- Network Optimization: Researchers can utilize optic fiber maps to study network performance, identify bottlenecks, and develop strategies for optimization.
- Technological Advancements: These maps provide valuable insights into the capabilities and limitations of current technology, paving the way for future advancements in network infrastructure.
Unveiling the Layers: Types of Optic Fiber Maps
Optic fiber maps are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Different types of maps cater to specific needs and provide varying levels of detail, each offering unique insights into the network:
1. Physical Maps: These maps depict the physical layout of the network, showcasing the location of cables, conduits, and other physical infrastructure. They are essential for planning new installations, conducting maintenance, and responding to network outages.
2. Logical Maps: Logical maps focus on the logical connections within the network, outlining the flow of data between different devices and systems. These maps are crucial for understanding network traffic patterns, identifying bottlenecks, and optimizing network performance.
3. Network Topology Maps: Topology maps illustrate the interconnectedness of different network components, showcasing the hierarchical structure of the network. These maps are helpful for understanding the overall network architecture and identifying potential vulnerabilities.
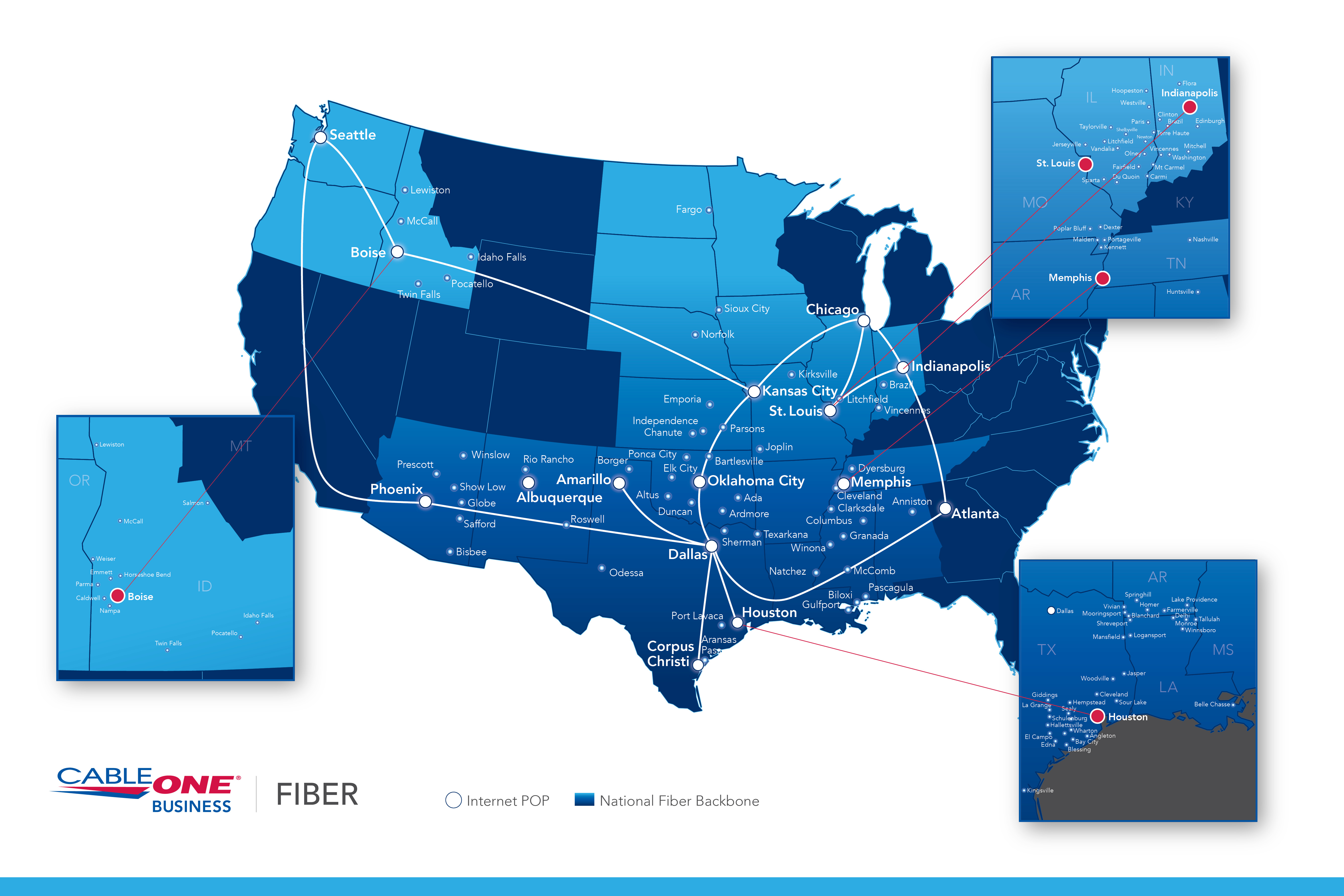
4. Geographic Information System (GIS) Maps: GIS maps integrate spatial data with network information, providing a comprehensive visual representation of the network’s geographic distribution. These maps are particularly useful for network planning, deployment, and maintenance, enabling efficient resource allocation and targeted interventions.
5. Interactive Maps: Interactive maps offer a dynamic and user-friendly experience, allowing users to zoom in and out, explore different layers of information, and interact with the data. These maps are ideal for visualization, analysis, and collaboration, enabling users to gain a deeper understanding of the network.
Navigating the Network: FAQs on Optic Fiber Maps
1. What information is typically included in an optic fiber map?
Optic fiber maps typically include details such as:
- Cable routes: The precise paths of optic fiber cables, both underground and overhead.
- Cable types: The specific types of cables used, including their core count, fiber diameter, and other technical specifications.
- Connection points: The locations where cables connect to other infrastructure, including distribution points, splice closures, and termination points.
- Network equipment: The location and type of network equipment, such as switches, routers, and amplifiers.
- Network services: The types of services provided over the network, such as internet access, telephony, and television.
2. Who uses optic fiber maps and why?
Optic fiber maps are used by a wide range of stakeholders, including:
- Network operators: For planning, deployment, management, and maintenance of the network.
- Telecommunications companies: For marketing, sales, and customer service.
- Government agencies: For disaster preparedness, emergency response, and infrastructure planning.
- Construction companies: For planning new infrastructure projects and ensuring minimal disruption to existing networks.
- Research institutions: For network analysis, optimization, and development of new technologies.
3. How are optic fiber maps created and updated?
Optic fiber maps are typically created using a combination of data sources, including:
- Field surveys: Technicians conduct physical surveys of the network, documenting cable routes, connection points, and other infrastructure details.
- GIS data: Geographic information systems provide spatial data that can be integrated with network information to create detailed maps.
- Network management systems: These systems track network performance and configuration, providing data for updating maps.
4. What are the challenges associated with maintaining optic fiber maps?
Maintaining accurate and up-to-date optic fiber maps presents several challenges:
- Network complexity: The ever-growing size and complexity of optic fiber networks make it challenging to keep maps current.
- Data accuracy: Ensuring the accuracy of data from multiple sources is crucial for map reliability.
- Data integration: Combining data from different sources, such as field surveys and network management systems, can be a complex process.
- Dynamic nature: The network is constantly evolving, requiring frequent map updates to reflect changes in infrastructure and services.
5. What are the future trends in optic fiber mapping?
The future of optic fiber mapping is likely to be shaped by:
- Integration with artificial intelligence (AI): AI can automate data collection, analysis, and map generation, improving efficiency and accuracy.
- Real-time updates: Maps will be increasingly updated in real-time, reflecting changes in the network as they occur.
- Interactive and immersive experiences: Maps will offer more interactive and immersive experiences, allowing users to explore the network in greater detail.
- Data visualization and analytics: Maps will incorporate advanced data visualization and analytics tools, enabling users to gain deeper insights into network performance and trends.
Guiding the Network: Tips for Effective Optic Fiber Map Use
- Establish clear objectives: Define the specific goals for using the map, whether for network planning, troubleshooting, or business development.
- Choose the right type of map: Select the map type that best suits the specific needs and objectives.
- Ensure data accuracy: Verify the accuracy of the data used to create the map, as inaccurate data can lead to incorrect decisions.
- Regularly update the map: Update the map regularly to reflect changes in the network and ensure its relevance.
- Utilize visualization tools: Employ data visualization tools to enhance understanding and communication of map data.
- Train users effectively: Provide users with proper training on map interpretation and utilization to maximize its value.
Conclusion: The Unseen Network, Now Visible
Optic fiber maps are more than just static diagrams; they are dynamic tools that provide invaluable insights into the intricate world of high-speed data transmission. By understanding the structure and functionality of the optic fiber network, stakeholders can make informed decisions, optimize network performance, and ensure the seamless flow of information in our increasingly digital world. As technology advances, the role of optic fiber maps will continue to evolve, becoming even more crucial for navigating the complex and ever-expanding network of our digital future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to Optic Fiber Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!