Unveiling The Power Of Geocoding: How To Convert Addresses Into Precise Coordinates
By admin / September 24, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Unveiling the Power of Geocoding: How to Convert Addresses into Precise Coordinates
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Geocoding: How to Convert Addresses into Precise Coordinates
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Geocoding: How to Convert Addresses into Precise Coordinates. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Geocoding: How to Convert Addresses into Precise Coordinates

In the digital age, where information is constantly flowing and location-based services are ubiquitous, the ability to pinpoint a specific location is paramount. This is where geocoding comes into play, a process that translates textual addresses into numerical coordinates, namely latitude and longitude. Google Maps API, a powerful tool offered by Google, empowers developers and users alike to leverage this functionality, transforming addresses into actionable data points for a wide range of applications.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Geocoding
Imagine a world map, a vast canvas where every point on Earth is represented by a unique pair of numbers: latitude and longitude. Latitude, measured in degrees north or south of the equator, defines a location’s position along a vertical line. Longitude, measured in degrees east or west of the prime meridian, defines a location’s position along a horizontal line. These coordinates, when combined, create a precise location marker, enabling navigation, mapping, and numerous other location-dependent tasks.
Geocoding is the bridge between the human-readable language of addresses and the numerical language of coordinates. It acts as a translator, converting street names, city names, and other address components into their corresponding latitude and longitude values. This process is essential for various applications, including:
- Navigation Apps: Geocoding is the backbone of navigation apps like Google Maps and Waze. When you input a destination address, the app utilizes geocoding to translate it into coordinates, enabling it to calculate routes and provide turn-by-turn directions.
- Location-Based Services: From weather apps that provide localized forecasts to e-commerce platforms that show nearby stores, geocoding is crucial for delivering location-specific information and services.
- Real Estate and Property Management: Geocoding helps real estate agents and property managers visualize properties on maps, analyze location data, and identify potential buyers or tenants based on their proximity to desired amenities or areas.
- Delivery and Logistics: Geocoding plays a vital role in optimizing delivery routes, tracking shipments in real-time, and ensuring efficient logistics operations.
- Emergency Response: Geocoding allows emergency services to quickly locate incidents based on caller addresses, improving response times and potentially saving lives.
- Market Research and Analysis: By understanding the geographical distribution of customers, businesses can tailor marketing campaigns, analyze market trends, and identify potential growth opportunities.
Harnessing the Power of Google Maps API
Google Maps API provides a comprehensive set of tools and services for developers to integrate geocoding functionalities into their applications. The API offers various methods for performing geocoding tasks, enabling developers to choose the approach that best suits their specific needs.
1. Geocoding an Address:
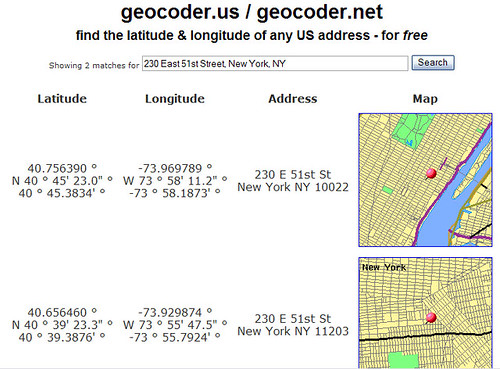
The most common use case involves converting a textual address into latitude and longitude. Google Maps API offers a straightforward method for this task. The developer simply needs to provide the address as input, and the API returns the corresponding coordinates.
2. Reverse Geocoding:
Reverse geocoding operates in the opposite direction, converting coordinates into their corresponding addresses. This functionality proves valuable for displaying location information in a human-readable format. For instance, a weather app might use reverse geocoding to display the city and state associated with a user’s current location.
3. Batch Geocoding:
For applications that involve processing large datasets of addresses, Google Maps API provides batch geocoding capabilities. This allows developers to geocode multiple addresses simultaneously, significantly improving efficiency and reducing processing time.
4. Geocoding with Place IDs:
Google Maps API also allows developers to use Place IDs, unique identifiers assigned to specific locations, for geocoding. This method ensures more accurate and consistent results, especially when dealing with locations that may have multiple addresses or ambiguous names.
5. Advanced Geocoding Options:
The API offers various advanced options for customizing geocoding requests. Developers can specify region biases, language preferences, and other parameters to fine-tune the results and ensure accuracy for specific use cases.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the limitations of Google Maps API for geocoding?
A: While Google Maps API offers robust geocoding functionalities, it’s important to understand its limitations:
- Rate Limits: Google Maps API enforces usage limits to prevent abuse and ensure fair access for all users. Exceeding these limits may result in service restrictions or charges.
- Data Accuracy: While Google Maps API strives for accuracy, geocoding results may not always be perfect. Factors like incomplete or ambiguous addresses, changes in street names, or the existence of multiple locations with the same name can impact accuracy.
- Privacy Considerations: Geocoding involves processing sensitive location data, and developers must adhere to privacy regulations and best practices when handling this information.
Q: What are the alternatives to Google Maps API for geocoding?
A: While Google Maps API is a popular and reliable option, other geocoding services are available:
- OpenStreetMap Nominatim: A free and open-source geocoding service powered by OpenStreetMap data.
- MapQuest Geocoding API: A commercial geocoding service offering various features and customization options.
- Bing Maps Geocoding API: A geocoding service offered by Microsoft, providing access to Bing Maps data and functionalities.
Q: How can I ensure accurate geocoding results?
A: To maximize geocoding accuracy, consider these tips:
- Provide complete and accurate addresses: Include all relevant details, such as street number, street name, city, state, and postal code.
- Use standardized address formats: Follow established address formatting guidelines to avoid ambiguity and inconsistencies.
- Specify region biases: If the address is ambiguous or could refer to multiple locations, specify the region or country to narrow down the search.
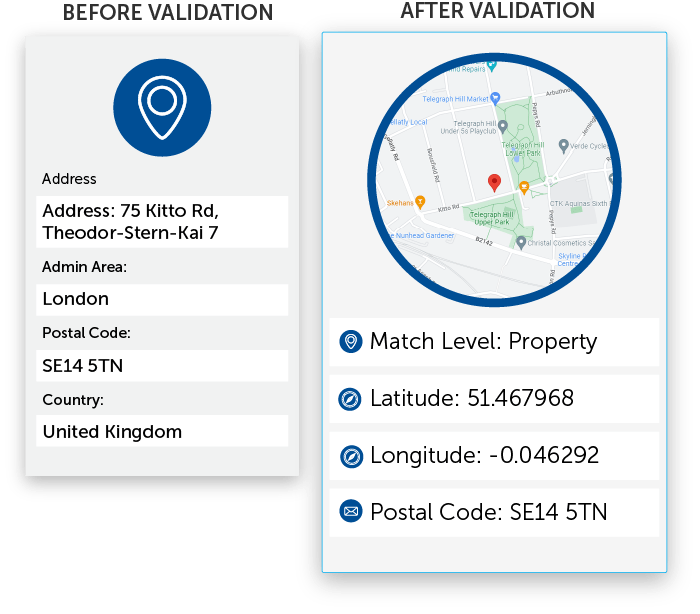
- Verify results: Always verify the returned coordinates against the provided address to ensure accuracy.
Conclusion
Geocoding, the process of converting addresses into coordinates, plays a crucial role in a wide range of applications, from navigation and location-based services to real estate and emergency response. Google Maps API provides a powerful and flexible tool for developers to integrate geocoding functionalities into their applications, enabling them to unlock the potential of location data and build innovative solutions. By understanding the fundamentals of geocoding, exploring the capabilities of Google Maps API, and following best practices for accuracy, developers can harness the transformative power of geocoding to enhance user experiences, optimize operations, and drive meaningful insights.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Geocoding: How to Convert Addresses into Precise Coordinates. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!