Unveiling The Secrets Of The Atmosphere: A Comprehensive Guide To Weather Isobar Maps
By admin / September 4, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Unveiling the Secrets of the Atmosphere: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Isobar Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of the Atmosphere: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Isobar Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Secrets of the Atmosphere: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Isobar Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Secrets of the Atmosphere: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Isobar Maps
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/isobarmap-56a9e0d25f9b58b7d0ffa3cf.gif)
The ever-changing canvas of the sky, with its swirling clouds and shifting winds, holds a complex story waiting to be deciphered. Weather, with its unpredictable nature, has captivated humankind for millennia. Yet, through scientific advancements, we have gained powerful tools to unravel its intricacies. One such tool, the weather isobar map, serves as a key to understanding the atmospheric forces that govern our daily lives.
Understanding the Foundation: What are Isobars?
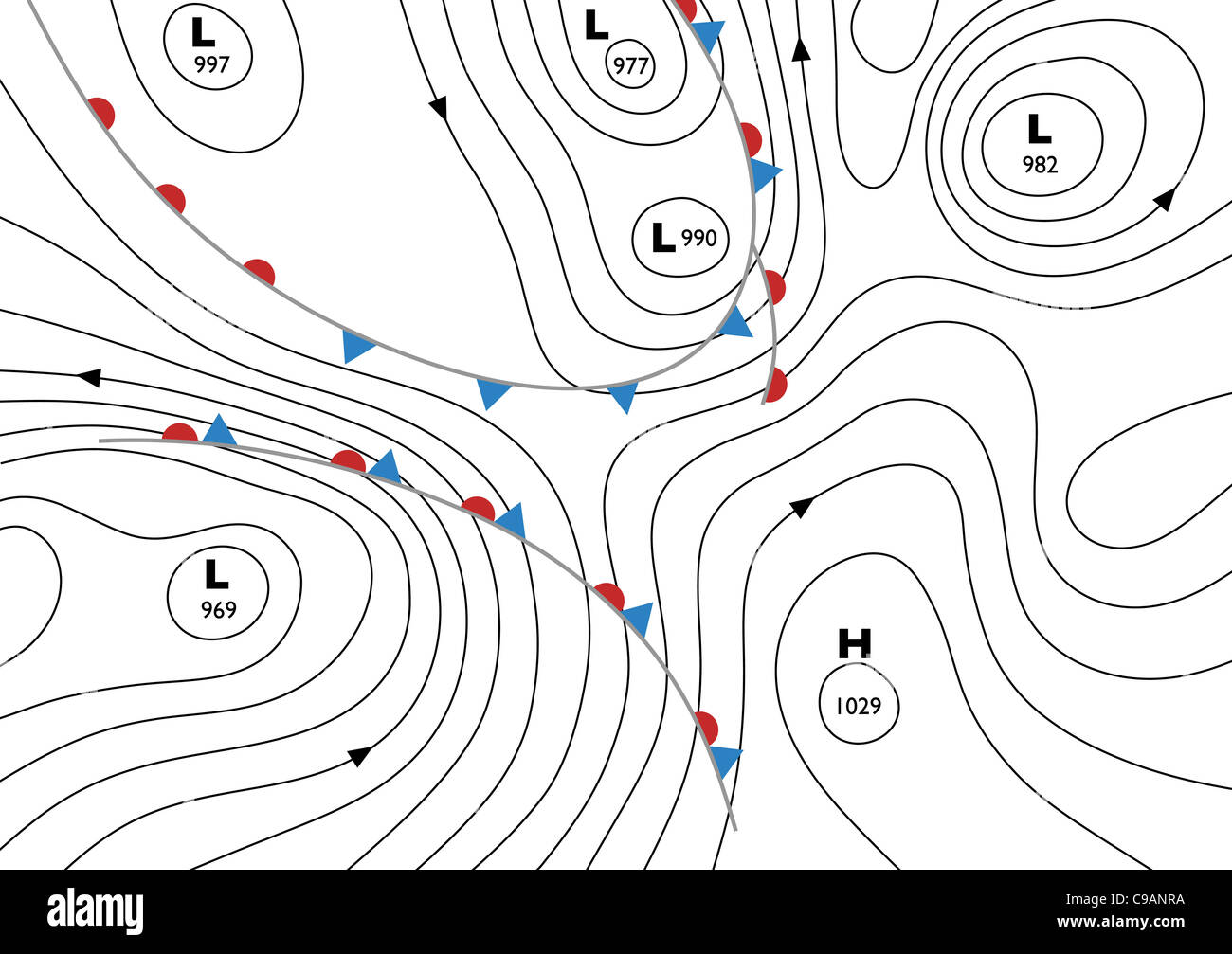
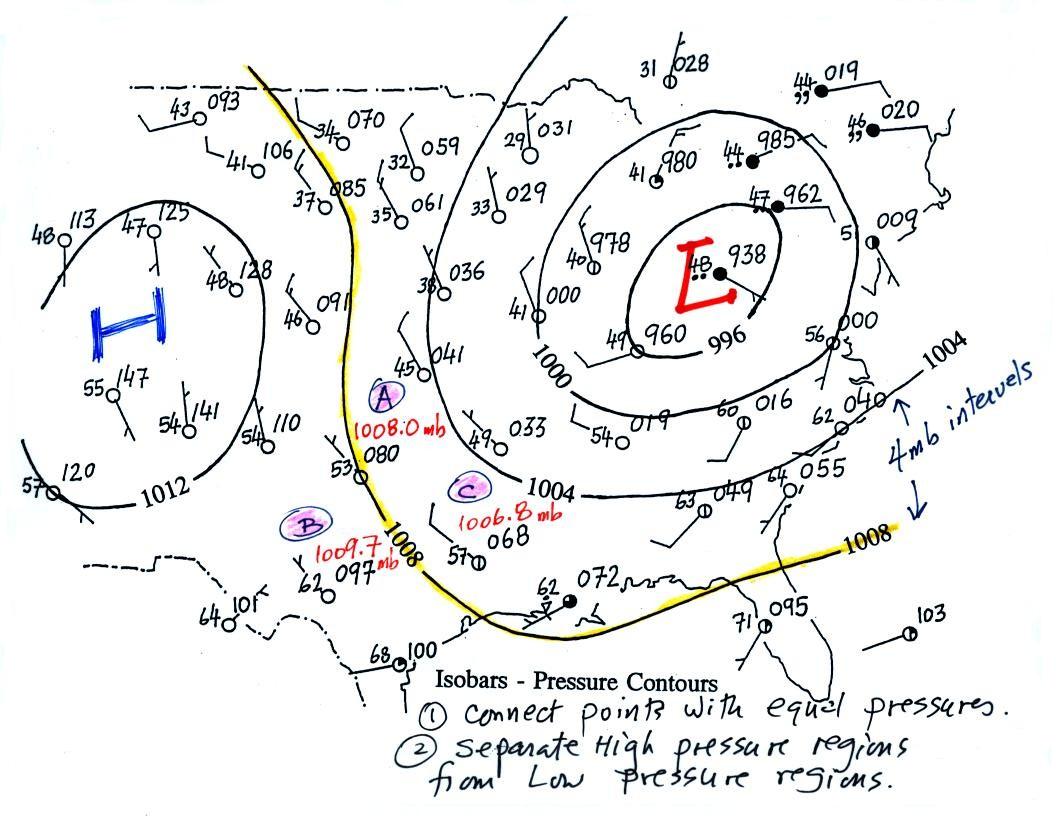
Isobars are lines on a weather map that connect points of equal atmospheric pressure. They are akin to contour lines on a topographic map, depicting the elevation of the land. In the context of weather, isobars represent the varying pressure levels in the atmosphere. The closer the isobars are to each other, the steeper the pressure gradient, indicating a stronger wind.
The Language of the Map: Deciphering the Patterns
A weather isobar map is a visual representation of atmospheric pressure distribution. It provides valuable insights into prevailing wind patterns, potential for precipitation, and the likelihood of various weather phenomena.
-
High-Pressure Systems: Depicted as closed loops of isobars with higher pressure values inside, high-pressure systems are associated with clear skies, calm winds, and stable weather conditions. Air flows outwards from these systems, leading to descending air masses and suppression of cloud formation.
-
Low-Pressure Systems: These systems are characterized by closed loops of isobars with lower pressure values inside. They are linked to unstable weather conditions, characterized by ascending air masses, cloud formation, and precipitation. Air flows inwards towards the low-pressure center, often creating turbulent winds and stormy weather.
-
Fronts: The transition zones between high and low-pressure systems are known as fronts. These are marked by sharp changes in temperature, humidity, and wind direction. Cold fronts, where cold air replaces warm air, are typically associated with strong winds, thunderstorms, and heavy precipitation. Warm fronts, where warm air displaces cold air, often bring gradual cloud formation, light precipitation, and rising temperatures.
Beyond the Lines: Additional Information on Isobar Maps
While isobars are the primary feature of these maps, they often incorporate additional information to enhance their utility:
-
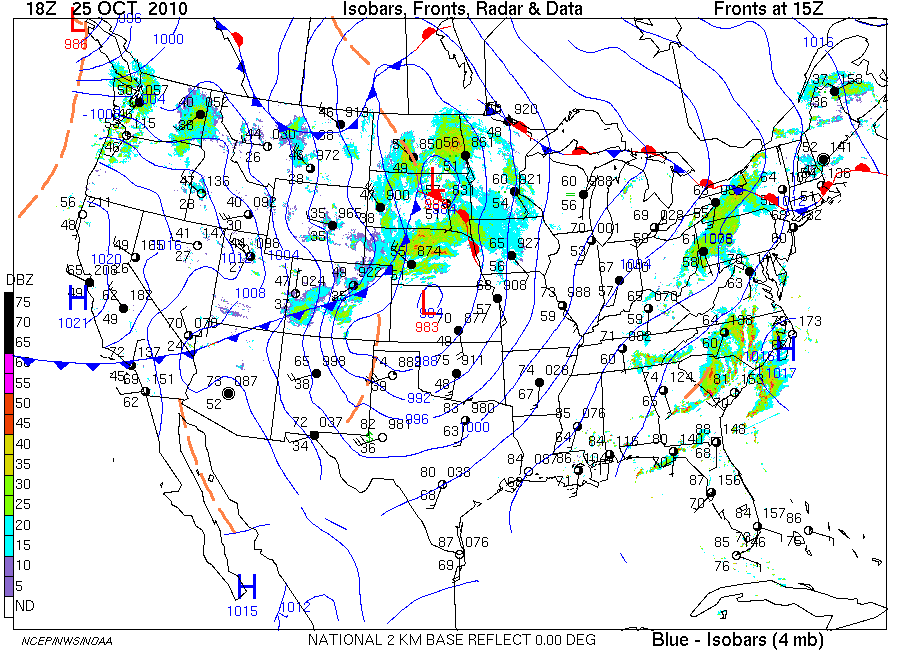
Wind Direction and Speed: Arrows on the map indicate wind direction, with their length representing wind speed. This information is crucial for understanding the movement of weather systems and potential hazards.
-
Temperature: Temperature readings are typically included at various locations on the map, providing a broader context for understanding the overall weather pattern.
-
Precipitation: Symbols or shading may be used to indicate areas of precipitation, offering insights into the intensity and type of rainfall expected.
The Power of Prediction: Harnessing the Information
Weather isobar maps are invaluable tools for meteorologists and forecasters. By analyzing the patterns and trends, they can make informed predictions about future weather conditions. This information is critical for various applications, including:
-
Public Safety: Accurate weather forecasts are essential for public safety, enabling authorities to issue timely warnings about potential hazards like thunderstorms, tornadoes, and hurricanes.
-
Agriculture: Farmers rely heavily on weather forecasts to plan their planting, harvesting, and irrigation schedules, ensuring optimal crop yields.
-
Aviation: Pilots use weather isobar maps to plan flight routes, avoiding turbulent weather conditions and ensuring safe air travel.
-
Marine Navigation: Mariners utilize these maps to navigate safely, avoiding storms and strong currents that could pose risks to their vessels.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Weather Isobar Maps
Q1: What are the units used for pressure on a weather isobar map?
A: The standard unit for atmospheric pressure on a weather isobar map is the millibar (mb). However, some maps may use other units such as hectopascals (hPa), where 1 hPa = 1 mb.
Q2: How are isobars drawn on a weather map?
A: Isobars are drawn based on pressure readings taken at various weather stations. These readings are then interpolated to create smooth lines connecting points of equal pressure.
Q3: Can isobars be used to predict the intensity of precipitation?
A: While isobars don’t directly indicate precipitation intensity, they can provide clues. Areas with closely spaced isobars, signifying a steeper pressure gradient, often experience stronger winds and more intense precipitation.
Q4: Are weather isobar maps still relevant in the age of satellite imagery?
A: While satellite imagery provides valuable data, weather isobar maps remain essential. They offer a concise and clear representation of atmospheric pressure distribution, which is crucial for understanding the underlying dynamics of weather systems.
Q5: Can I create my own weather isobar map?
A: While it’s possible to create a basic isobar map using pressure readings from local weather stations, professional maps are generated using sophisticated computer models and data analysis techniques.
Tips for Understanding and Using Weather Isobar Maps
- Pay attention to the pressure values: Higher pressure values indicate high-pressure systems, while lower values indicate low-pressure systems.
- Observe the spacing of isobars: Closely spaced isobars indicate a steeper pressure gradient and stronger winds.
- Identify fronts: Look for sharp changes in pressure and wind direction, indicating the presence of fronts.
- Consider additional information: Analyze wind direction, temperature, and precipitation symbols for a comprehensive understanding of the weather pattern.
- Consult reliable sources: Refer to official weather forecasts and maps from reputable organizations for accurate information.
Conclusion: A Window into the Atmosphere
Weather isobar maps serve as a powerful tool for understanding and predicting the complex dynamics of the atmosphere. By deciphering the patterns and trends, we gain insights into the forces that shape our weather, enabling us to prepare for potential hazards, plan our activities, and navigate our world with greater awareness. As technology continues to advance, weather isobar maps will continue to play a vital role in helping us understand and navigate the ever-changing tapestry of the sky.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Secrets of the Atmosphere: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Isobar Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!